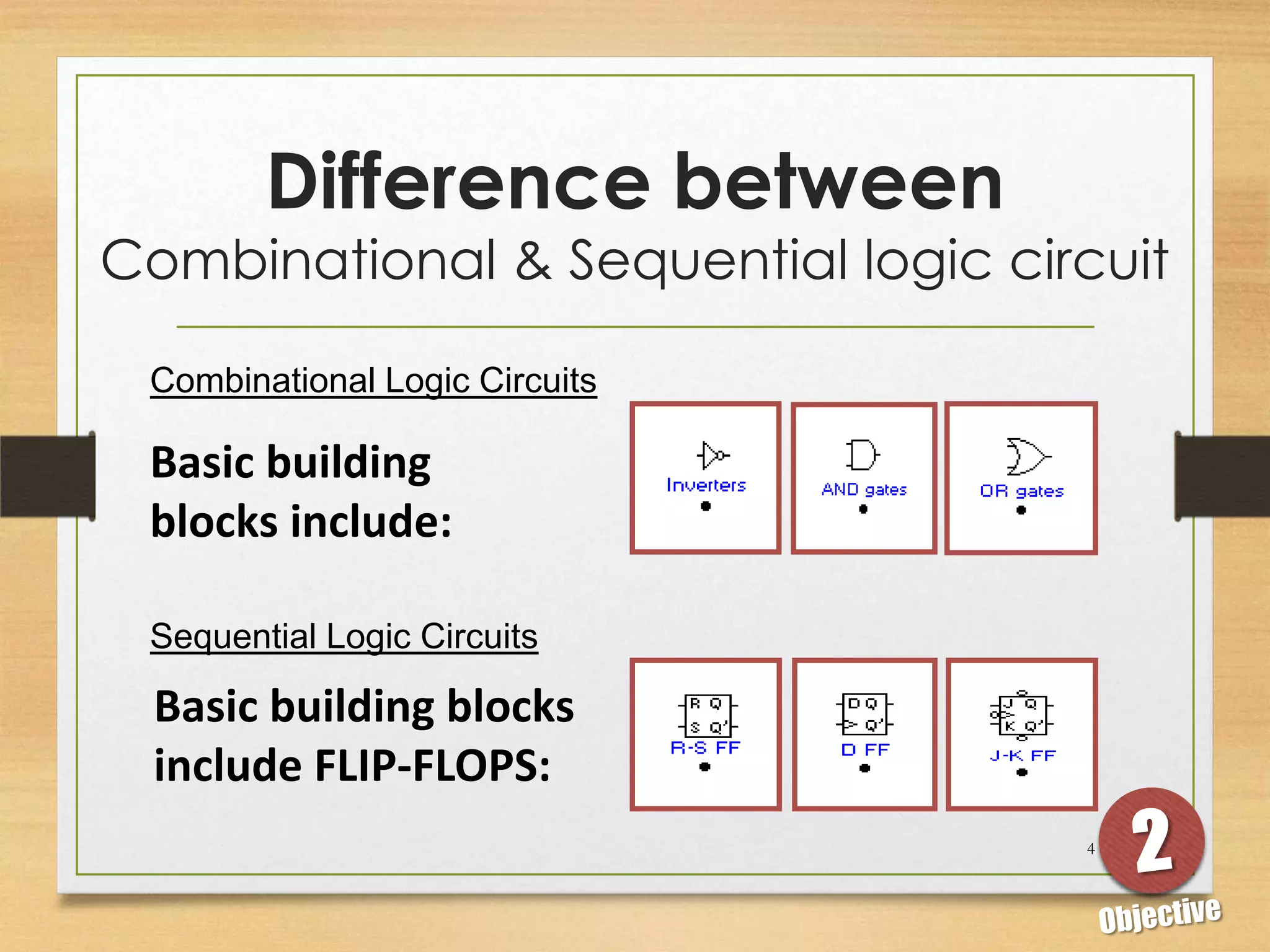
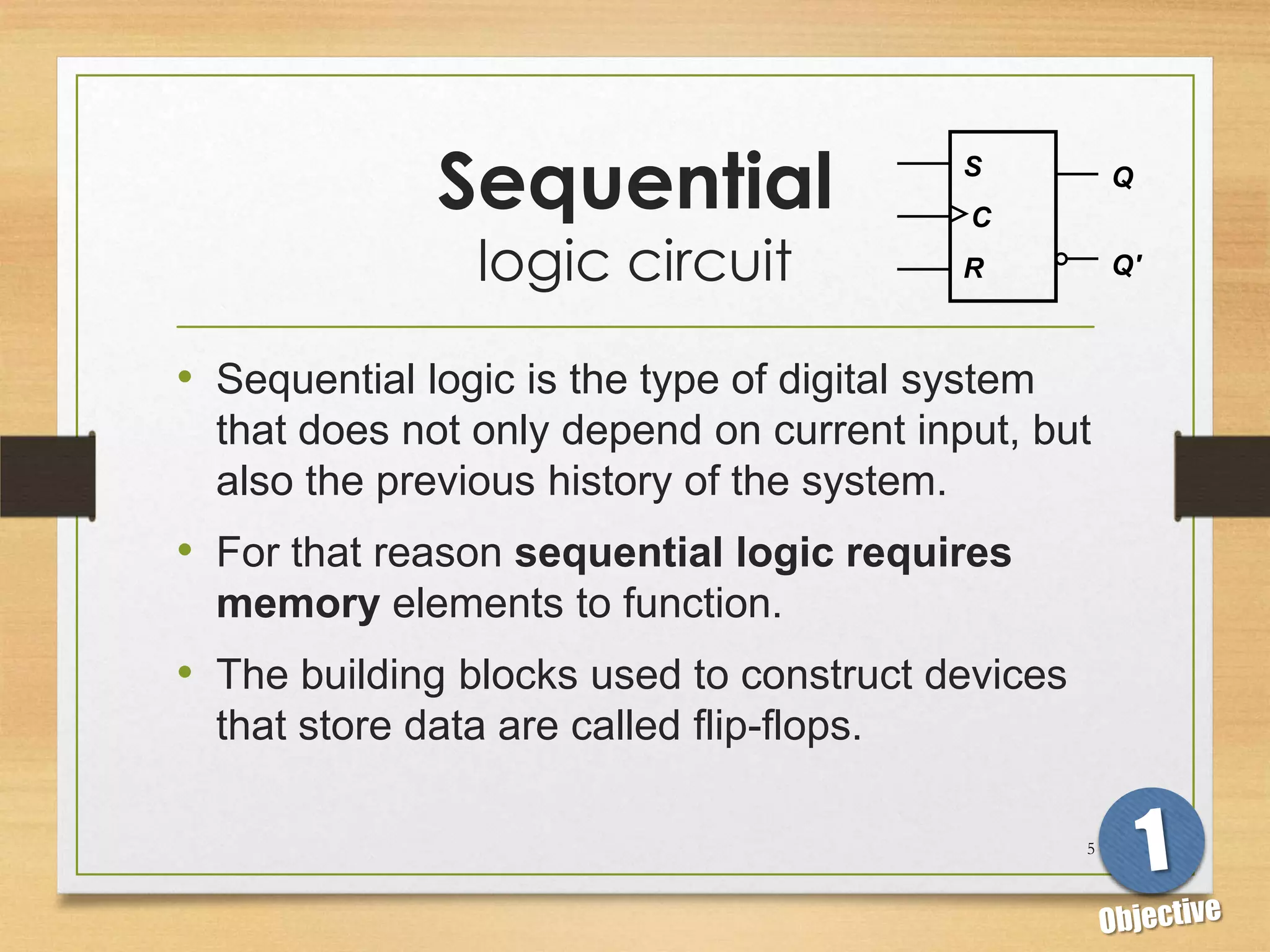
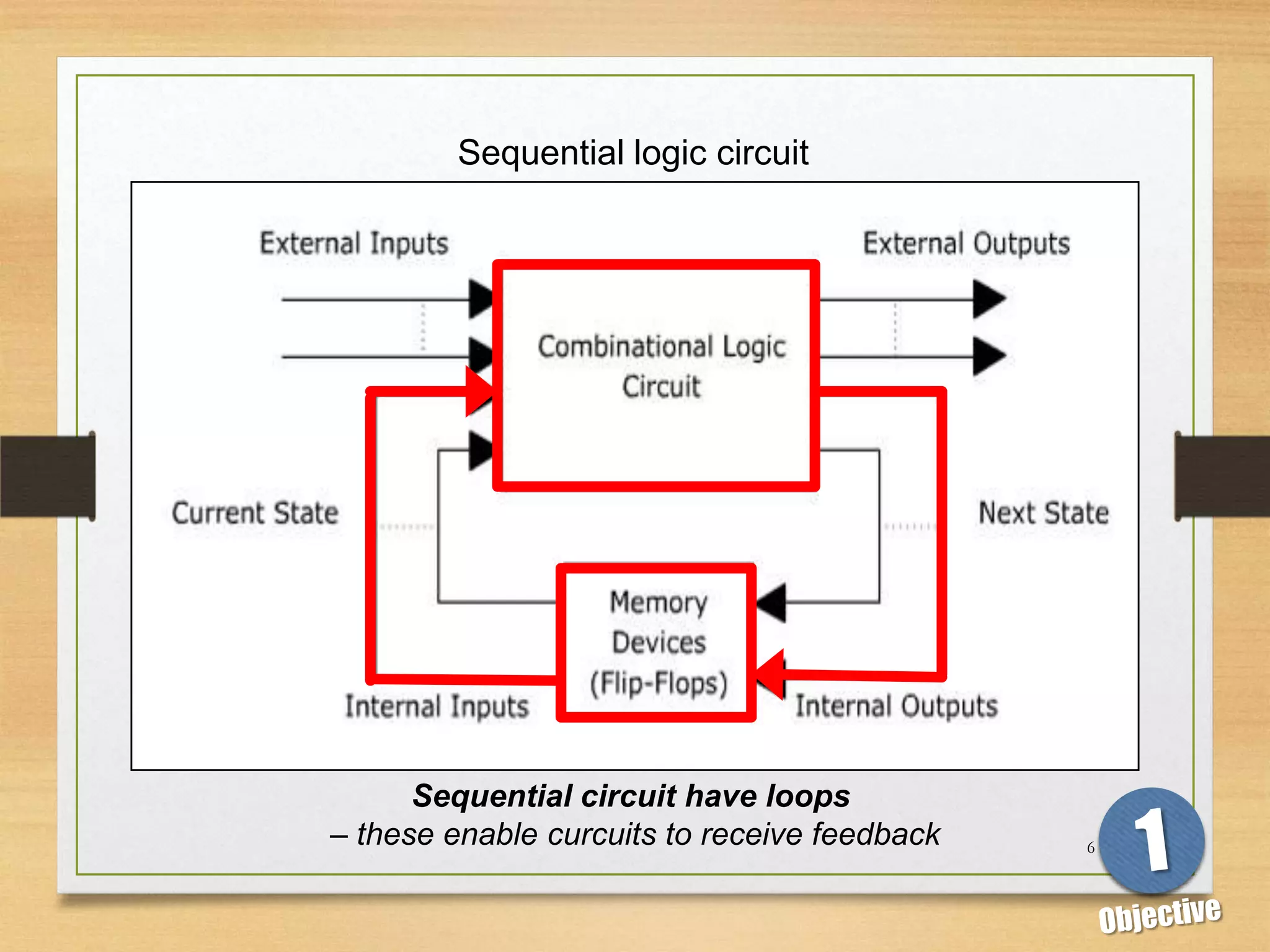
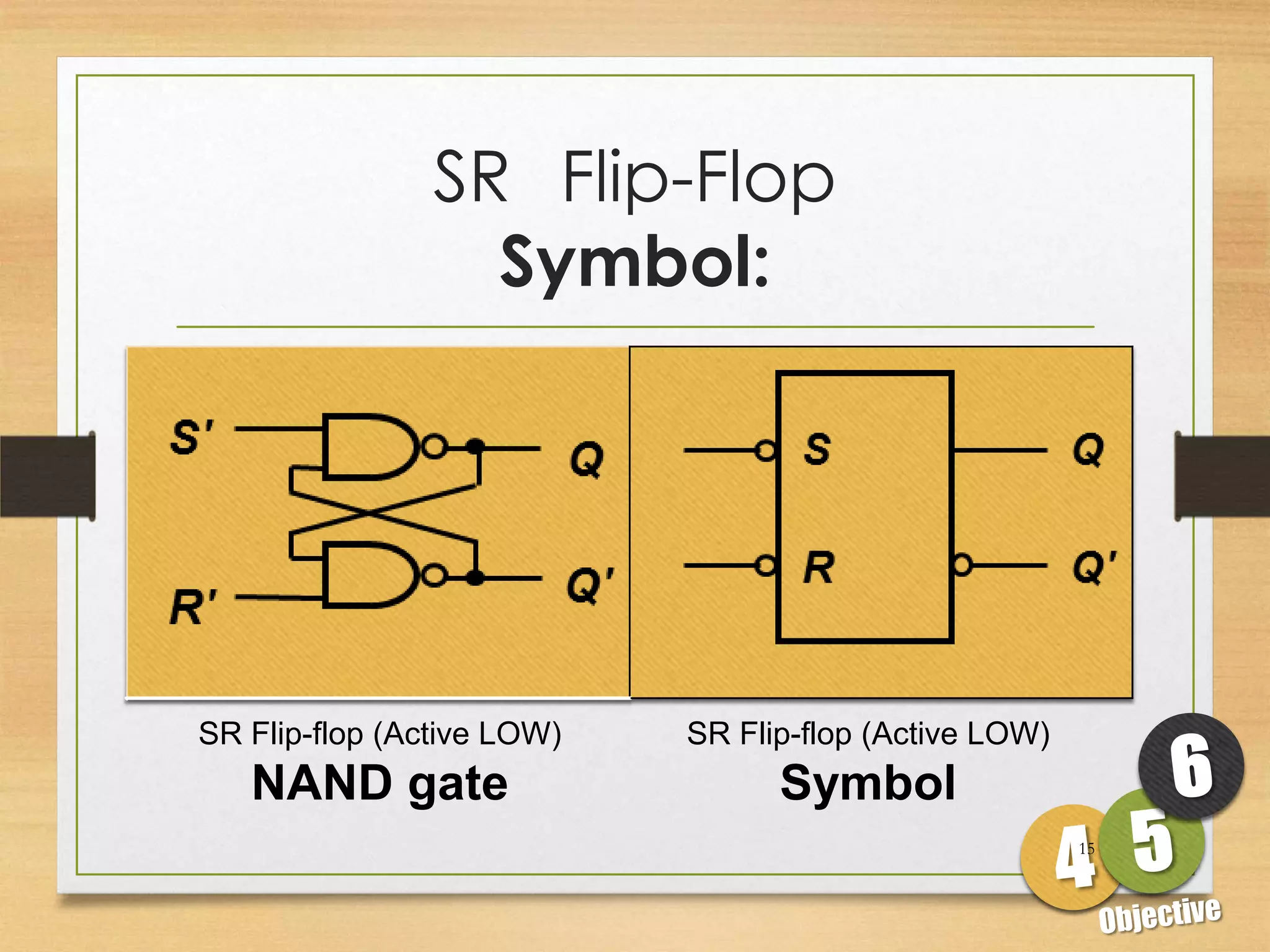
