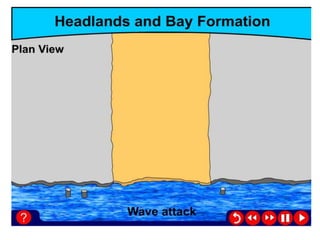
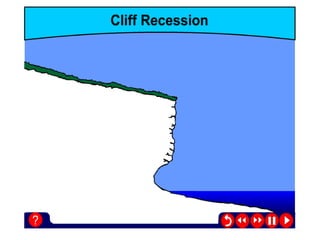
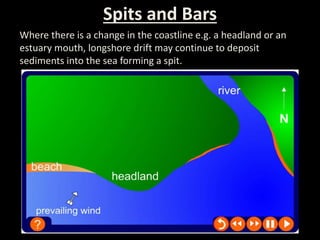
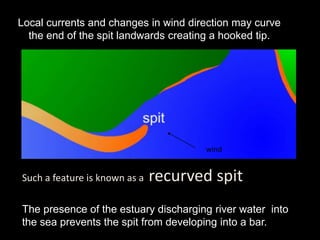
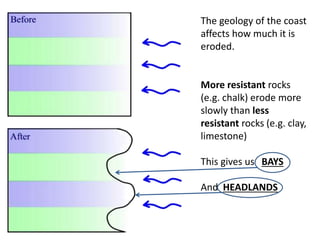
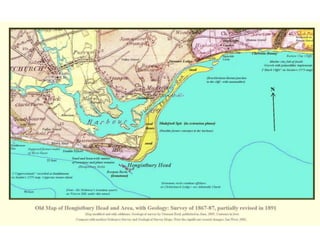
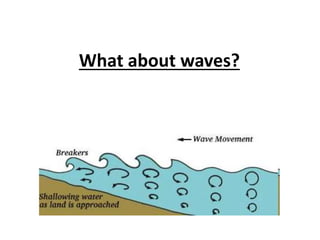
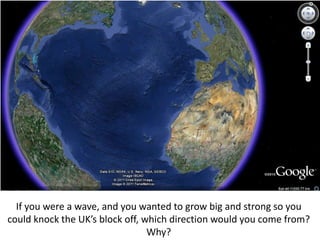
Coastal erosion is influenced by four main processes: corrosion from saltwater, attrition from pebbles hitting cliffs and other materials, abrasion from waves throwing stones that smooth materials, and hydraulic action from water forcing into cracks and splitting rocks apart. These processes create landforms like headlands and bays, wave-cut platforms and notches, beaches, spits, and bars. The geology of the coast determines how resistant the rocks are to erosion - more resistant rocks like chalk erode more slowly than less resistant rocks like clay and limestone. Waves coming directly onto shore are more destructive than waves hitting the coast at an angle, as destructive waves have more energy to erode the land.
![Exam Q
• Including keywords where possible, describe
and explain how erosion can influence the
coast. You may use a diagram.
[3marks]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/revision-whataregeomorphicprocessesandgeology-140430162810-phpapp02/75/Coastal-geomorphic-processes-and-geology-1-2048.jpg)









![Exam Q
• How does geology influence the speed of
erosion at the coast?
[2marks]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/revision-whataregeomorphicprocessesandgeology-140430162810-phpapp02/85/Coastal-geomorphic-processes-and-geology-15-320.jpg)

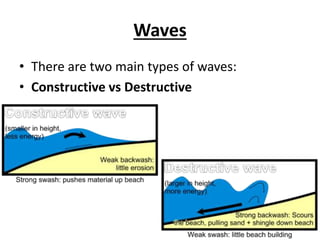
![Exam Q
Describe and explain how constructive and
destructive waves work. Use keywords or
examples where possible. [4marks]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/revision-whataregeomorphicprocessesandgeology-140430162810-phpapp02/85/Coastal-geomorphic-processes-and-geology-22-320.jpg)


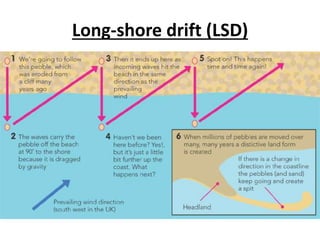
![Exam Q:
“With the use of a diagram, explain the process
and effects of longshore drift, and how it can be
managed”
[6marks]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/revision-whataregeomorphicprocessesandgeology-140430162810-phpapp02/85/Coastal-geomorphic-processes-and-geology-26-320.jpg)

