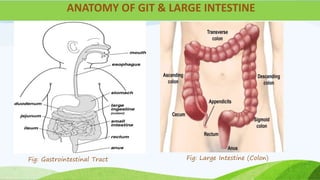
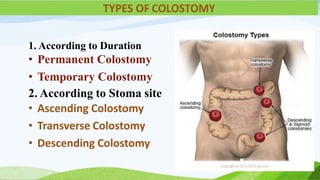
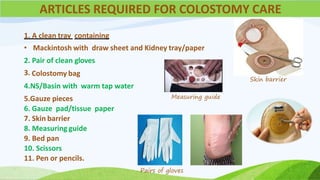
This document provides information about colostomy care presented by Ms. Sakun Rasaily. It includes an outline covering topics like anatomy of the gastrointestinal tract, types of colostomies, indications for colostomy, complications, guidelines for care, nursing assessment, and family teaching. The presentation covers the procedure for colostomy care including required supplies, steps to change the bag, monitoring the patient, and assessing for complications after surgery.


![1 which is not a types of colostomy………
[a] ascending [b] descending
[c] transverse [d] jejunostomy
2 What is the Indication of colostomy……………..
[a] HSP [b] peptic ulcer
[c] SLE [C] All of the above](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalcolostomycareppt-230228181508-ff364c31/85/colostomy-care-ppt-pptx-3-320.jpg)
![3 Adequate blood supply of stoma color is……
[a] white [b] red
[c] pink [d] B&C
4 Colostomy care documentation includes…….
[a] date/time [b] color
[c] both a&b [d] none
5 Complication of colostomy…….
[a] bleeding [b] obstruction
[c] prolapce [d] all
GOOD LUCK](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalcolostomycareppt-230228181508-ff364c31/85/colostomy-care-ppt-pptx-4-320.jpg)



























![POST TEST
1 which is not a types of colostomy………
[a] ascending [b] descending
[c] transverse [d] jejunostomy
2 What is the Indication of colostomy……………..
[a] HSP [b] peptic ulcer
[c] SLE [C] All of the above](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalcolostomycareppt-230228181508-ff364c31/85/colostomy-care-ppt-pptx-35-320.jpg)
![3 Adequate blood supply of stoma color is……
[a] white [b] red
[c] pink [d] B&C
4 Colostomy care documentation includes…….
[a] date/time [b] color
[c] both a&b [d] none
5 Complication fo colostomy…….
[a] bleeding [b] obstruction
[c] prolapce [d] all
GOOD LUCK](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalcolostomycareppt-230228181508-ff364c31/85/colostomy-care-ppt-pptx-36-320.jpg)
