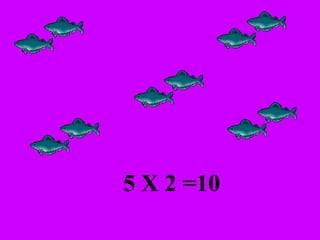
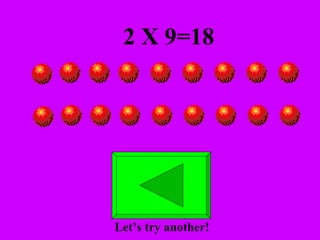
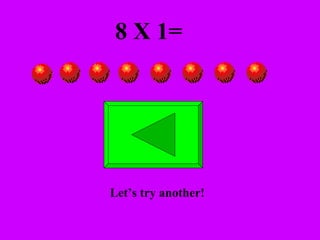
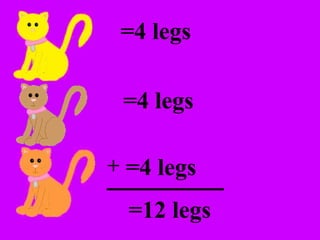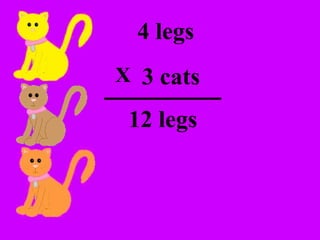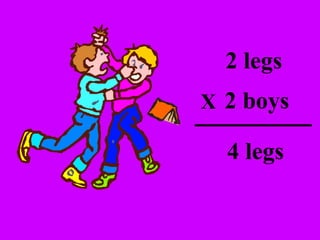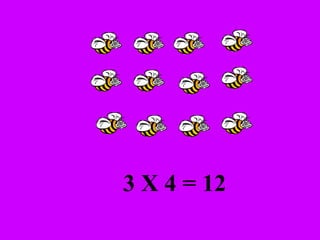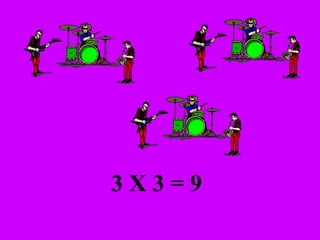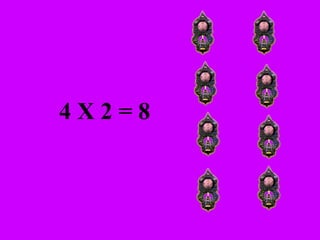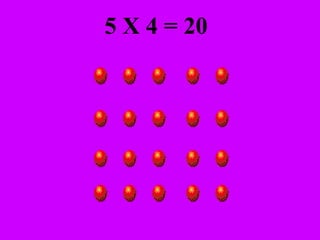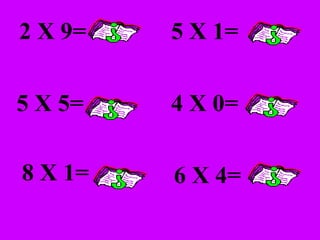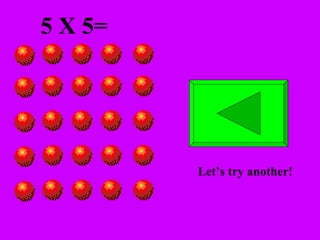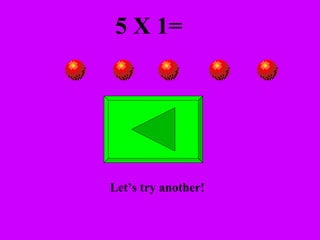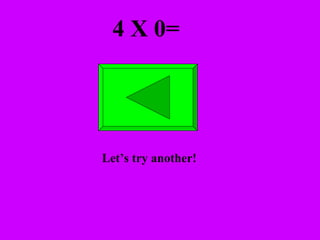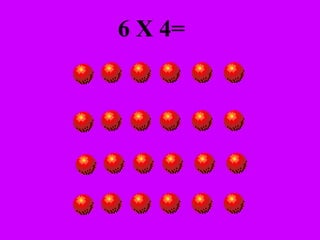The document introduces multiplication as a way to efficiently calculate the total number of objects when grouped into equal sets. It provides examples of multiplying the number of sets by the number of objects in each set to find the total number of legs for multiple cats, number of crayons in multiple boxes, number of books for multiple teachers, and number of apples on multiple desks. The document encourages representing multiplication problems using sets and solving related problems.