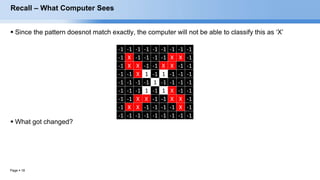
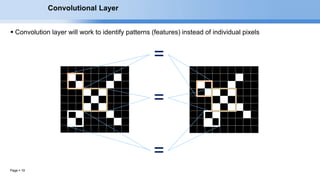
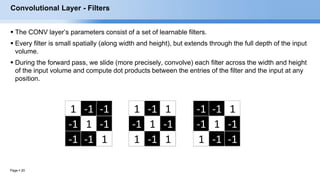
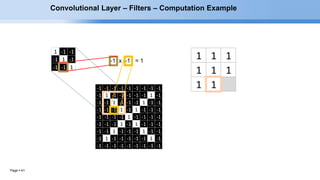
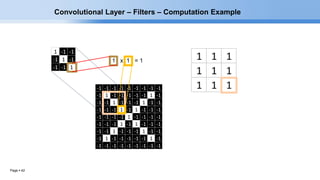
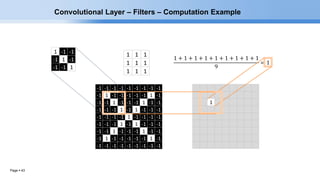
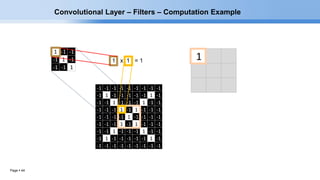
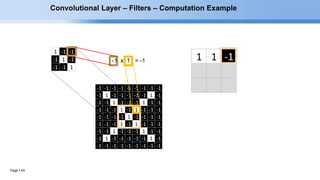
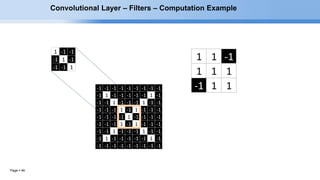
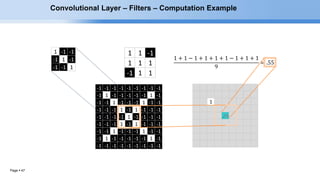
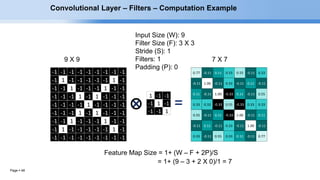
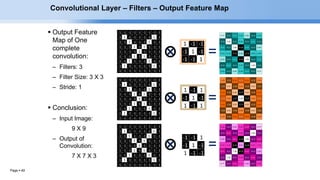
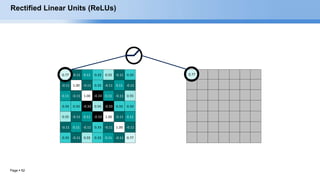
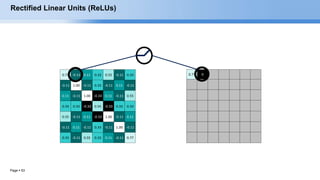
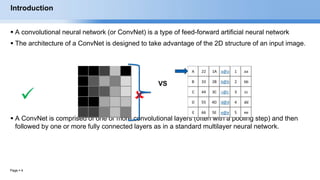
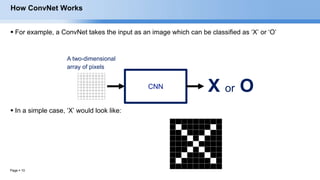
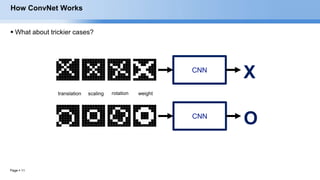
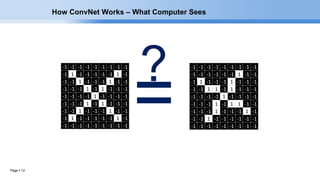
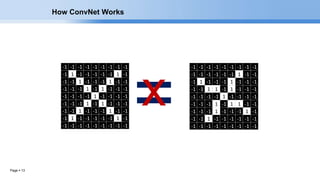
The document provides an overview of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and their layers. It begins with an introduction to CNNs, noting they are a type of neural network designed to process 2D inputs like images. It then discusses the typical CNN architecture of convolutional layers followed by pooling and fully connected layers. The document explains how CNNs work using a simple example of classifying handwritten X and O characters. It provides details on the different layer types, including convolutional layers which identify patterns using small filters, and pooling layers which downsample the inputs.




![Page 16
ConvNet Layers (At a Glance)
CONV layer will compute the output of neurons that are connected to local regions in the input,
each computing a dot product between their weights and a small region they are connected to in
the input volume.
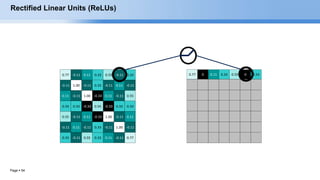
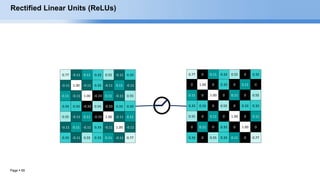
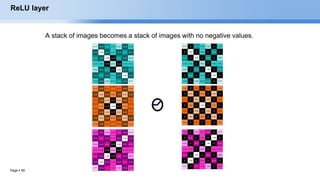
RELU layer will apply an elementwise activation function, such as the max(0,x) thresholding at
zero. This leaves the size of the volume unchanged.
POOL layer will perform a downsampling operation along the spatial dimensions (width, height).
FC (i.e. fully-connected) layer will compute the class scores, resulting in volume of size [1x1xN],
where each of the N numbers correspond to a class score, such as among the N categories.
EECS6980:006 Social Network Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convnets-180216180350/85/Convolutional-Neural-Networks-16-320.jpg)