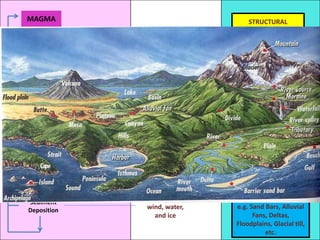
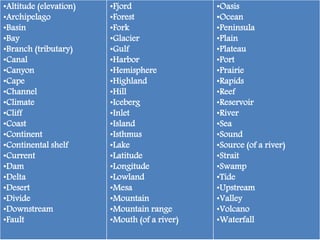
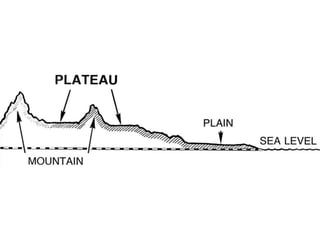
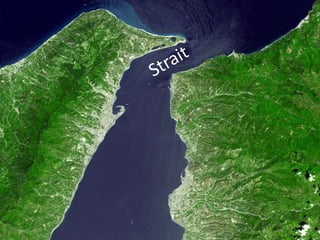
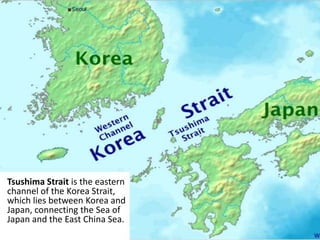
The document defines landforms as natural features on the Earth's surface created by geological processes. It describes how landforms are formed through processes like magma solidification, weathering, erosion, deposition, and tectonic activity. The document then lists and provides examples of major landform types including mountains, hills, plateaus, plains, bays, canyons, and straits.