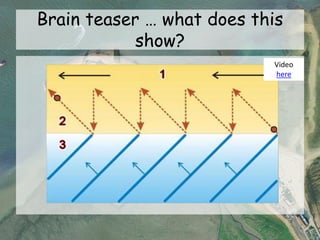
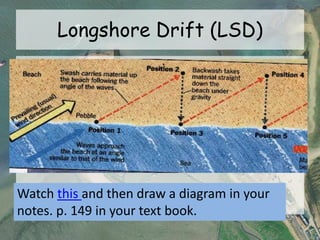
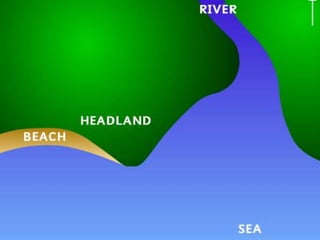
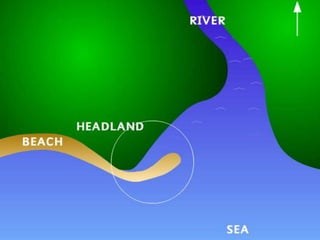
This document discusses three coastal landforms produced by deposition: beaches, spits, and bars.
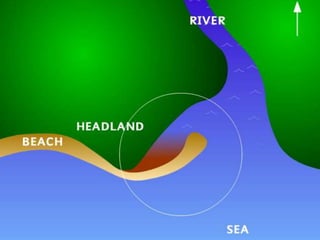
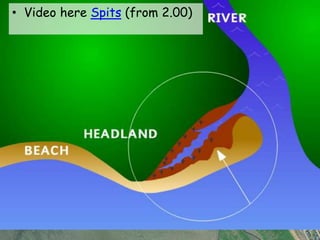
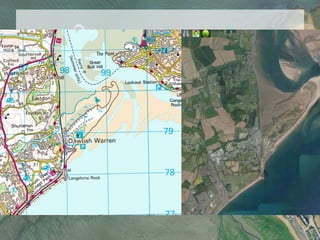
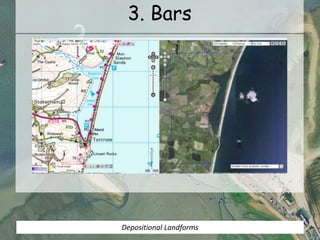
It describes beaches as landforms formed by wave deposition of material along the shore. Spits are described as depositional landforms that form when longshore drift carries sediment along a coastline until the coastline changes direction, causing sediment to build up into a ridge. Bars are described as forming when a spit develops across the mouth of an estuary, building sediment deposits across the two sides and creating a barrier landform across the estuary. Examples and diagrams are provided to illustrate each landform.