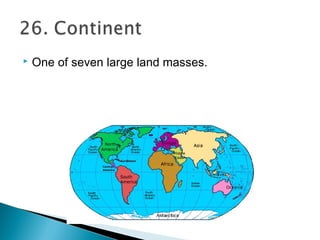
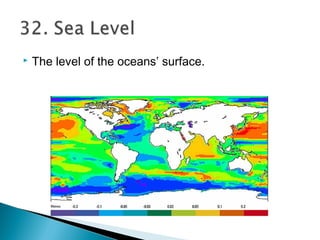
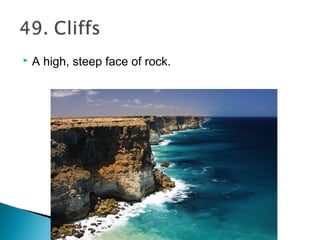
This document defines various geographic and hydrologic terms. It describes different types of bodies of water like oceans, seas, gulfs, straits, rivers, streams, lakes, and reservoirs. It also defines landforms such as continents, islands, peninsulas, mountains, hills, valleys, plains, and deserts. Additionally, it explains geographic coordinate systems and important lines like the equator, prime meridian, latitude and longitude.