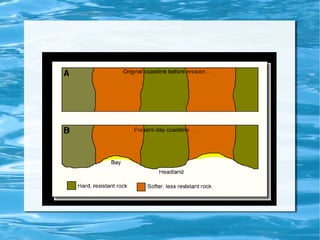
Beaches, spits, and bars are landforms created by coastal depositional processes. Beaches form along shorelines through the deposition of sediment by wave action. As sediment is transported along the shoreline by longshore drift, it can build up into narrow peninsulas called spits. Spits often form at the mouths of estuaries, where the changing direction of the coastline causes sediment to deposit. Bars may develop offshore or near the mouths of rivers, made of sediment that has been deposited and built up over time.