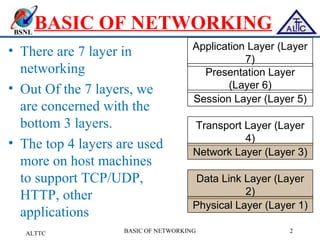
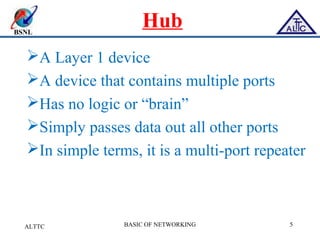
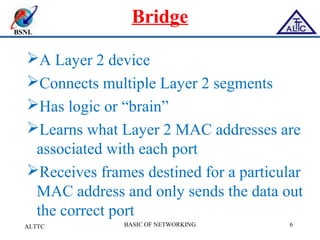
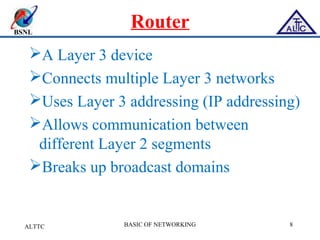
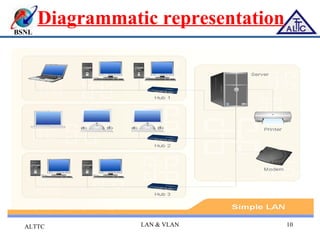
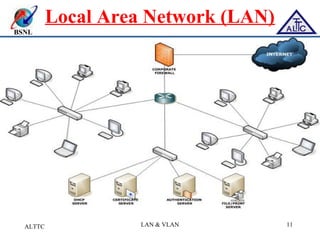
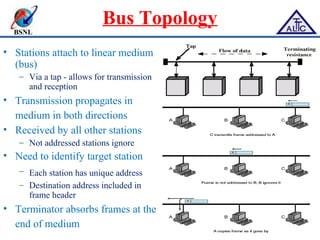
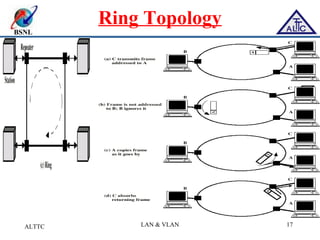
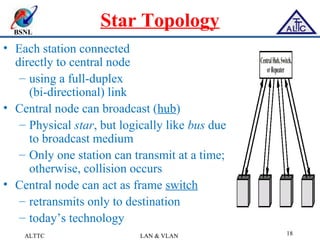
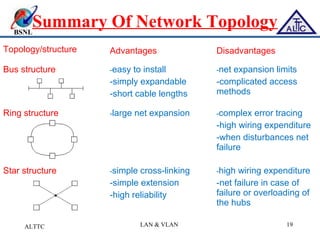
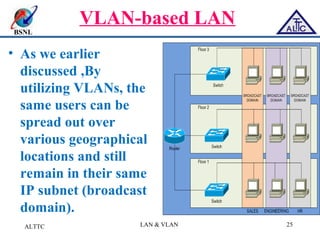
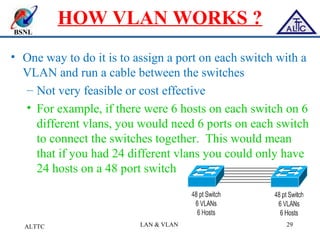
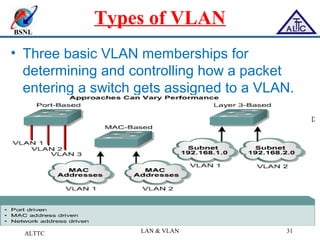
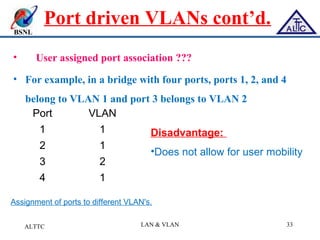
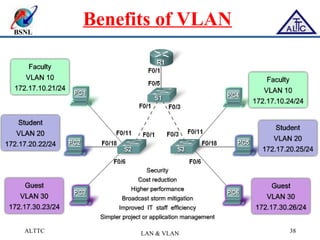
This document provides an overview of local area networks (LANs) and virtual LANs (VLANs). It defines LAN as a network covering a small area like a home, office or campus to connect computers in close proximity. The document discusses common LAN topologies like bus, ring and star. It then introduces VLAN as a way to logically segment devices within a LAN even if they share the same infrastructure. The document explains how VLANs work using tags and trunking between switches. It outlines benefits of VLANs like improved security, flexibility and traffic management compared to traditional LANs.