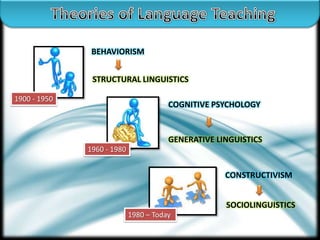
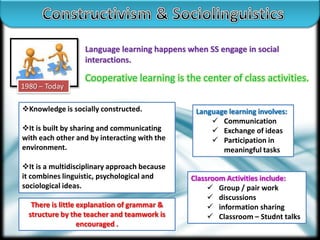
The document outlines different approaches to language teaching from 1900 to today. It discusses behaviorism from 1900-1950 which viewed language as a system of sounds, words and sentences learned through practice and repetition with a focus on drills. From 1960-1980, generative linguistics emerged which saw language as systematic and best learned through detailed grammar explanations. Constructivism from 1980 to today holds that language is socially constructed through interactions and cooperative learning activities like group work.