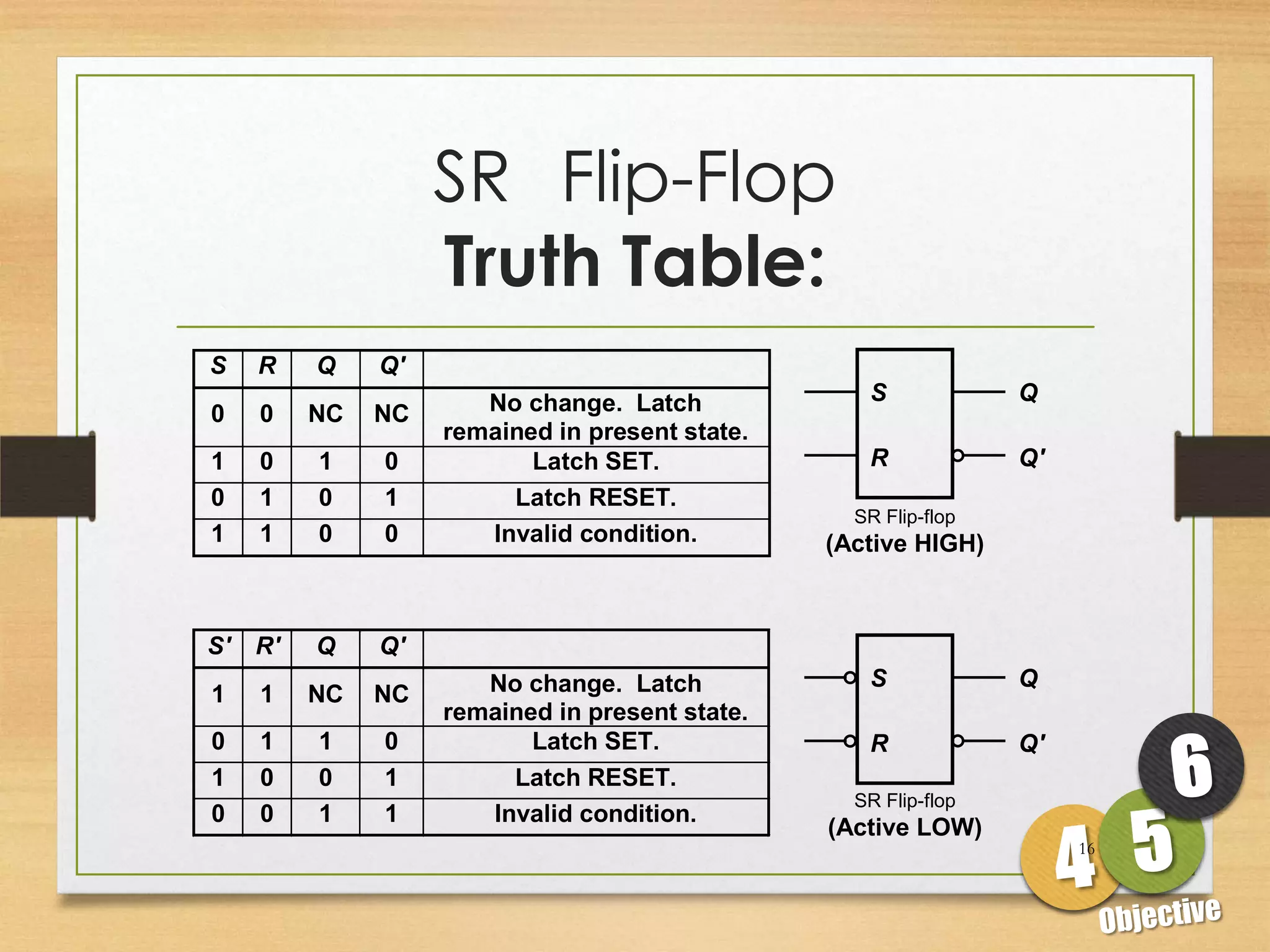
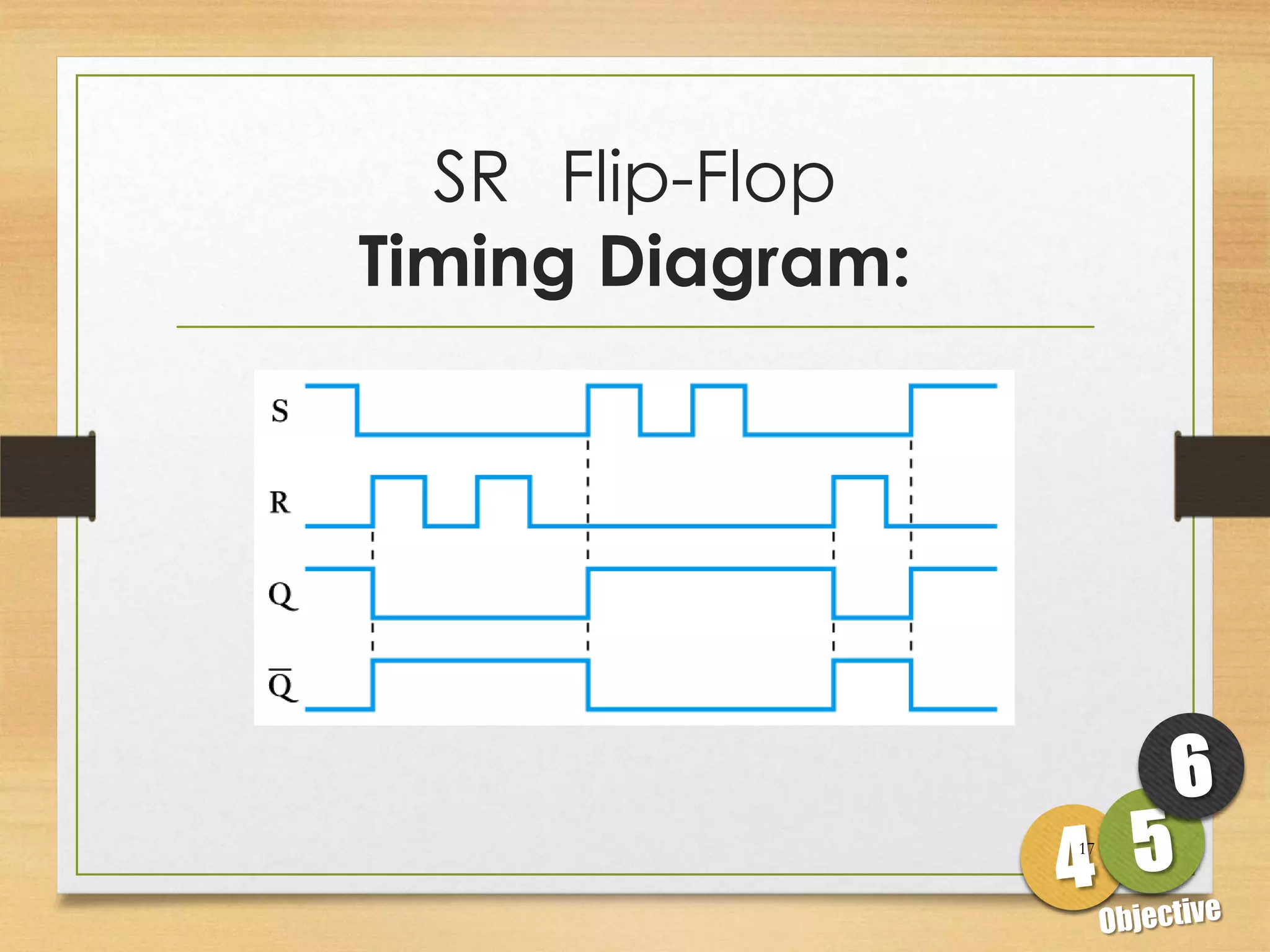
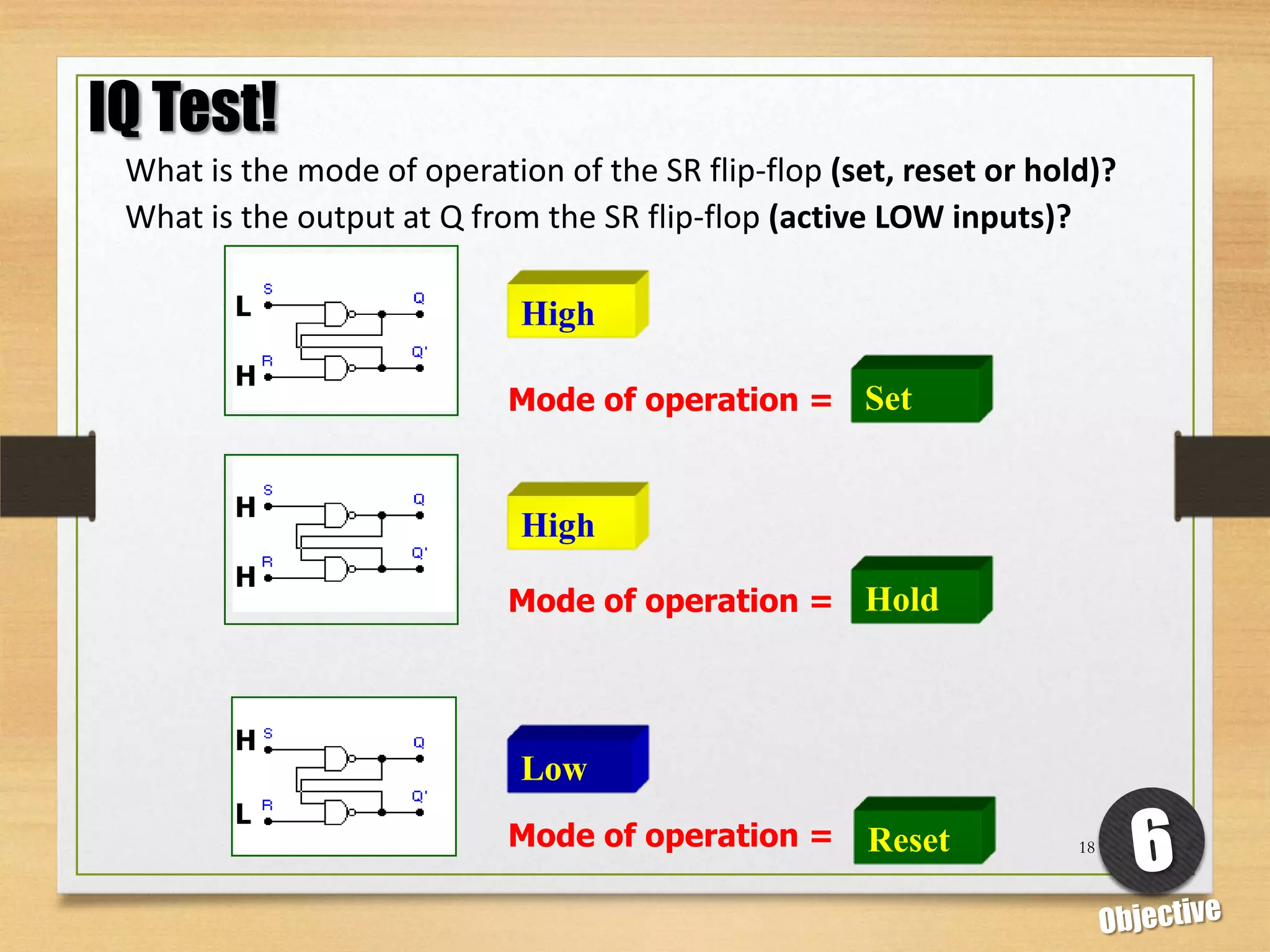
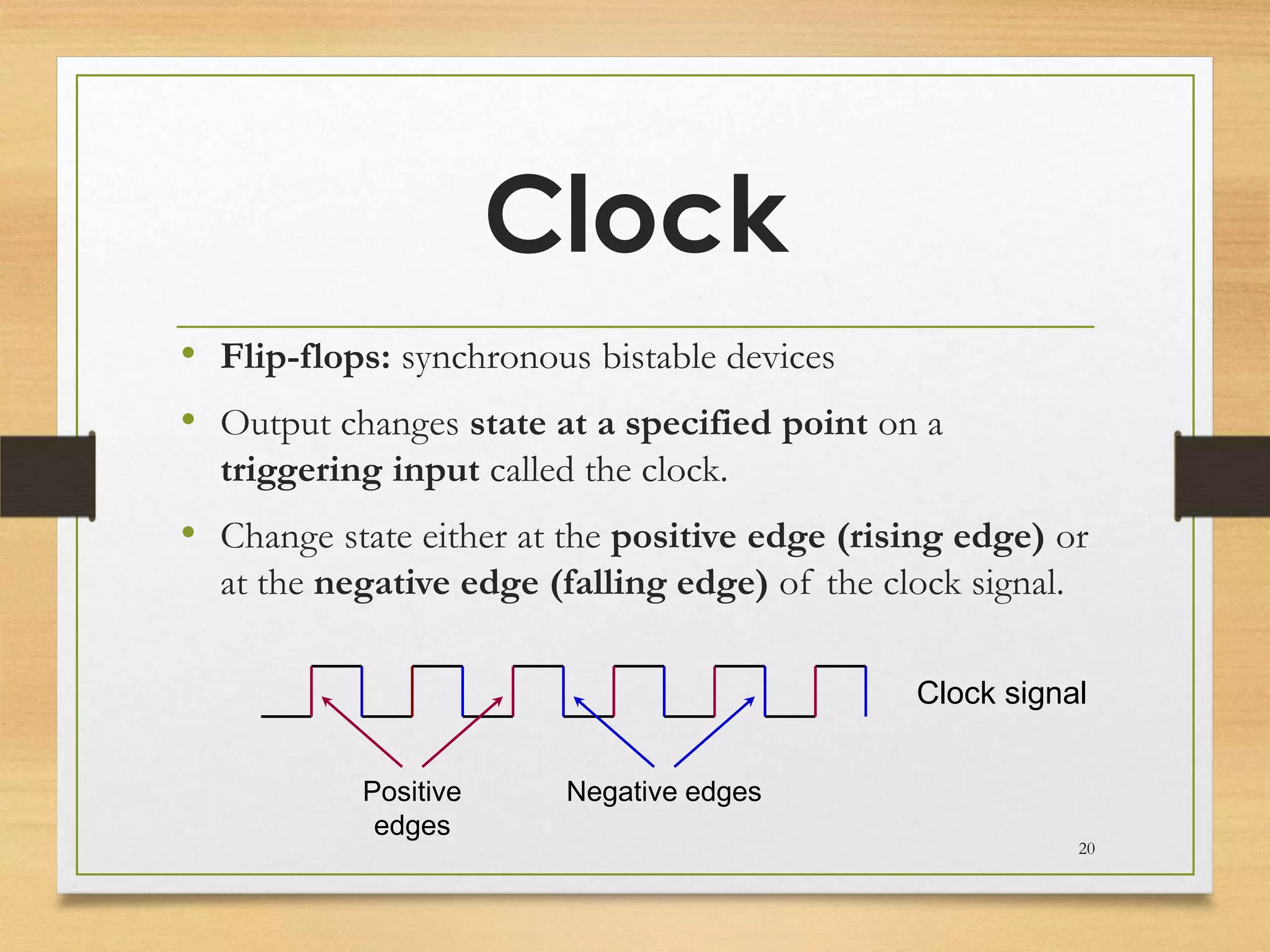
