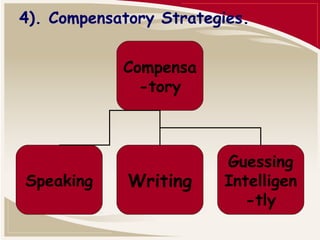
This document is a paper submitted by Solanki Pratiksha M. about language learning strategies as discussed in the book by Rebecca L. Oxford. It discusses six main categories of language learning strategies: cognitive strategies, mnemonic strategies, metacognitive strategies, compensatory strategies, affective strategies, and social strategies. It also addresses influences on strategy choice and current and future trends in strategies research.