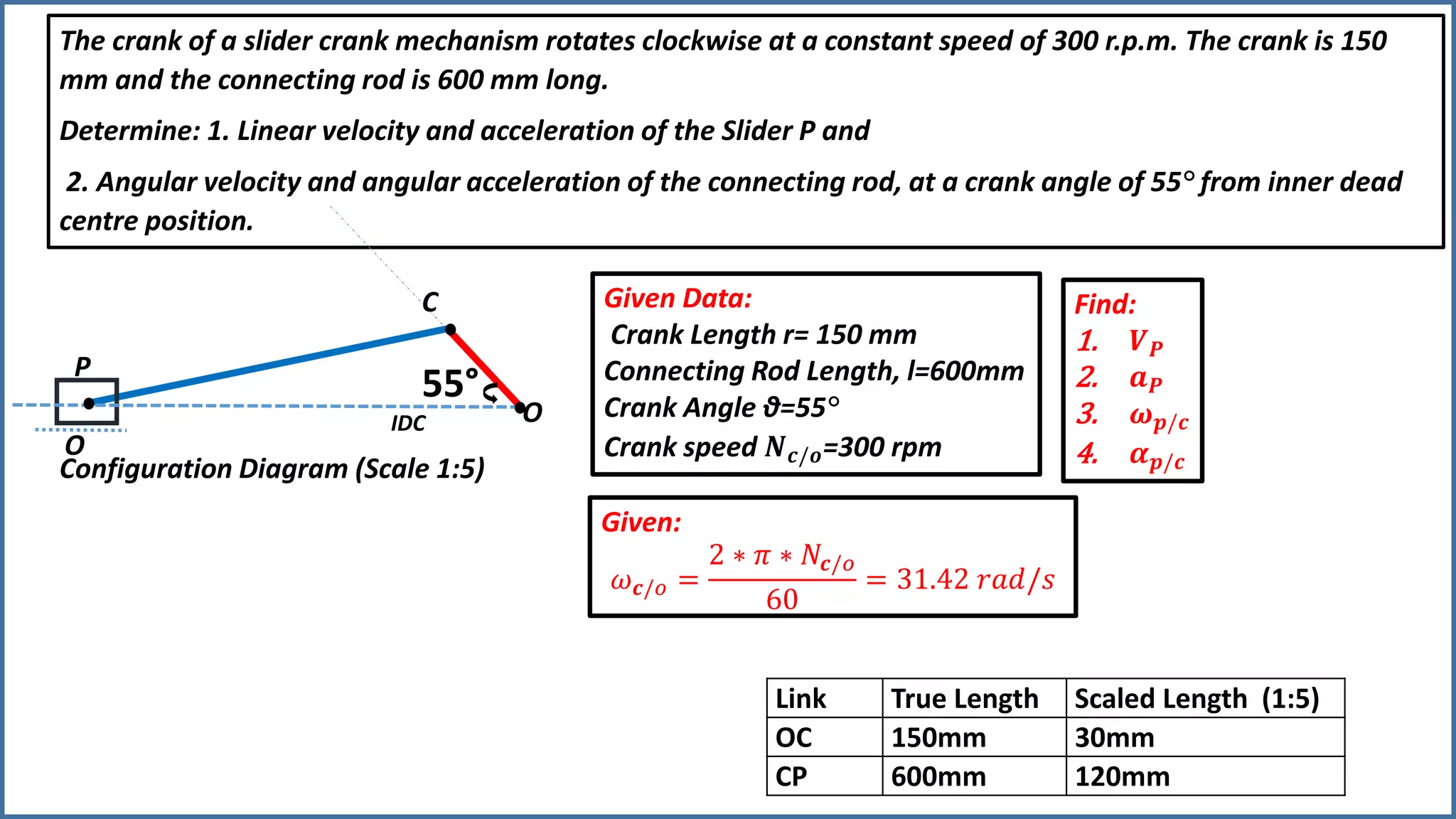