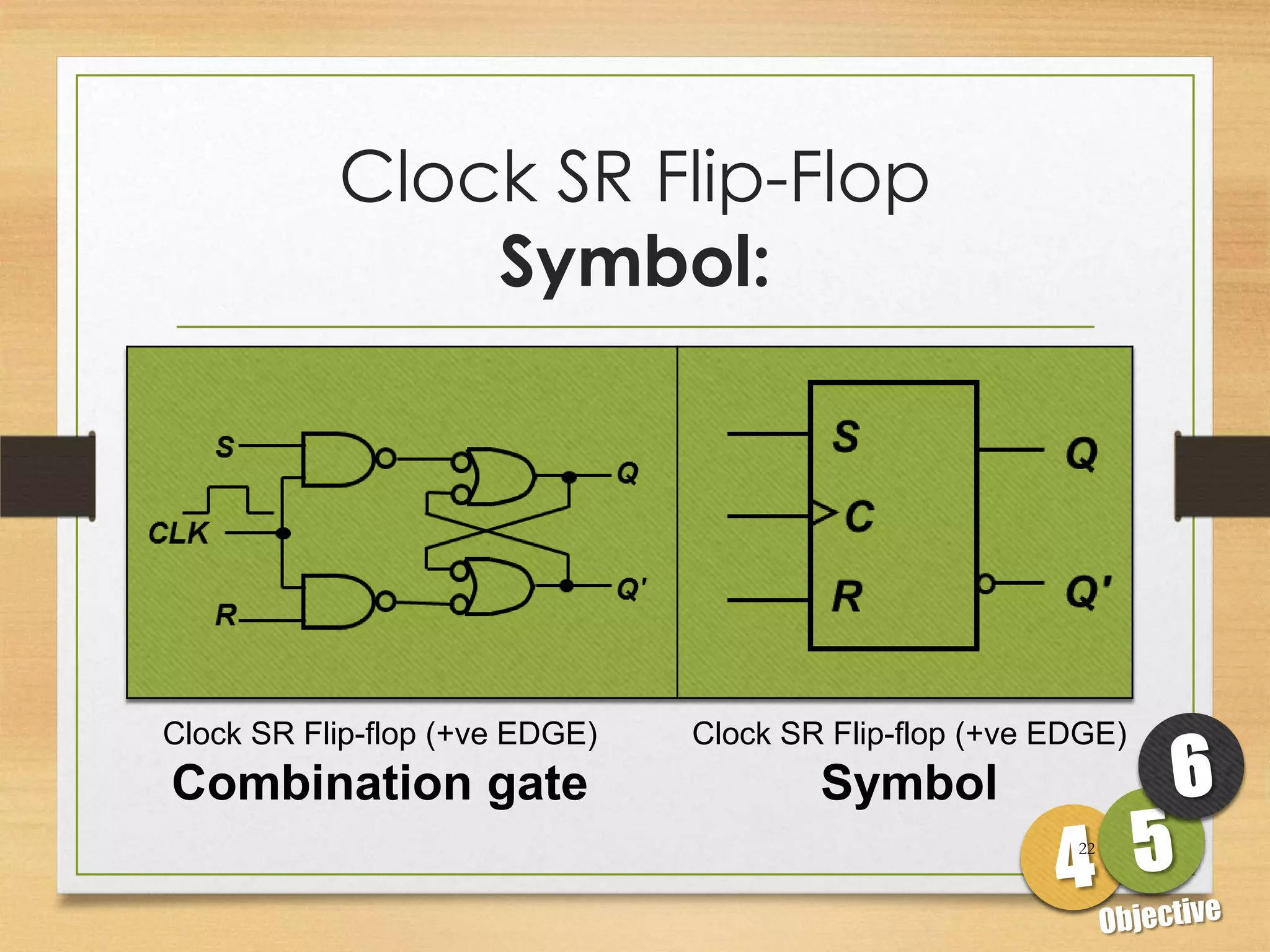
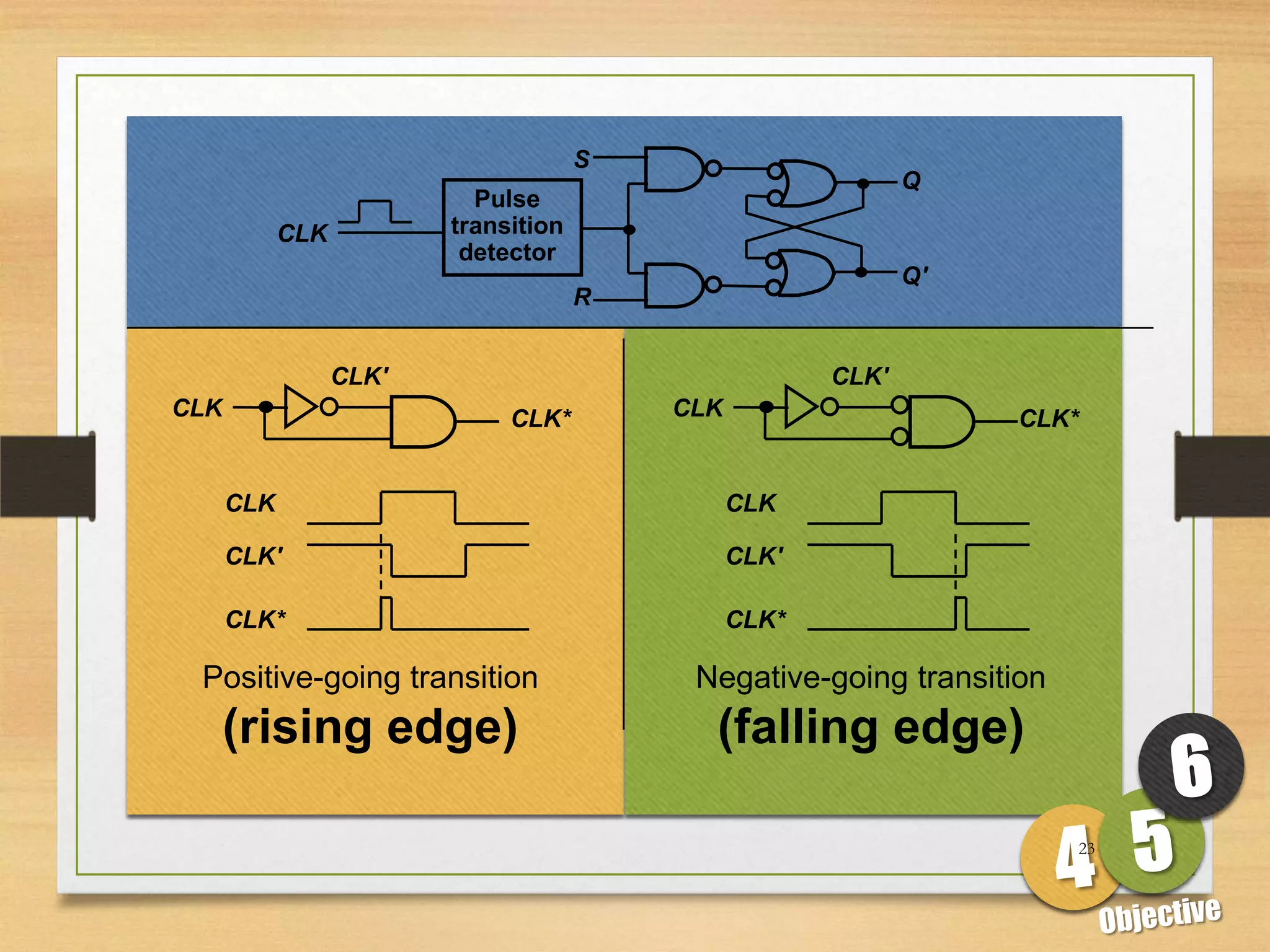
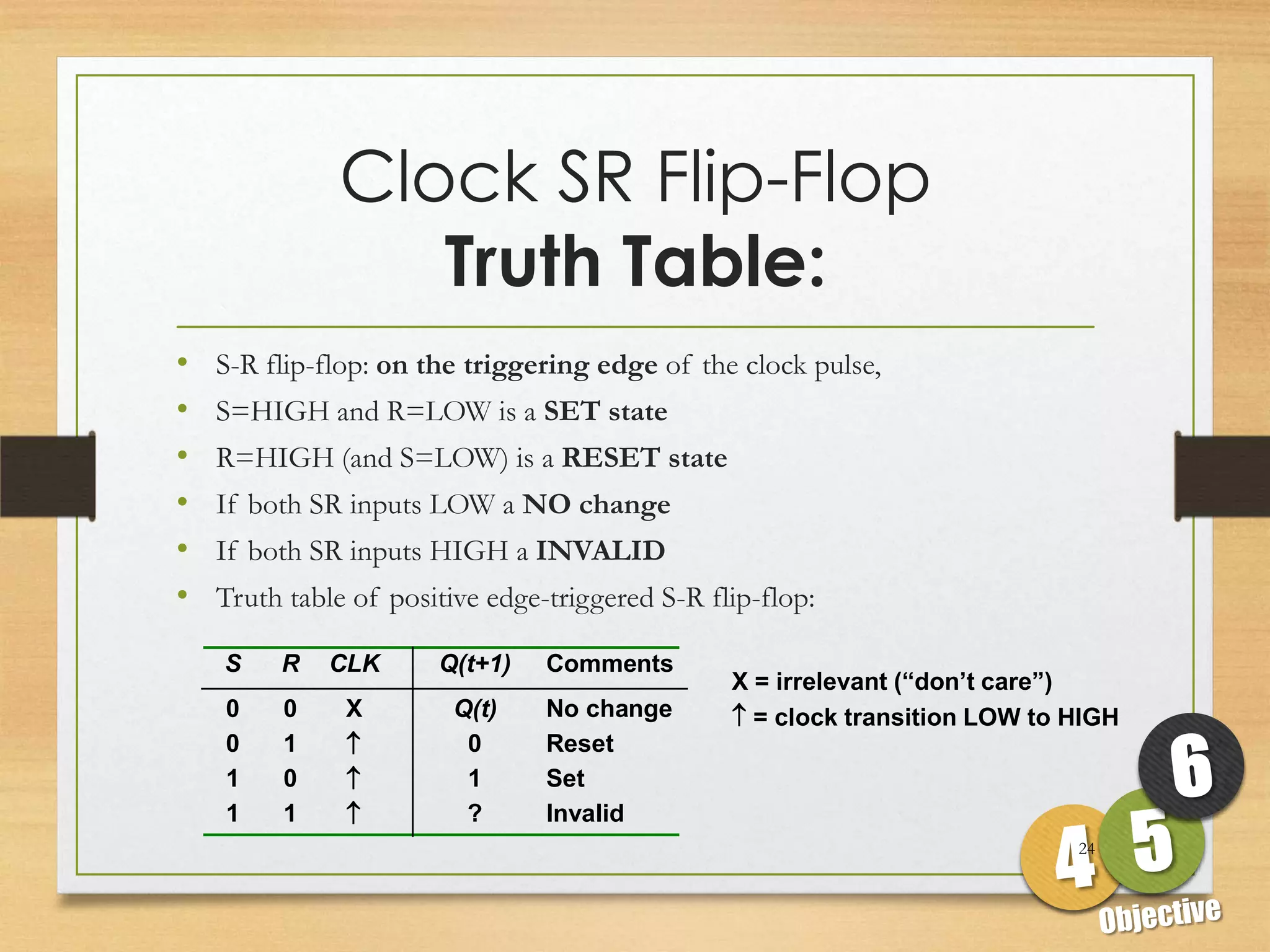
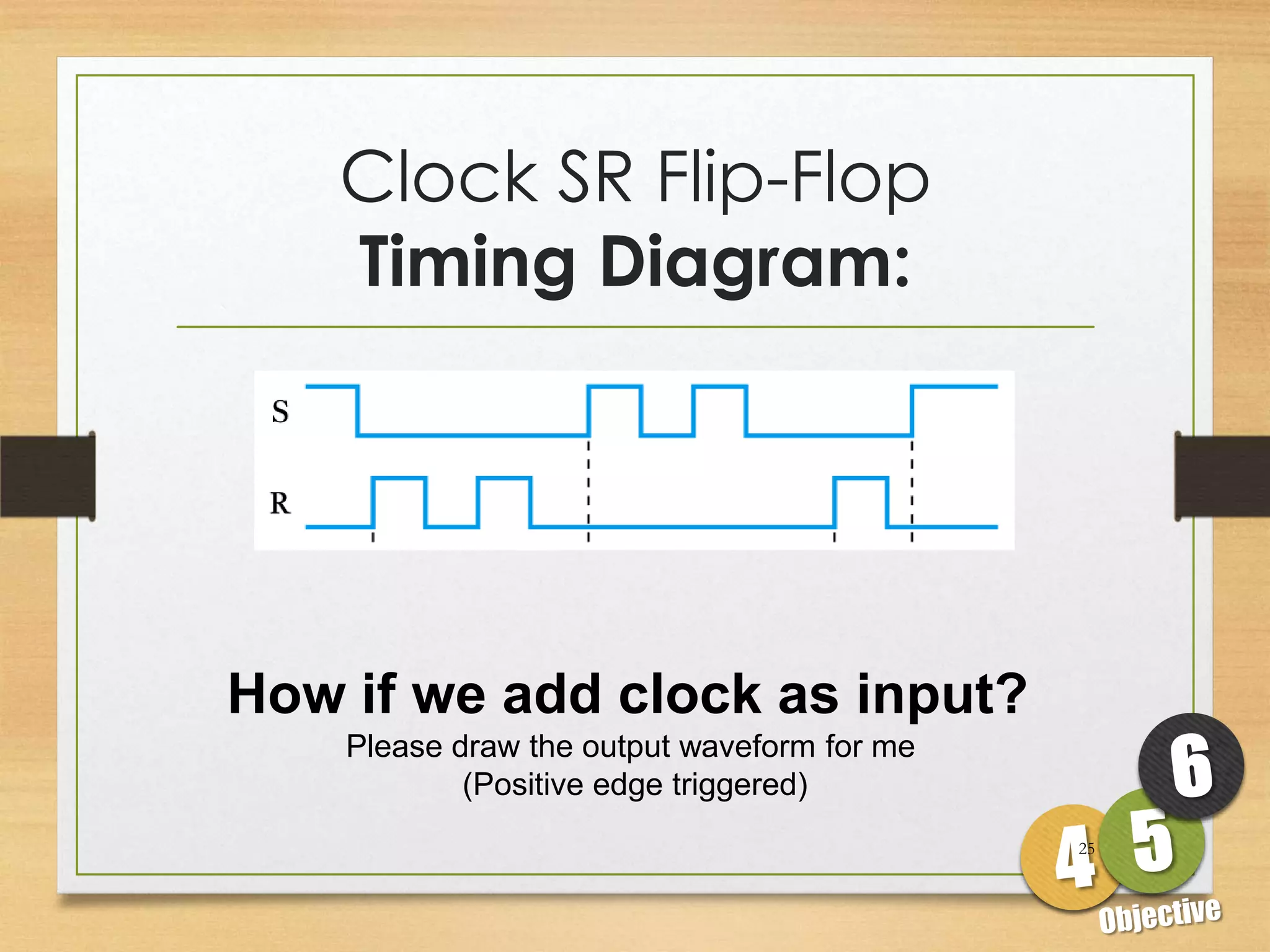
