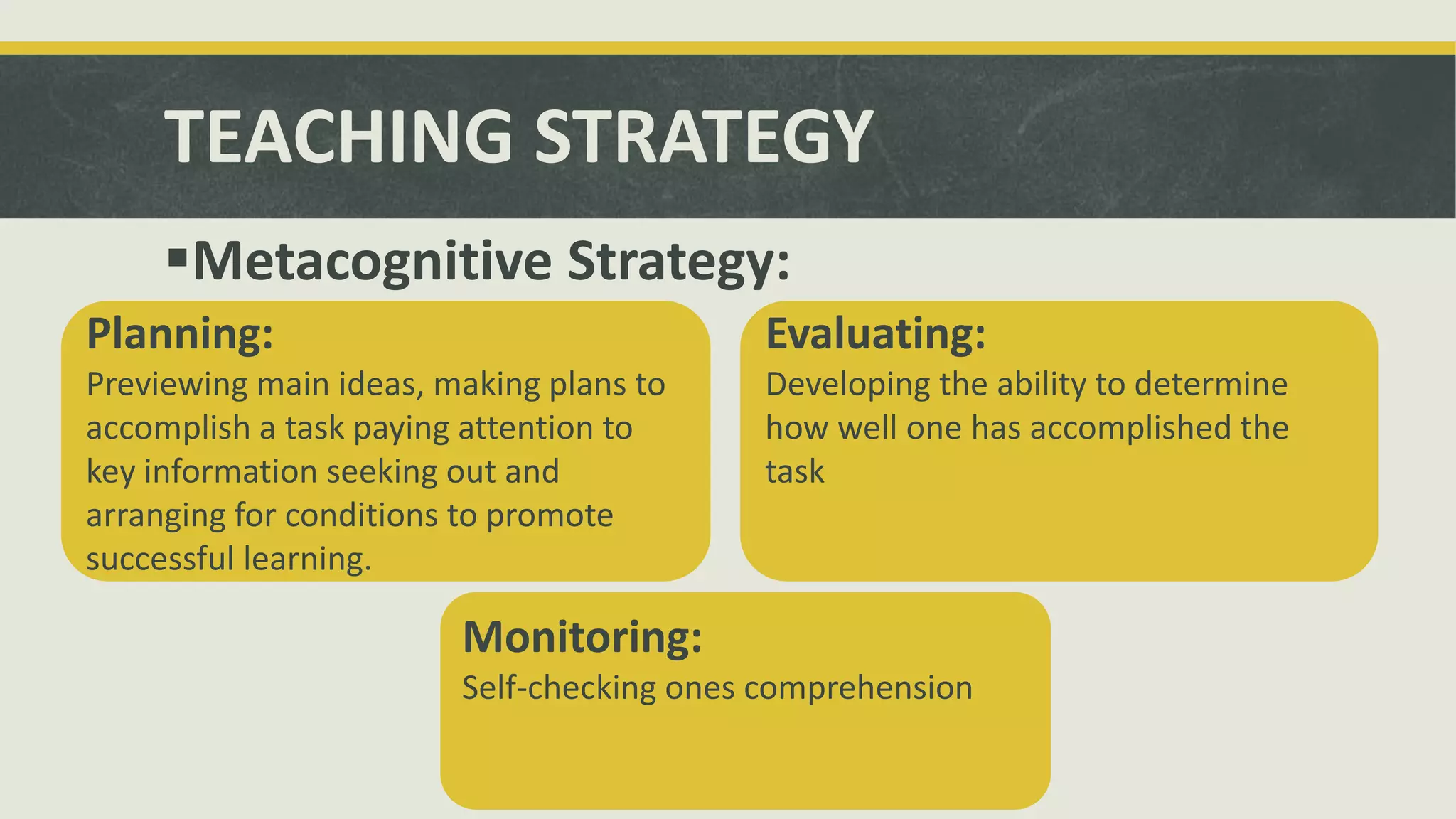
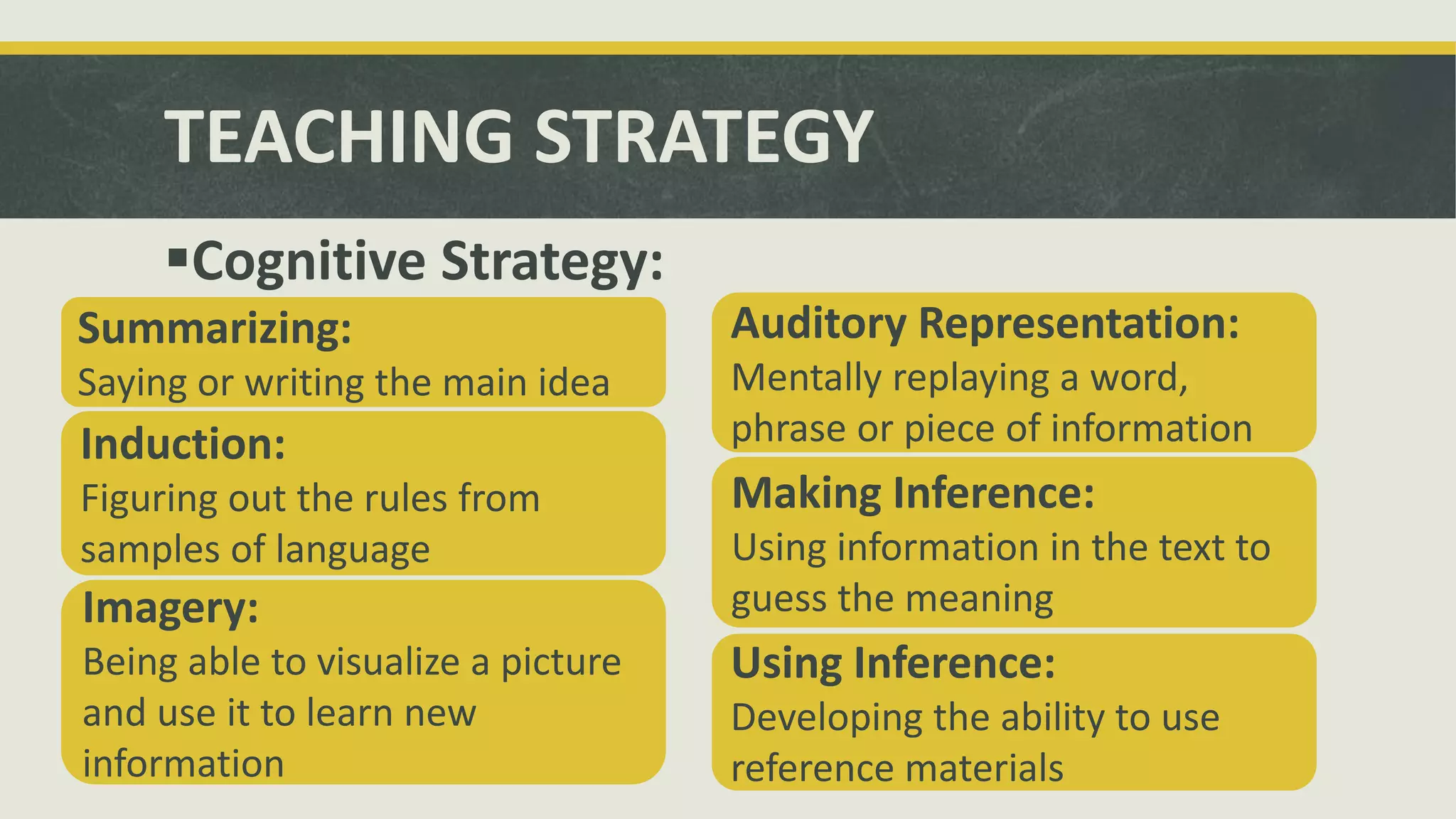
This document discusses learning styles and strategies. It begins by outlining the objectives and sequence of topics to be presented. These include how people learn through visual, auditory and tactile means. It then provides background on learning styles and strategies based on the work of psychologists Jung and Piaget. Key definitions are given for learning styles as natural habitual preferences for absorbing information and strategies as characteristics teachers stimulate in students. The importance of understanding learning styles for diverse classrooms is highlighted. Various types of learning styles are then described, including cognitive, sensory and personality styles. Finally, principles for teaching different styles and strategies are outlined.