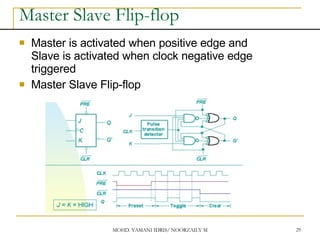
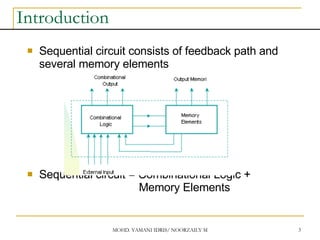
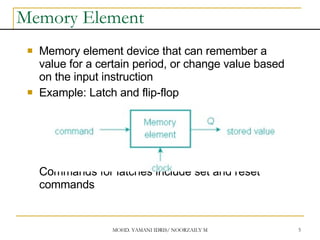
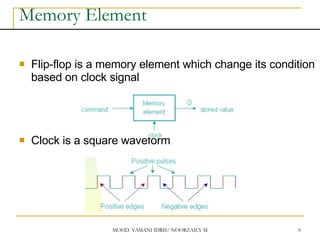
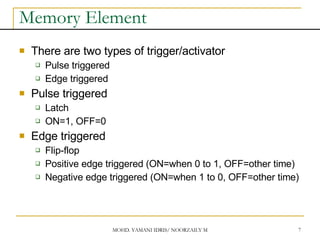
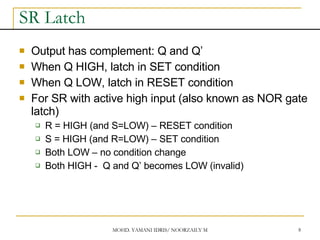
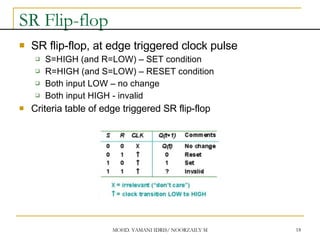
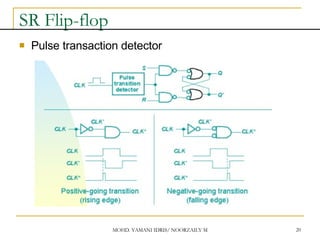
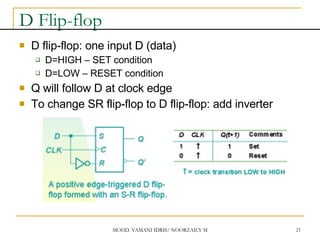
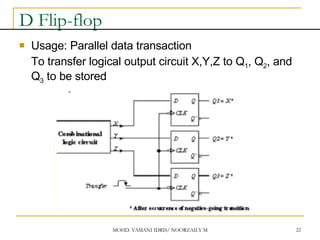
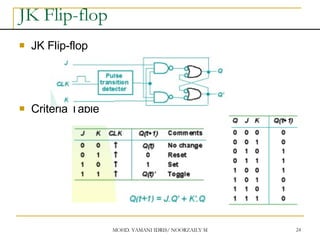
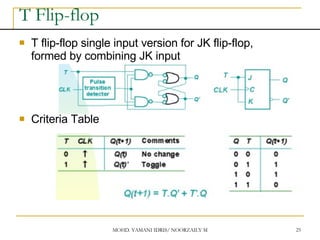
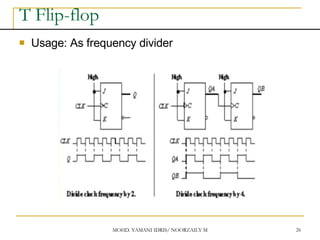
This document discusses sequential circuits and various memory elements. It introduces latches and flip-flops, which are bistable logic devices that can store one bit of information. SR latches and D latches are described as well as edge-triggered SR, D, JK, and T flip-flops. Their operations are summarized through truth tables. Asynchronous preset and clear inputs are also discussed. The document concludes by mentioning master-slave flip-flops which reduce glitches by separating the master and slave stages.





![MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY MOHAMED NOOR 27
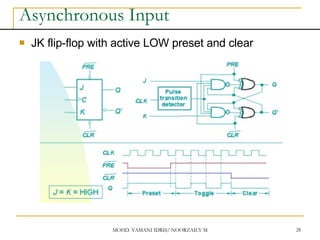
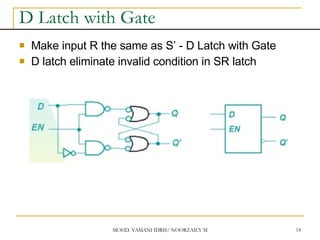
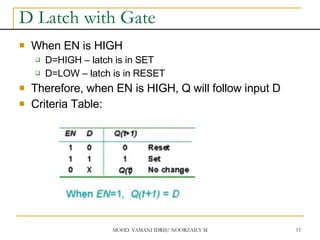
Asynchronous Input
SR input, D and JK is synchronous input. Where
data from input will be transferred to flip-flop
output only when edge triggered of clock pulse
Asynchronous Input free change condition from
pulse clock. Example: preset (PRE) and clear
(CLR) [or direct set (SD) and direct reset (RD)]
When PRE=HIGH, Q immediately HIGH
When CLR=HIGH, Q immediately LOW
Flip flop function as normal when both PRE and
CLR is LOW](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sequentialcircuitsppt-230104082028-d31f434f/85/sequential-circuits-PPT-pdf-27-320.jpg)