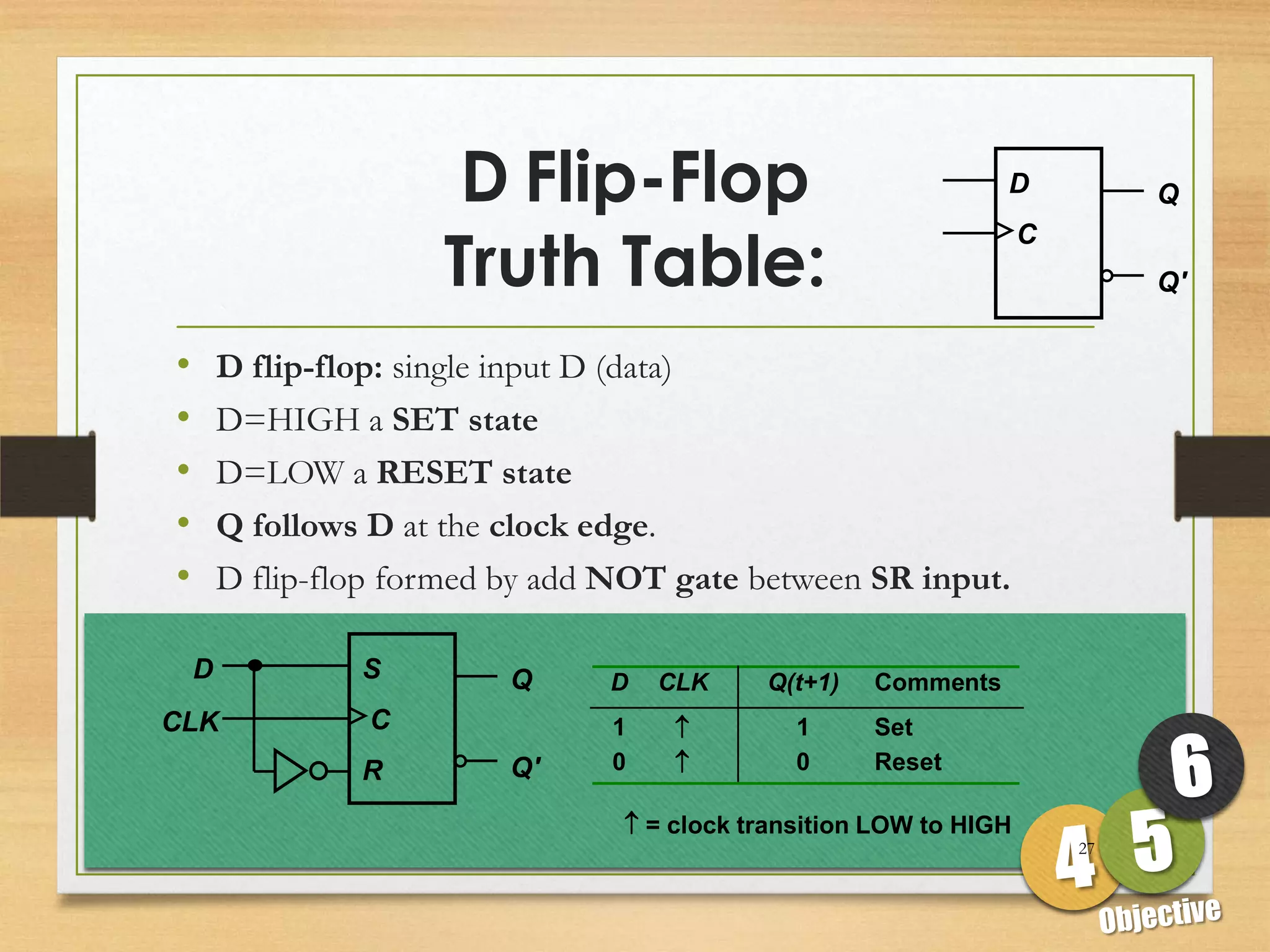
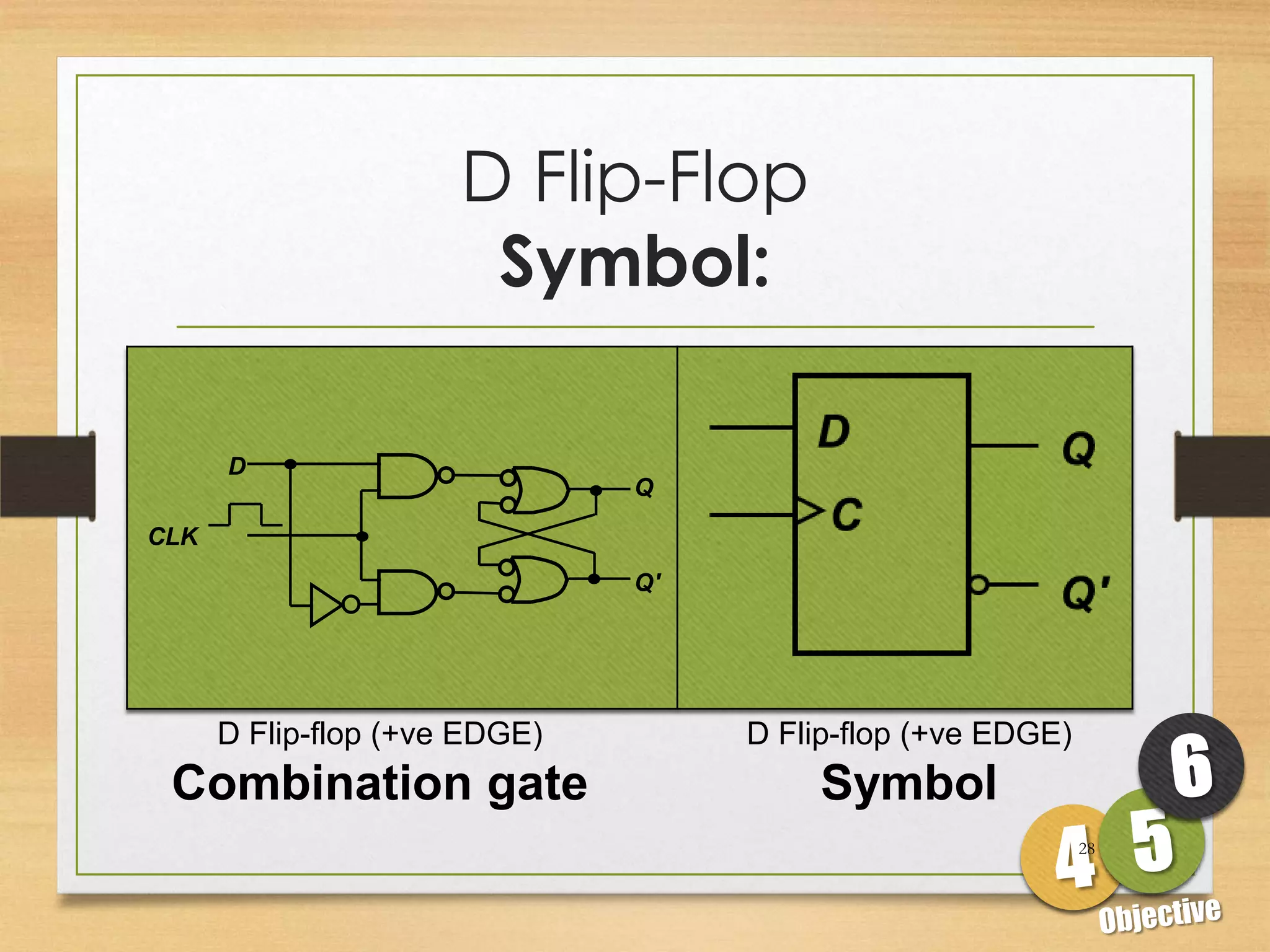
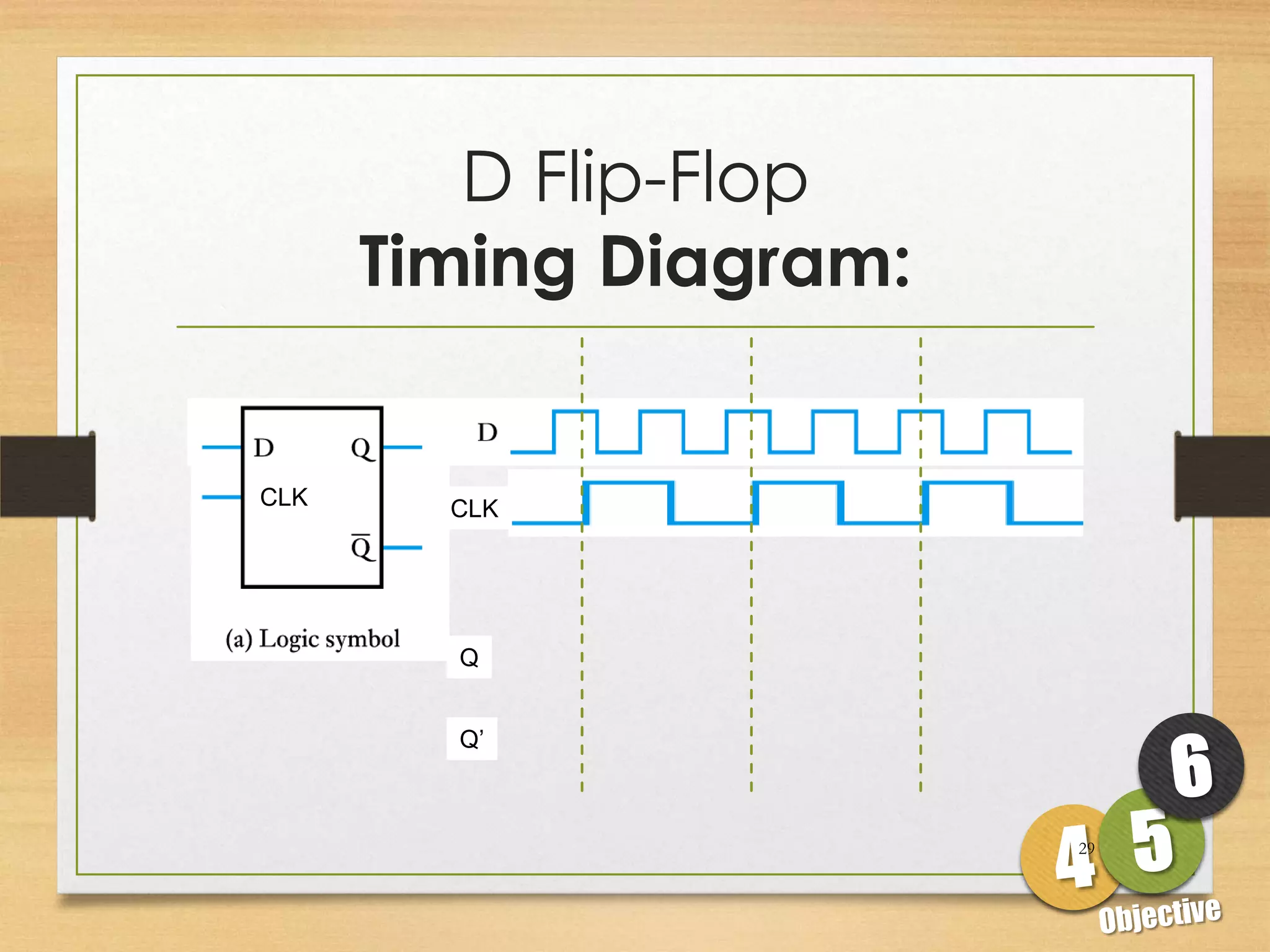
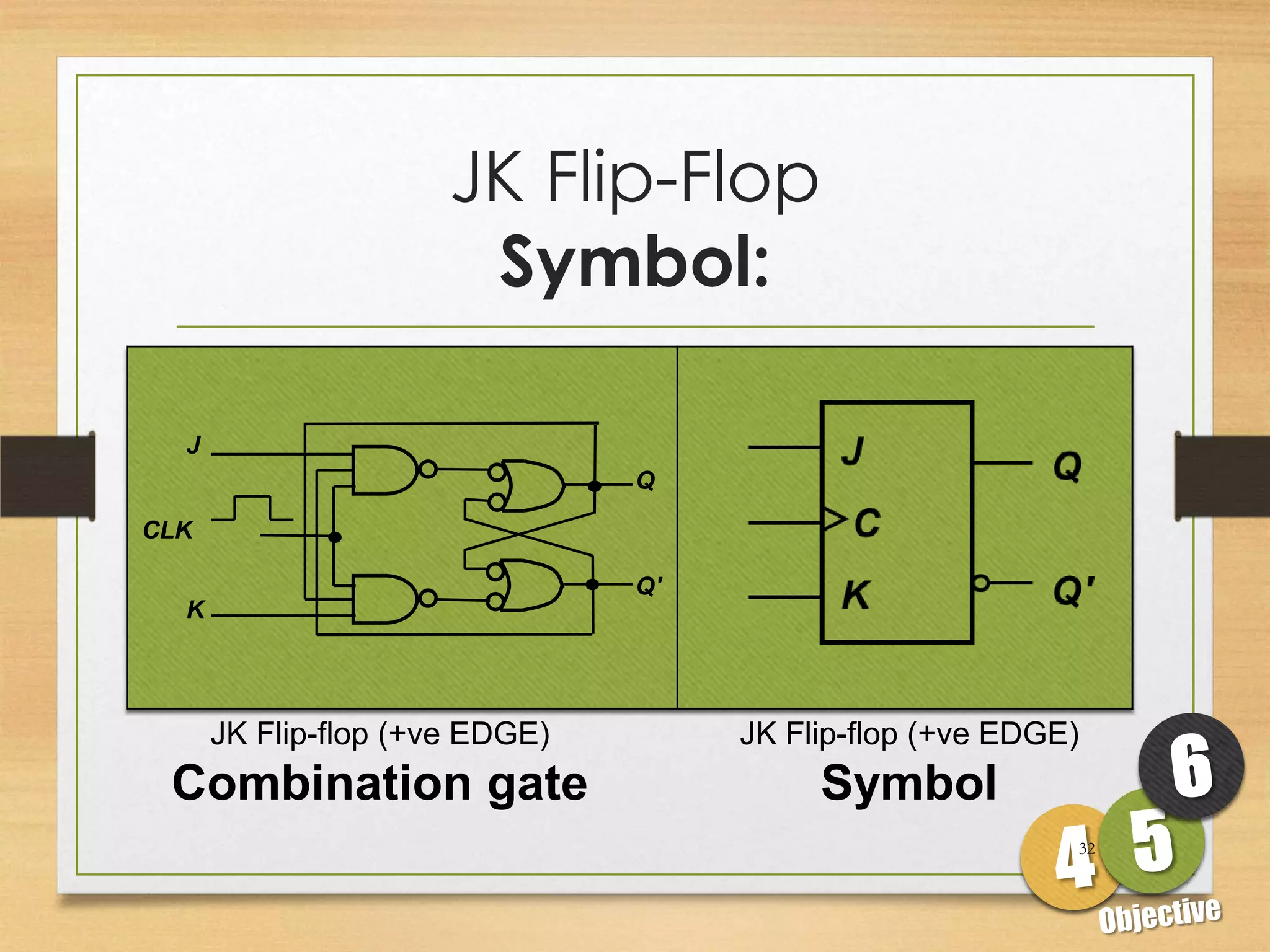
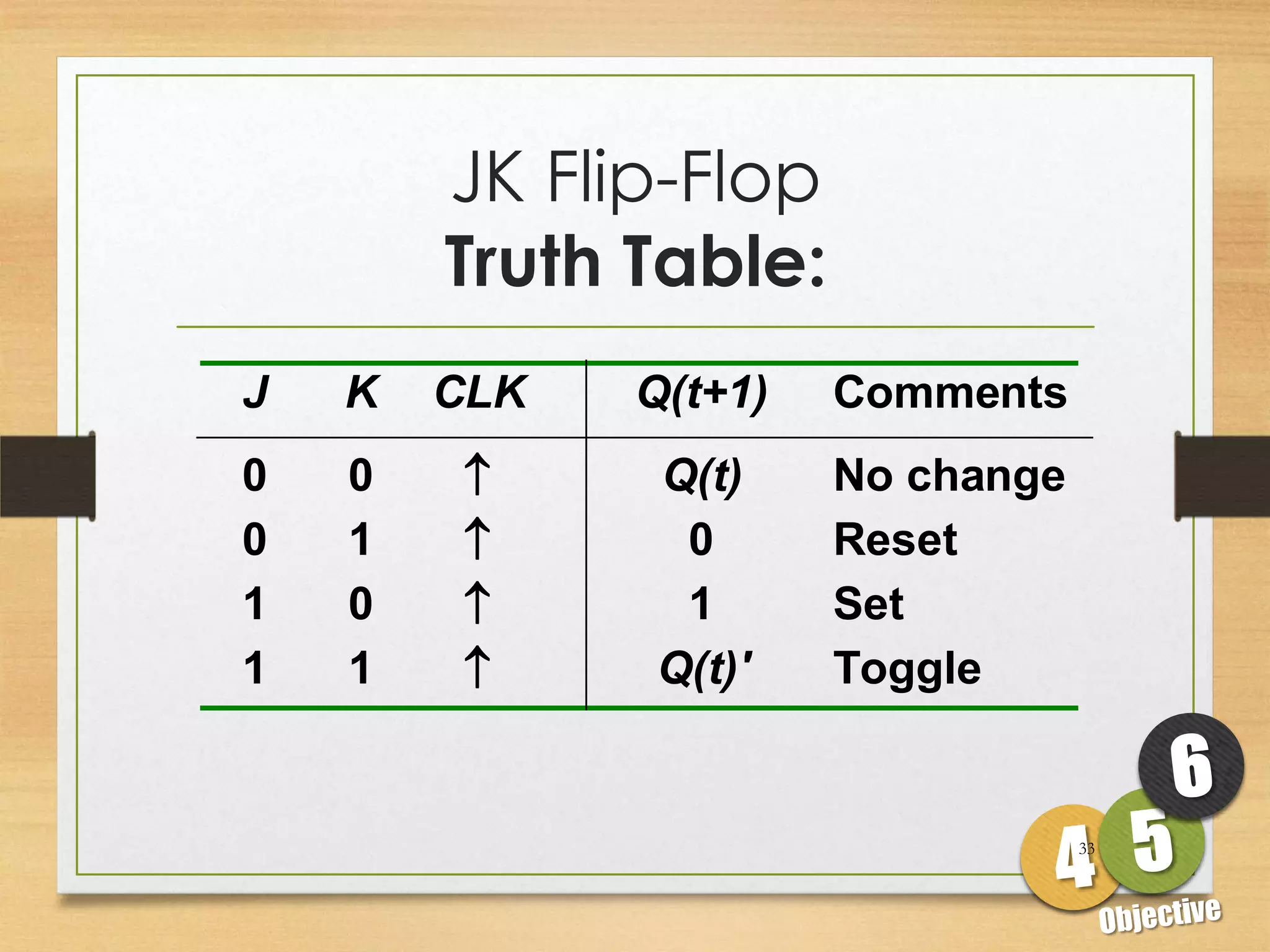
