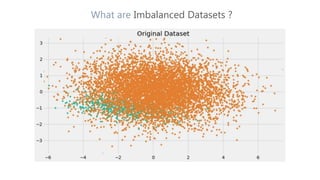
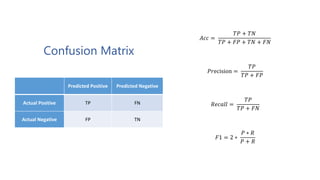
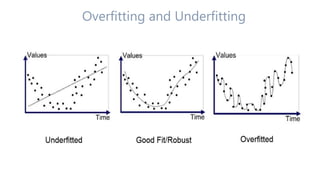
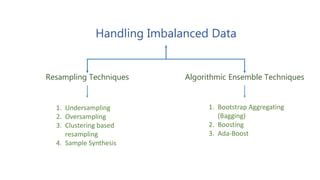
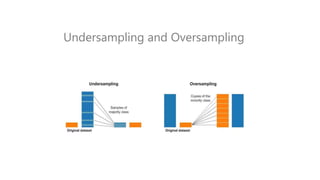
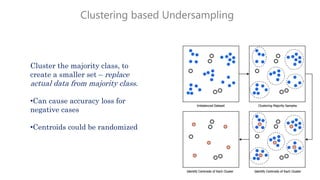
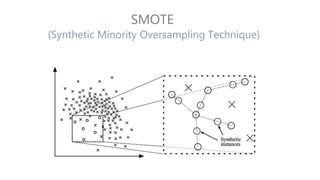
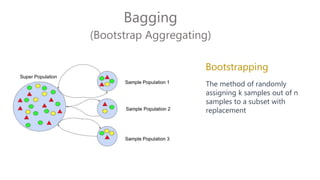
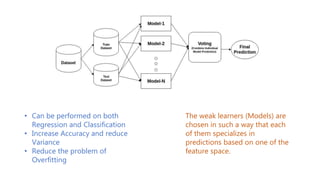
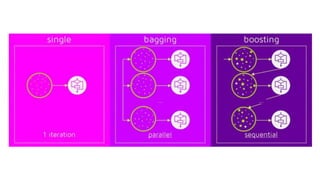
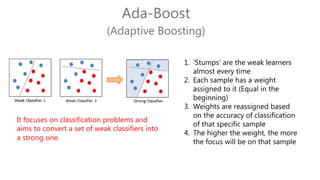
The document discusses multiclass classification of imbalanced datasets, outlining their significance and applications such as in fraud detection and disease identification. It details various handling techniques, including resampling methods (undersampling, oversampling) and algorithmic ensemble techniques (bagging, boosting) to improve model accuracy and reduce overfitting. Additionally, it explains specific methods like SMOTE and AdaBoost for enhancing predictive performance.