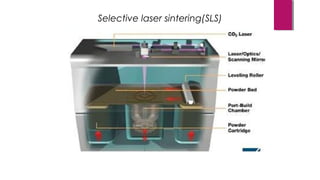
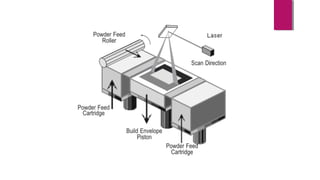
Selective laser sintering (SLS) is a rapid prototyping technology that produces physical models layer by layer directly from CAD files, without tools or fixtures. In SLS, a laser fuses powdered material, like nylon or metal, to build the final part. The process begins with an STL file and uses a laser to sinter powder materials together with high accuracy. SLS allows for quick fabrication of complex parts and reduces design errors compared to traditional manufacturing.