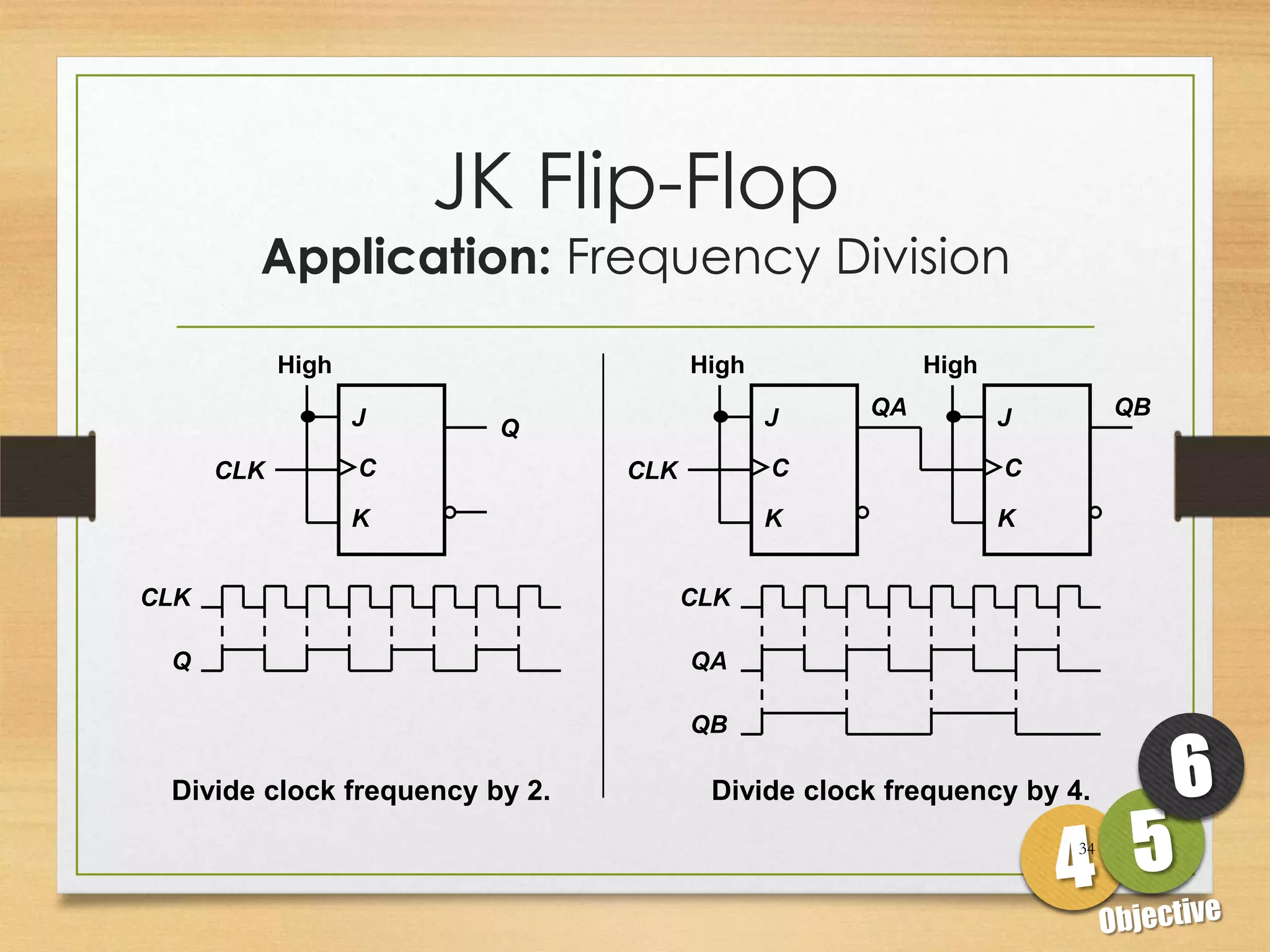
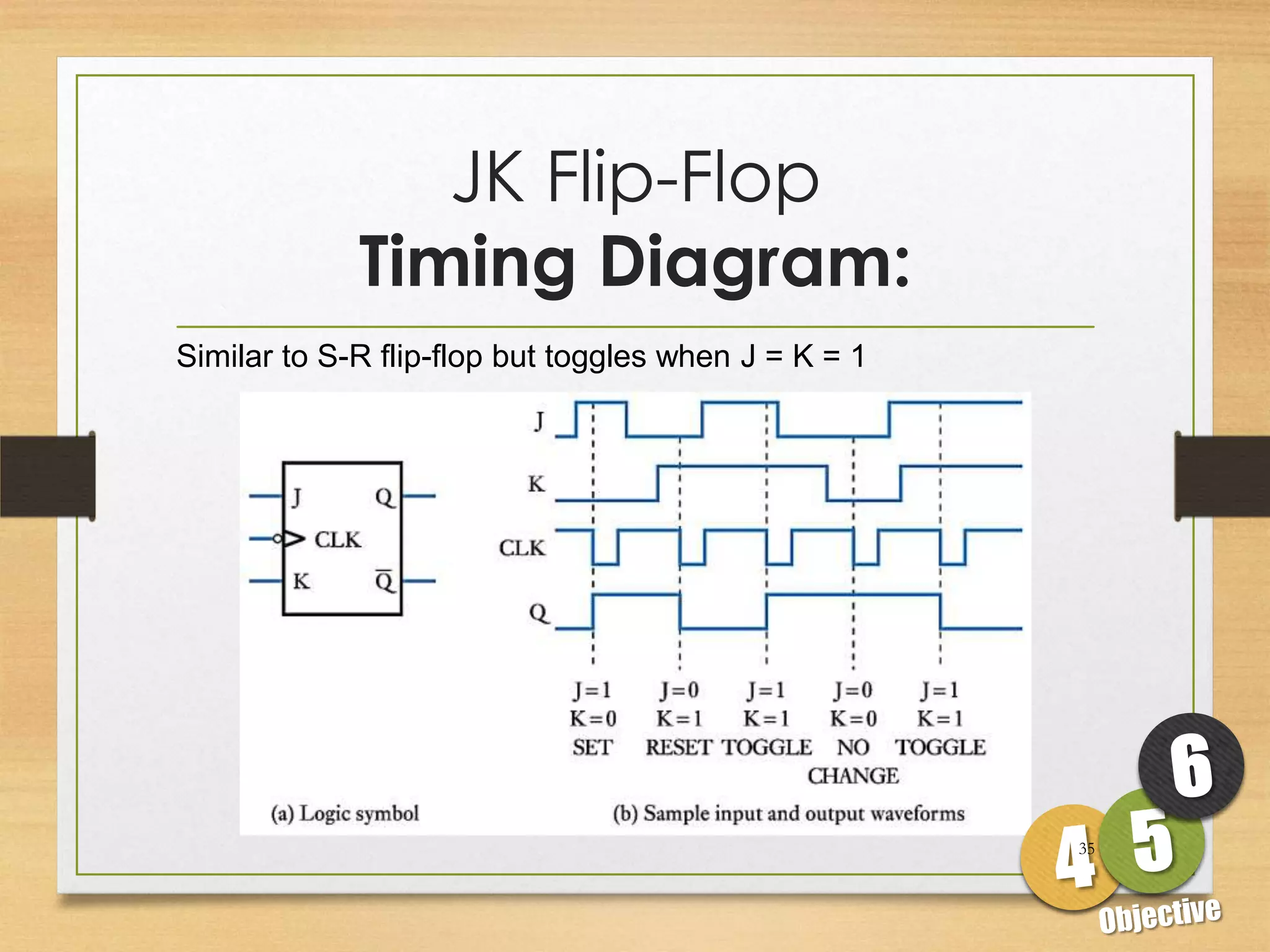
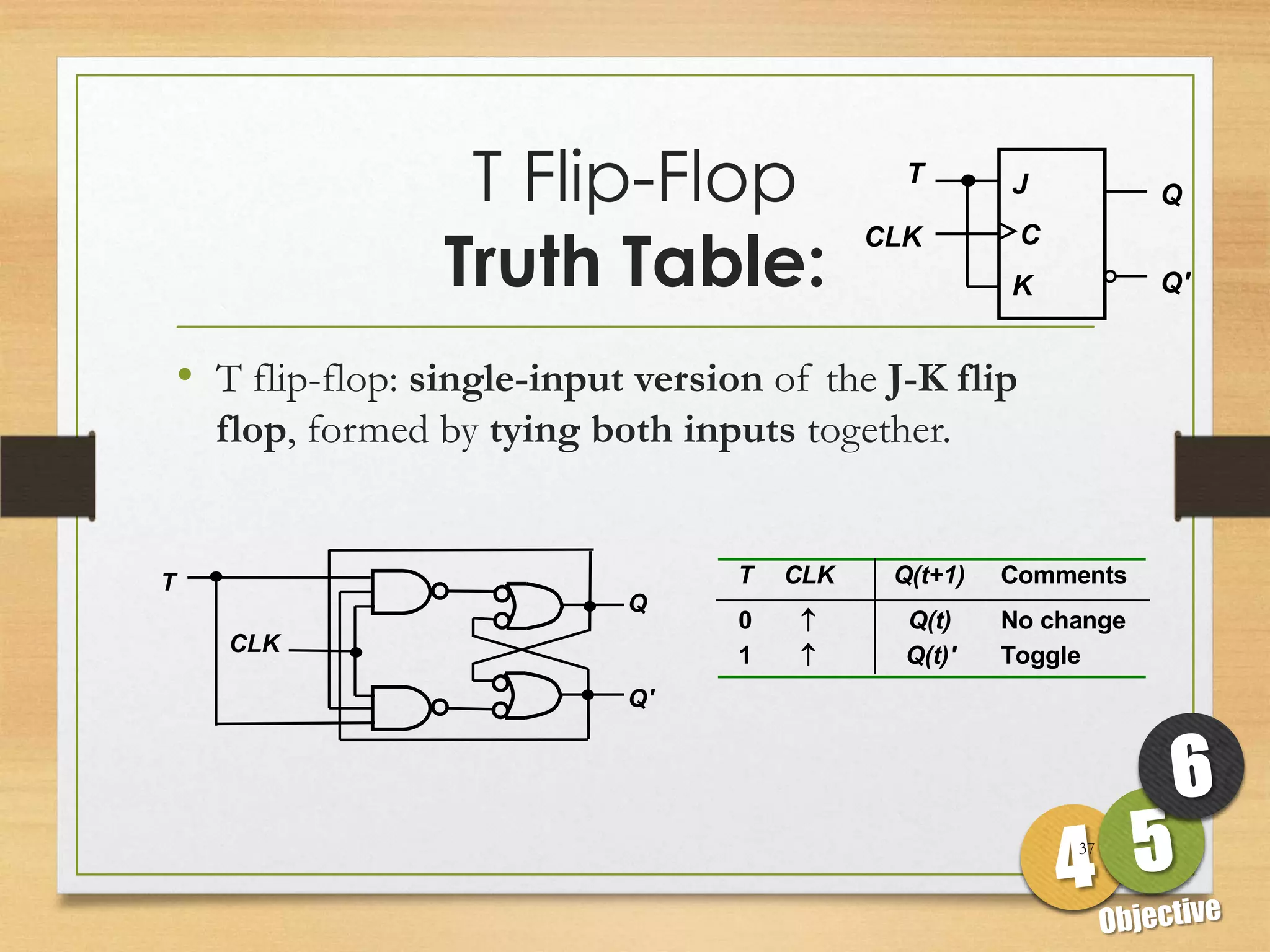
This document discusses sequential logic circuits and flip-flops. It begins by defining sequential logic and differentiating it from combinational logic. It then describes flip-flops as the basic building blocks of sequential logic that provide memory. It identifies four common types of flip-flops - SR, JK, D and T - and describes their operation, truth tables and implementation using logic gates. The document provides details on each type of flip-flop to help understand their functionality and applications in sequential logic circuits.