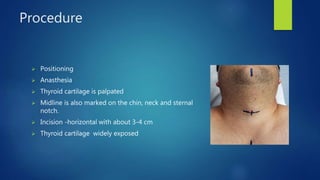
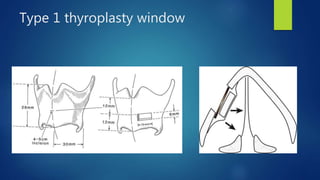
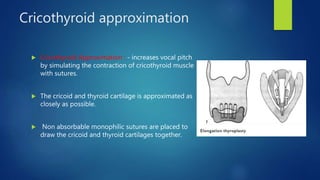
This document provides an overview of laryngeal framework surgery techniques. It discusses the anatomy of the laryngeal cartilages and muscles involved in voice production. It then describes the history and types of thyroplasty procedures developed to improve voice, including type 1-4 thyroplasties. Type 1 involves medialization of the vocal fold while types 2-4 are used to expand, relax or increase tension on the vocal folds. Other techniques discussed include arytenoid adduction, thyroarytenoid myomectomy, cricothyroid approximation and femlar surgery. Complications and limitations of the procedures are also summarized.