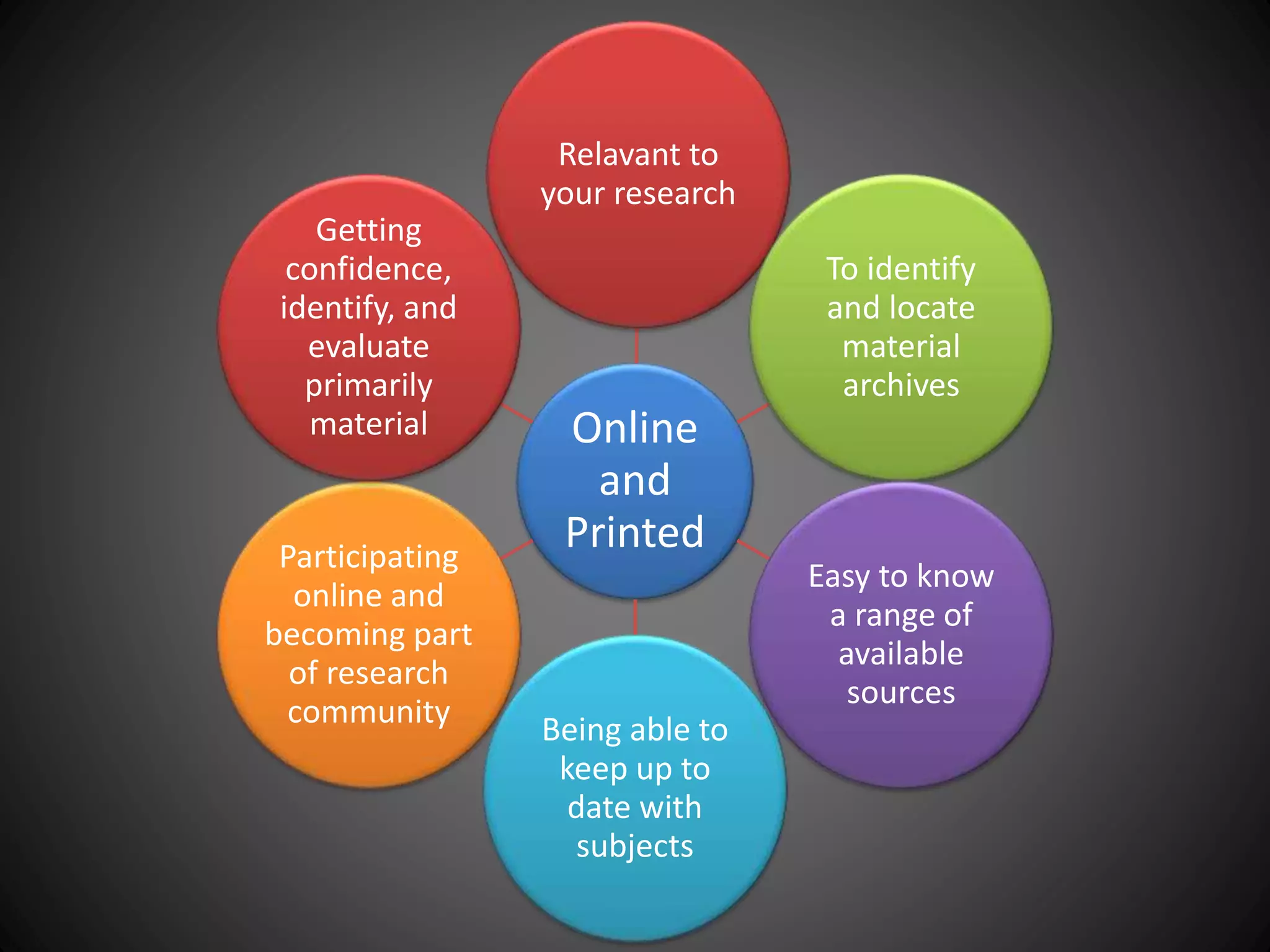
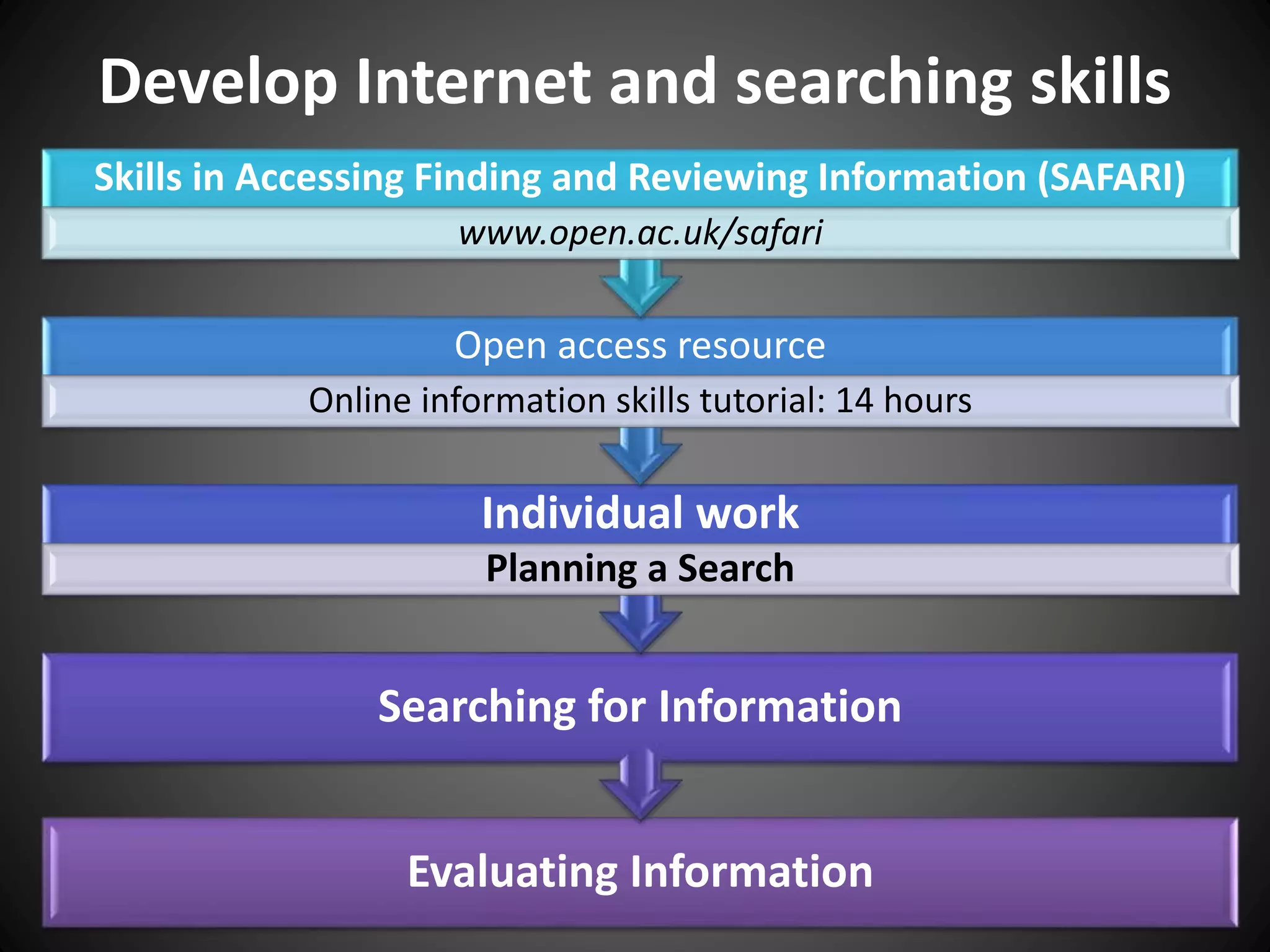
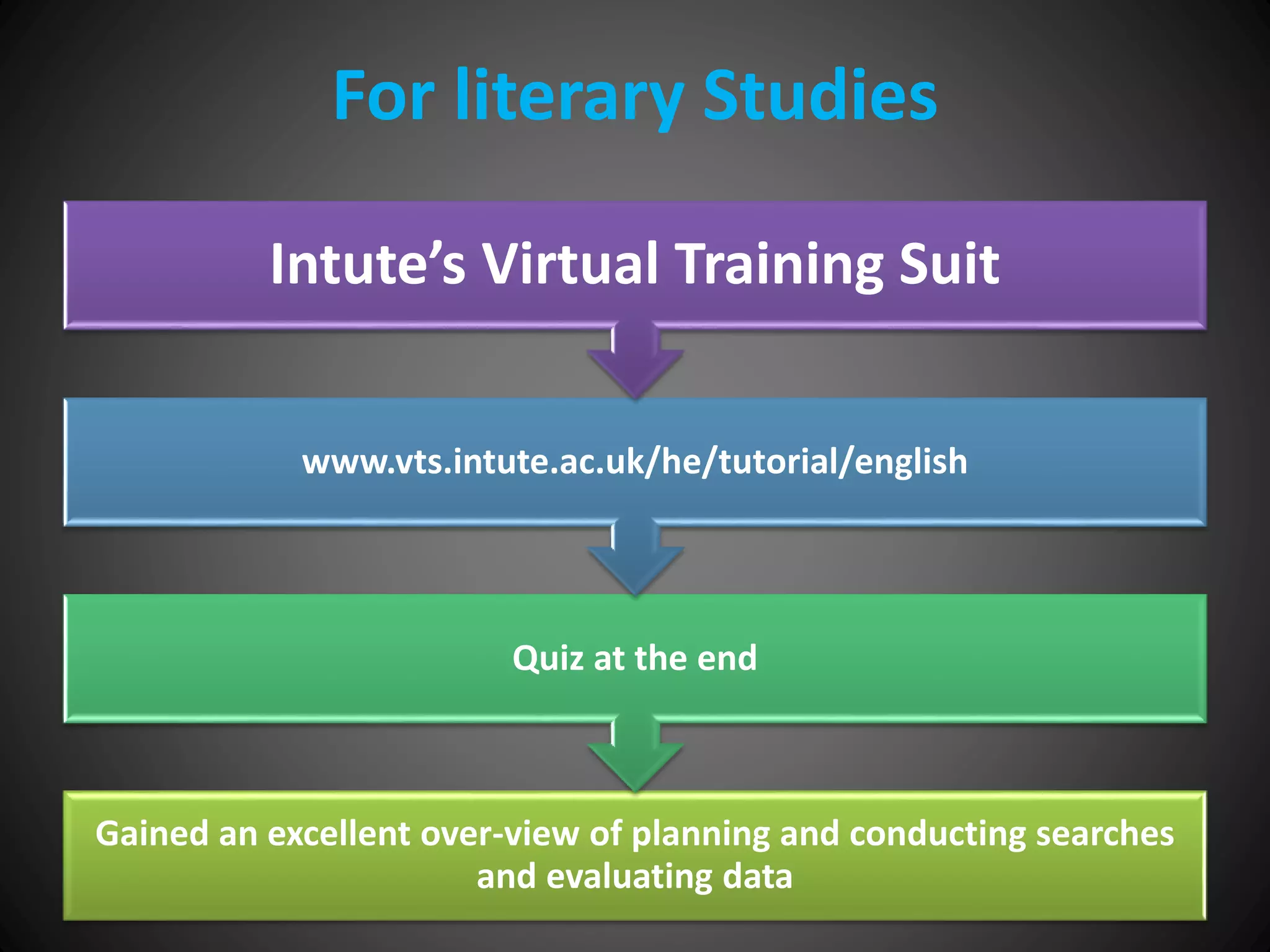
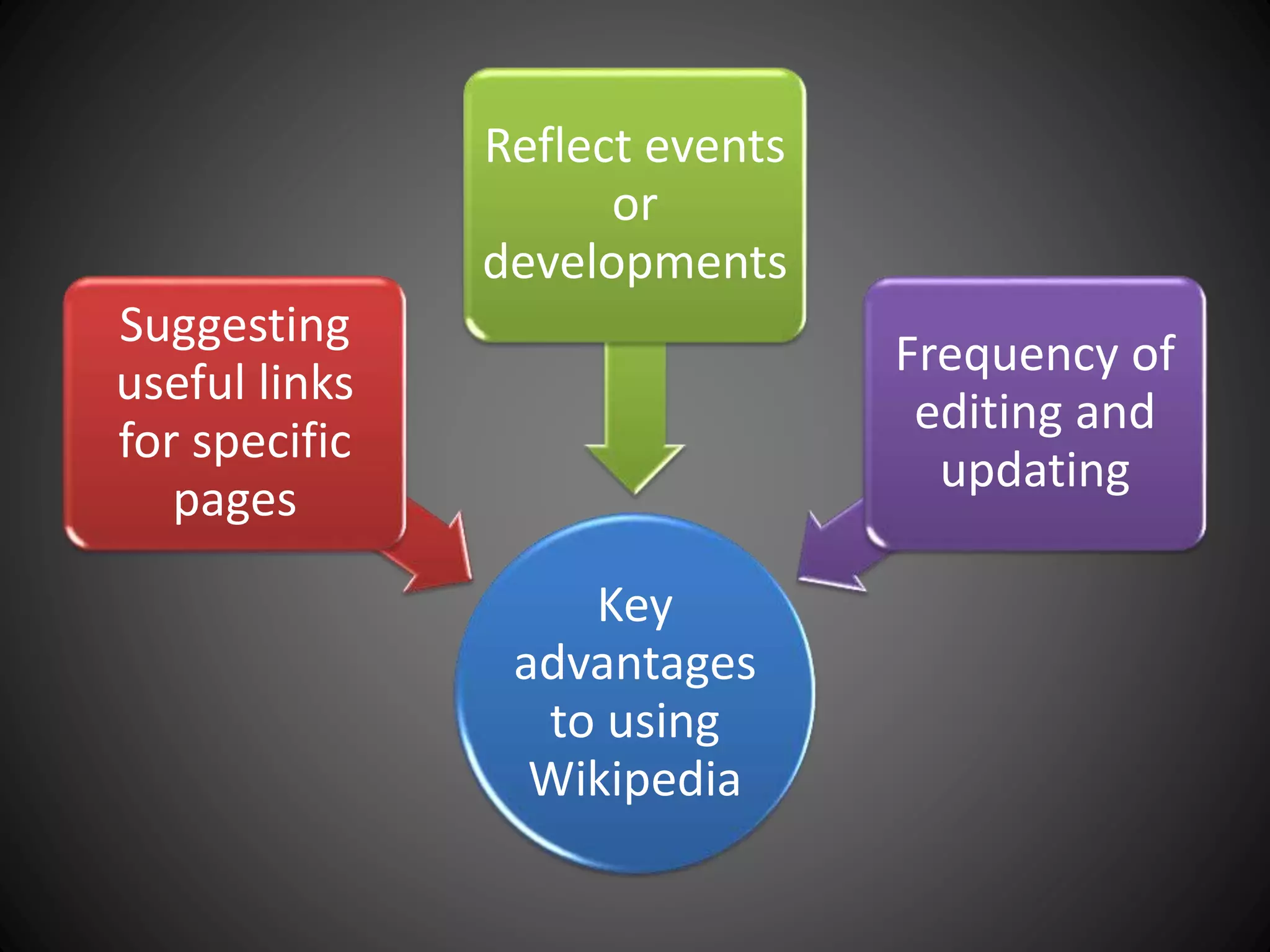
This document provides information about an individual's research paper on using online sources for literary purposes. It discusses various online tools and techniques that can be used, including the internet, Google, Wikipedia, bookmarking sites, bibliographic management tools, and the importance of properly citing sources. It emphasizes the need to evaluate online information and prepare effective search strategies when conducting scholarly research online.