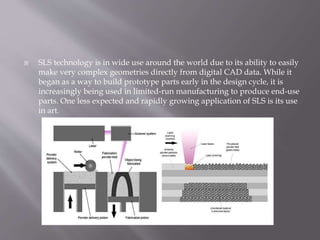
Selective laser sintering (SLS) is an additive manufacturing technique that uses a laser to fuse powdered material like metal or plastic according to a 3D model. It was developed in the 1980s at the University of Texas and allows for the creation of complex geometries. SLS works by using a high-power laser to selectively fuse layers of powdered material based on a digital 3D design. After each layer is scanned, a new layer of powder is applied and the process repeats until the part is completed. SLS can produce parts from a variety of materials like polymers, metals, and composites.