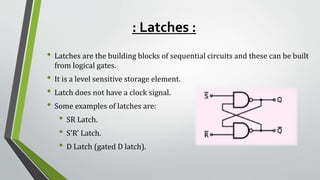
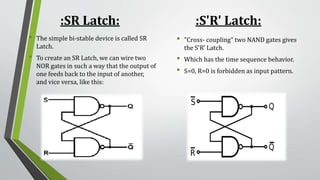
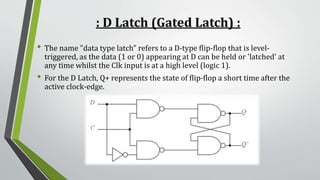
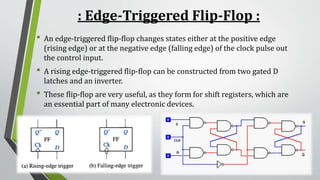
This document summarizes sequential circuits and their basic components - latches and flip-flops. It describes how latches like the SR, S'R', and D latches work based on inputs but no clock signal, while flip-flops like edge-triggered flip-flops change state based on the clock edge. Examples of additional flip-flop inputs like preset, clear and clock enable are provided to control the output independent of the clock. Asynchronous sequential circuits can override the clock input using preset and clear inputs to directly control the output states.