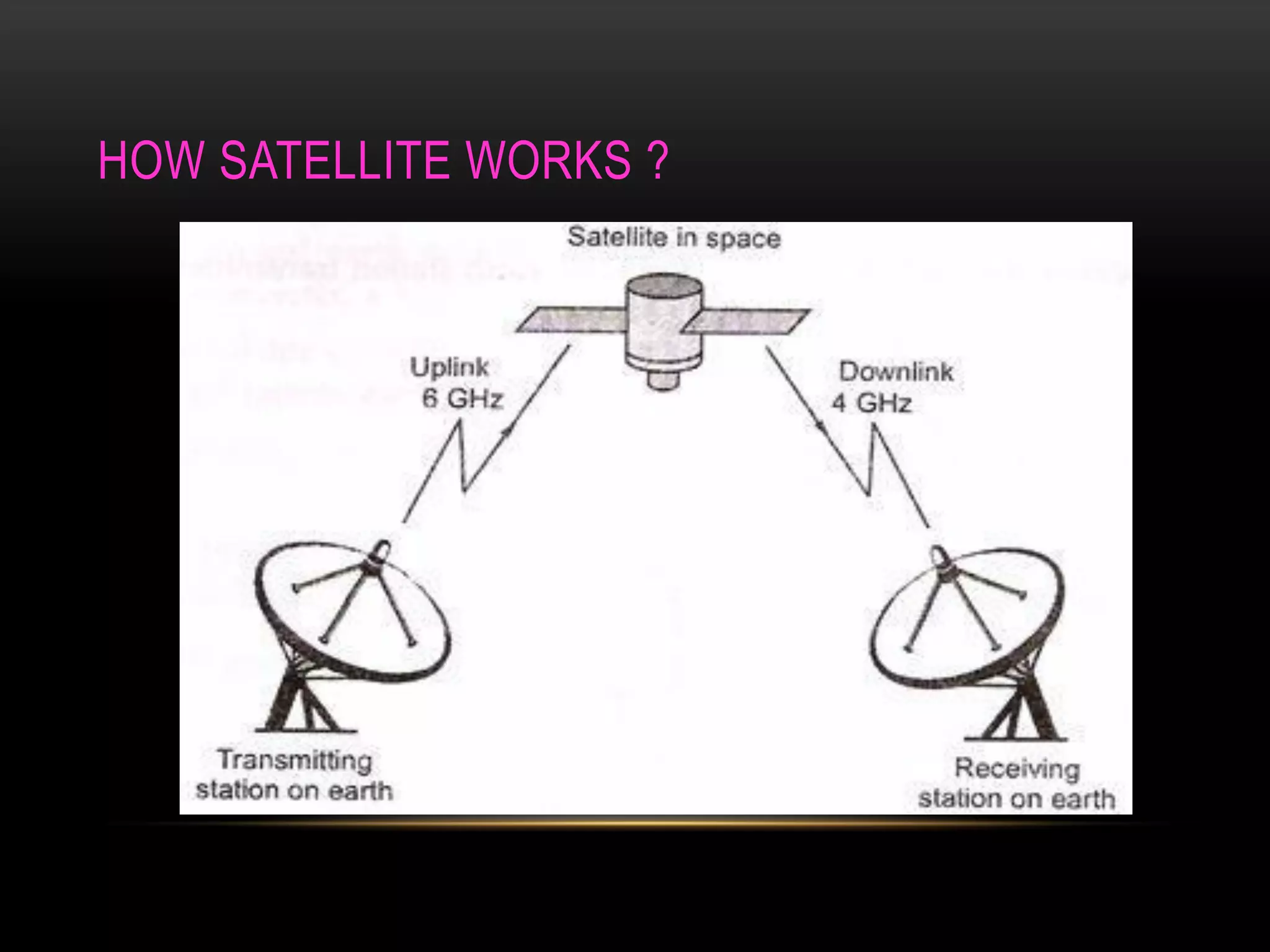
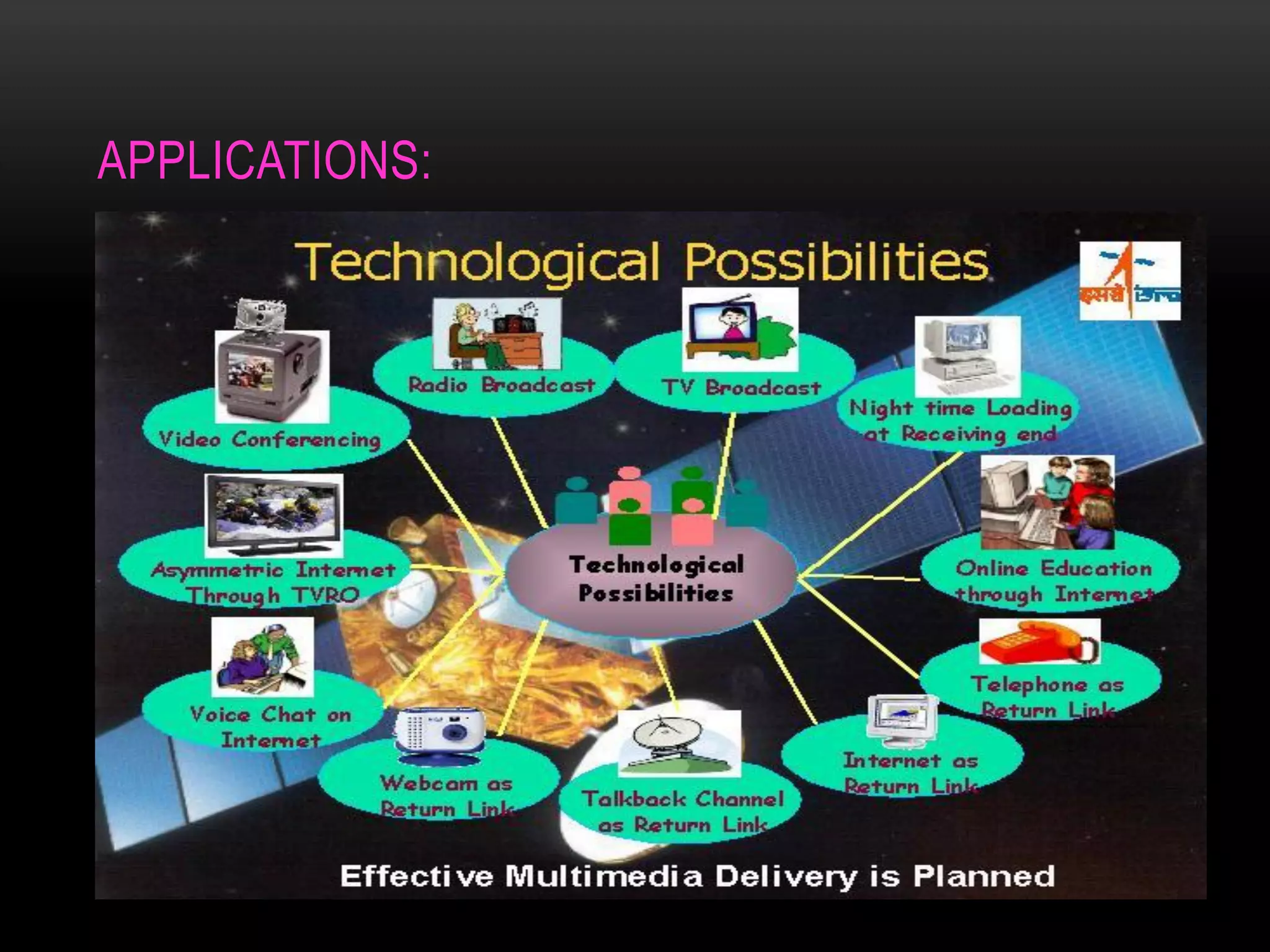
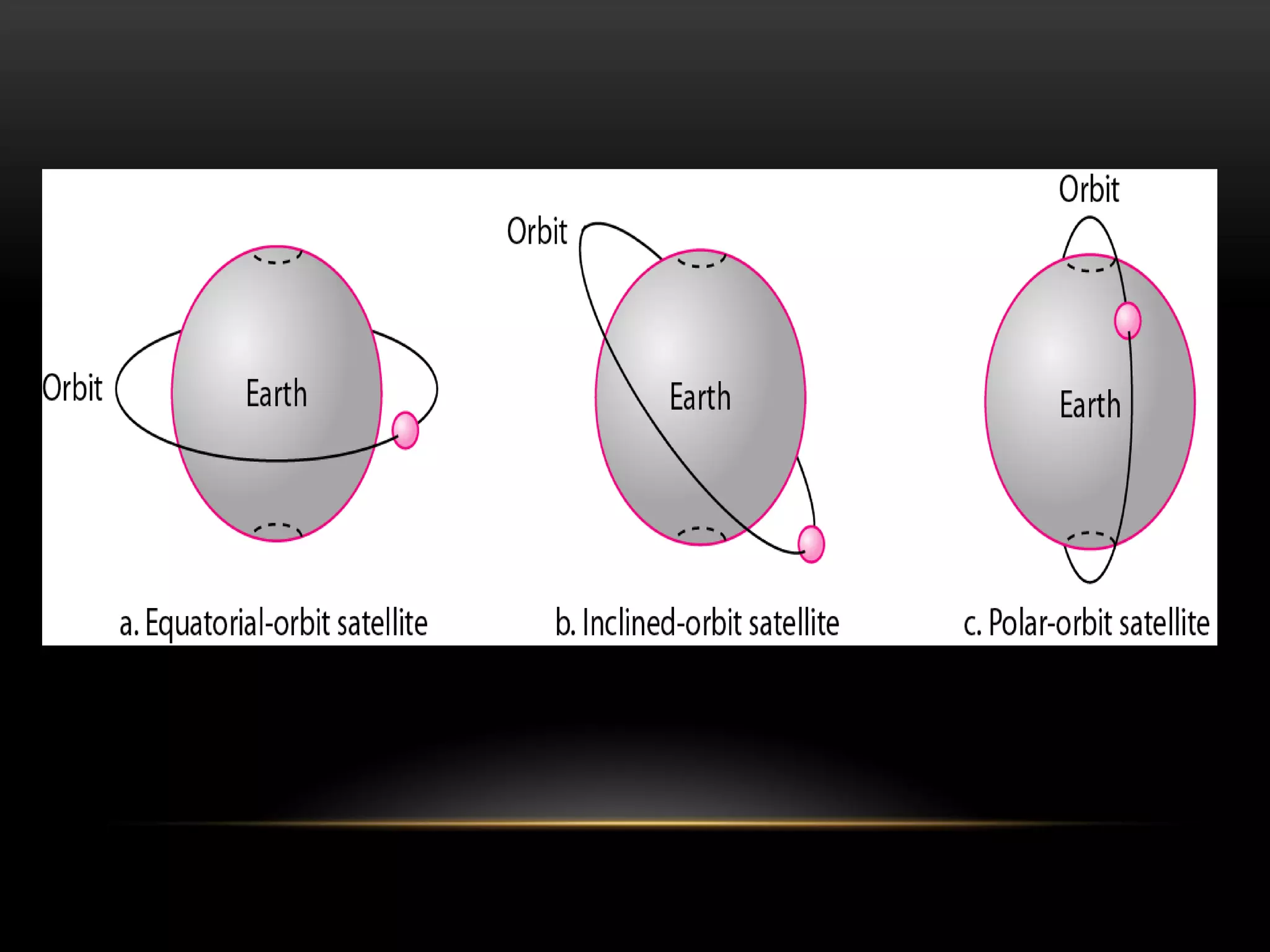