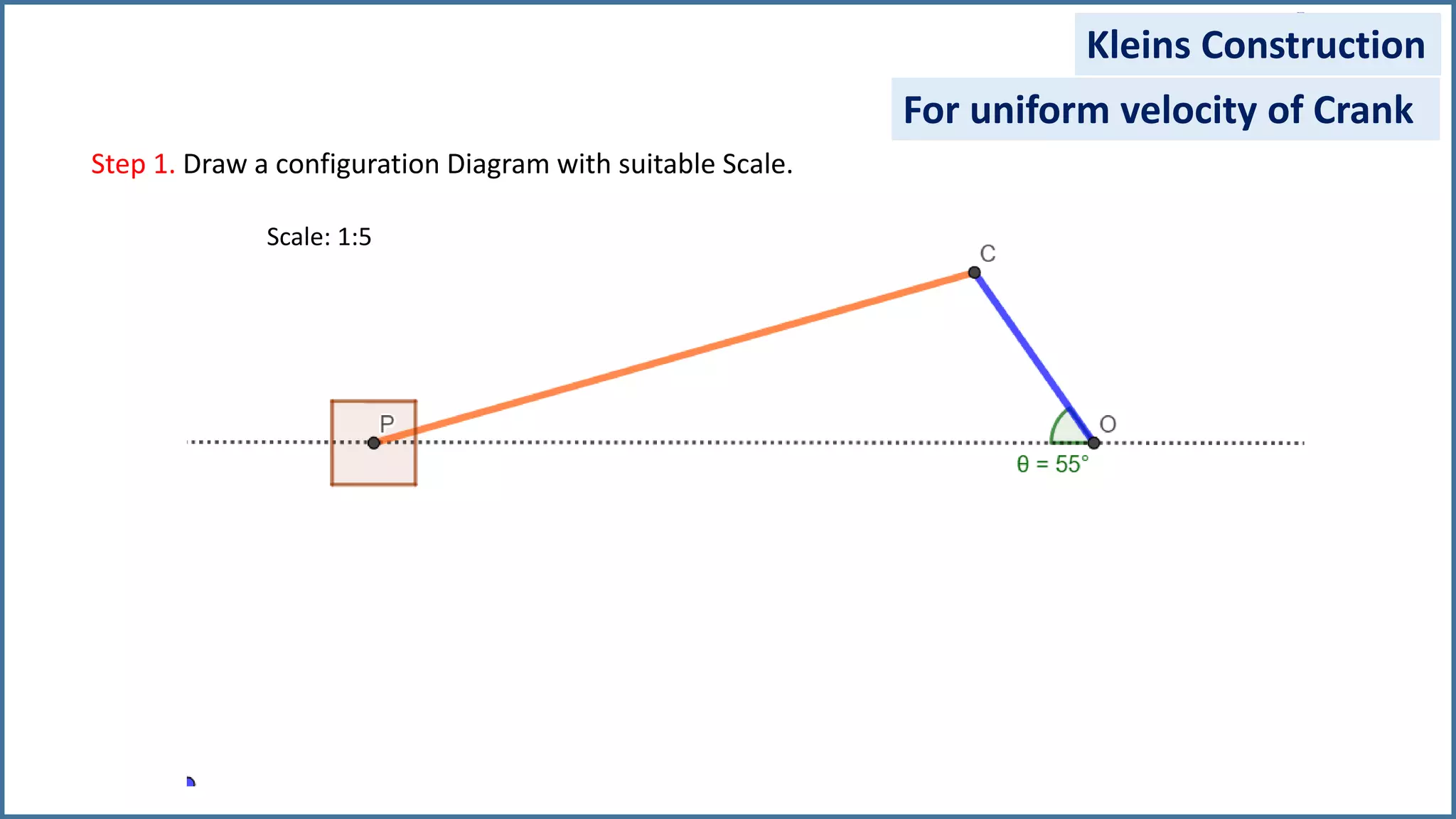
