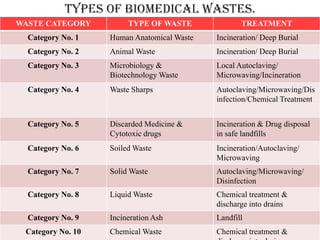
The document outlines safety standards and protocols for clinical laboratories as recommended by OSHA and CDC, including elements such as formal safety programs, the identification of hazards, and the role of safety officers. It highlights various laboratory hazards (biological, chemical, electrical, and fire) and provides specific prevention steps and necessary safety equipment to mitigate risks. Additionally, the document addresses biomedical waste management, providing guidelines for categorization, treatment, and safe disposal of different types of waste.