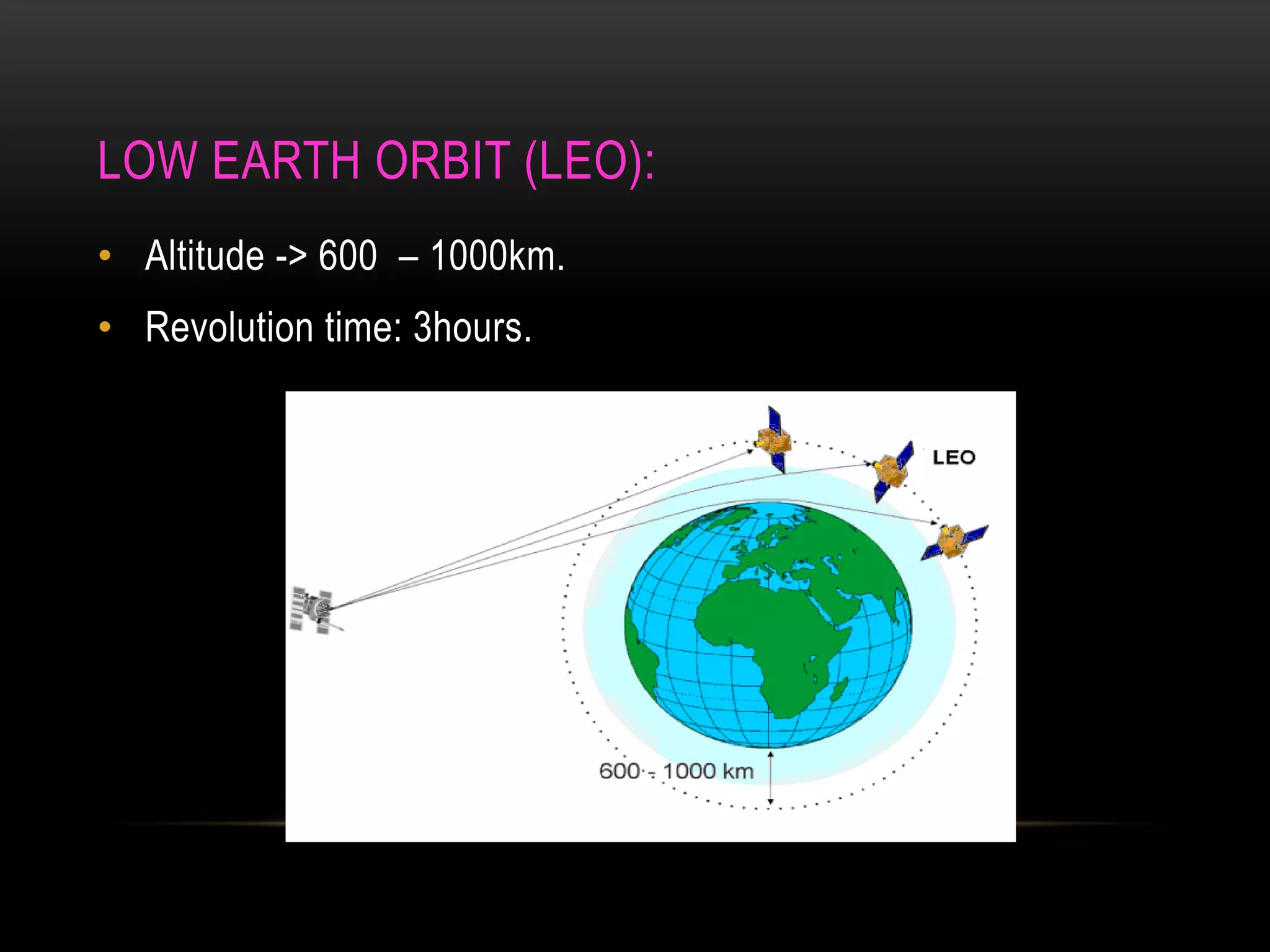
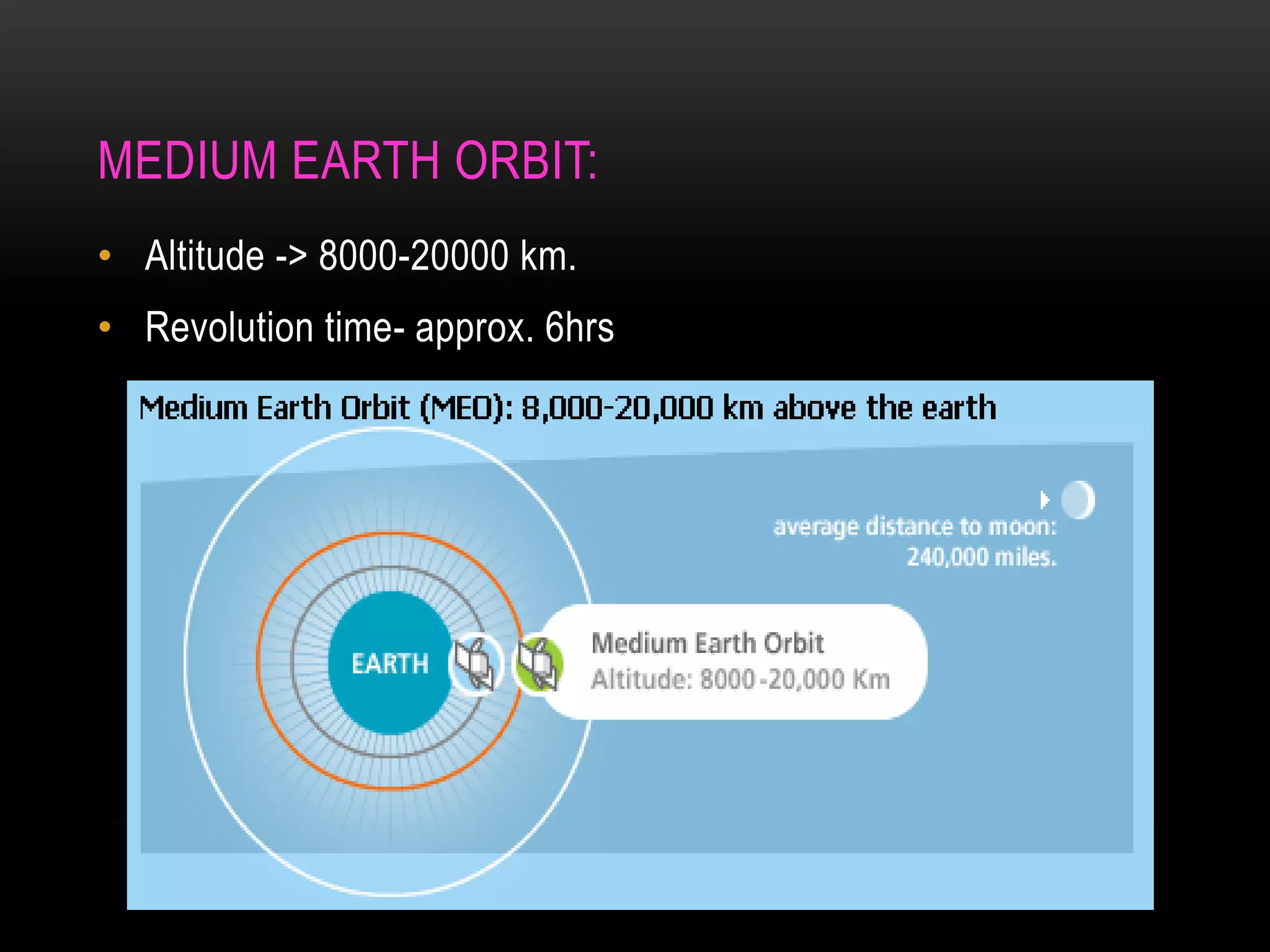
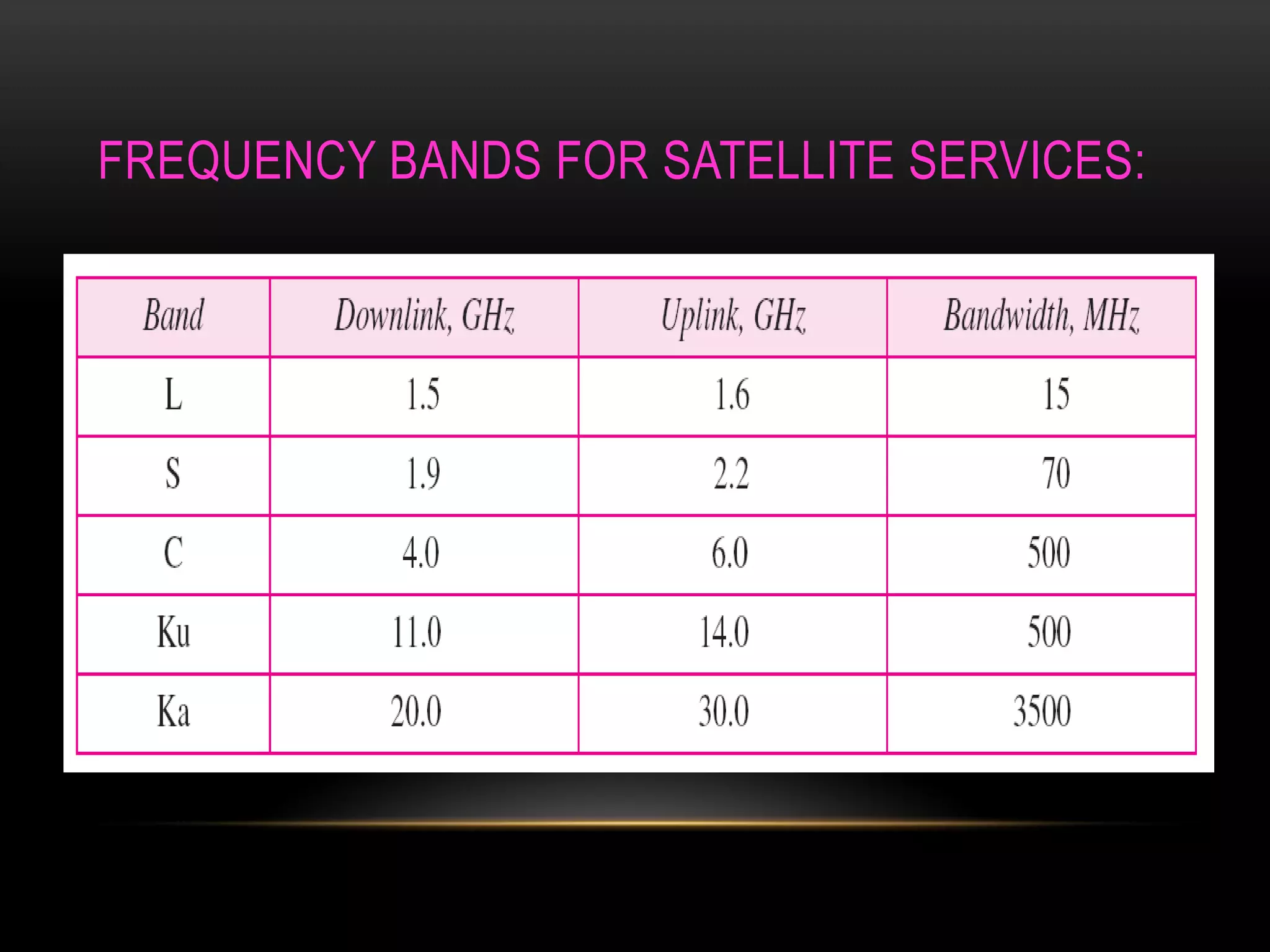
Satellite communication allows people to communicate across long distances. Arthur C. Clarke first proposed the idea of communication satellites in 1945. The first satellite launched was Sputnik 1 by Russia in 1957, though it did not have communication capabilities. Commercial satellite communication began with the launch of Early Bird in 1965. Satellites can be in low, medium or geostationary orbits and operate in different frequency bands like C-band and Ku-band. They provide advantages like global coverage and reliability over terrestrial networks.