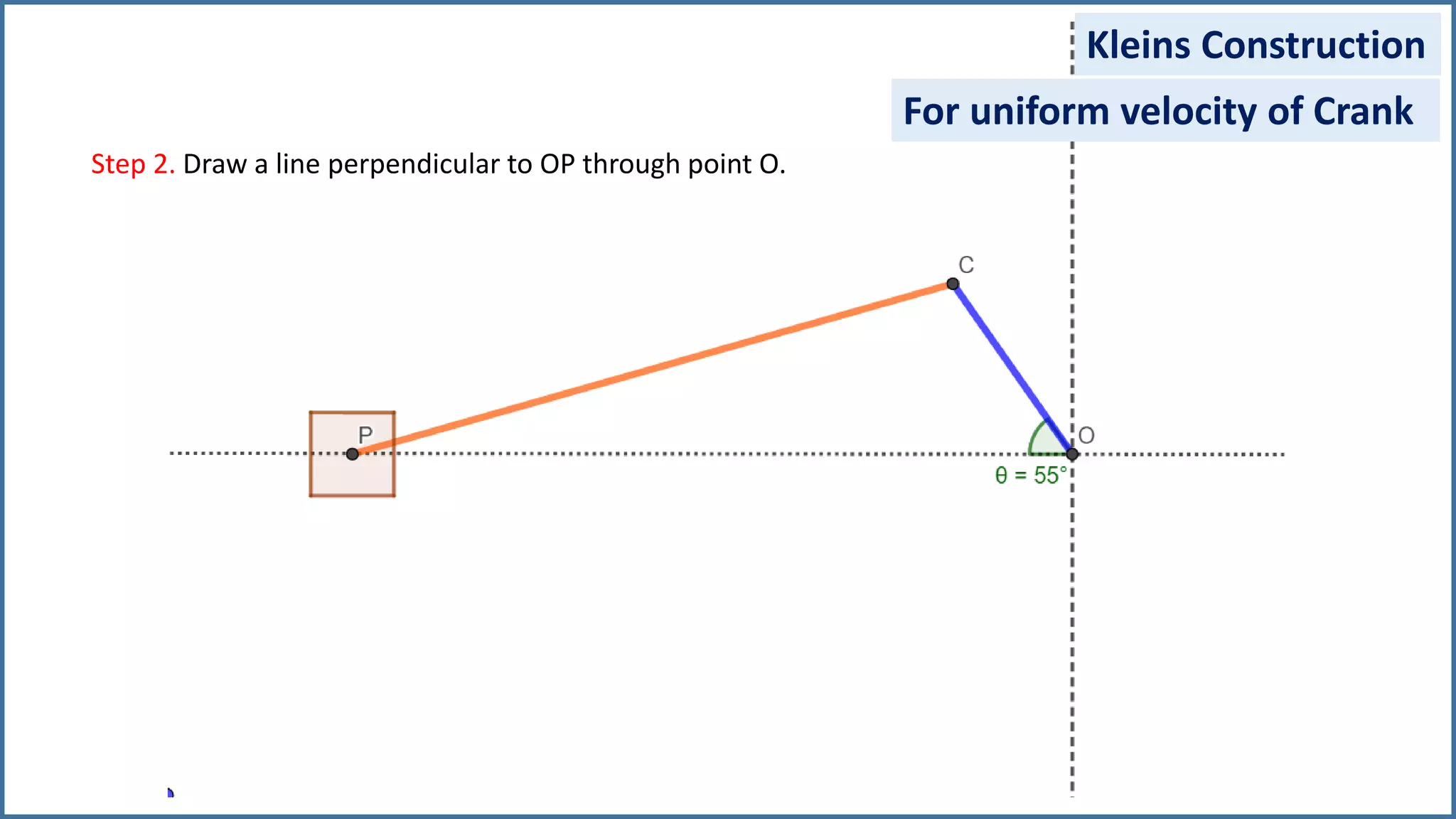
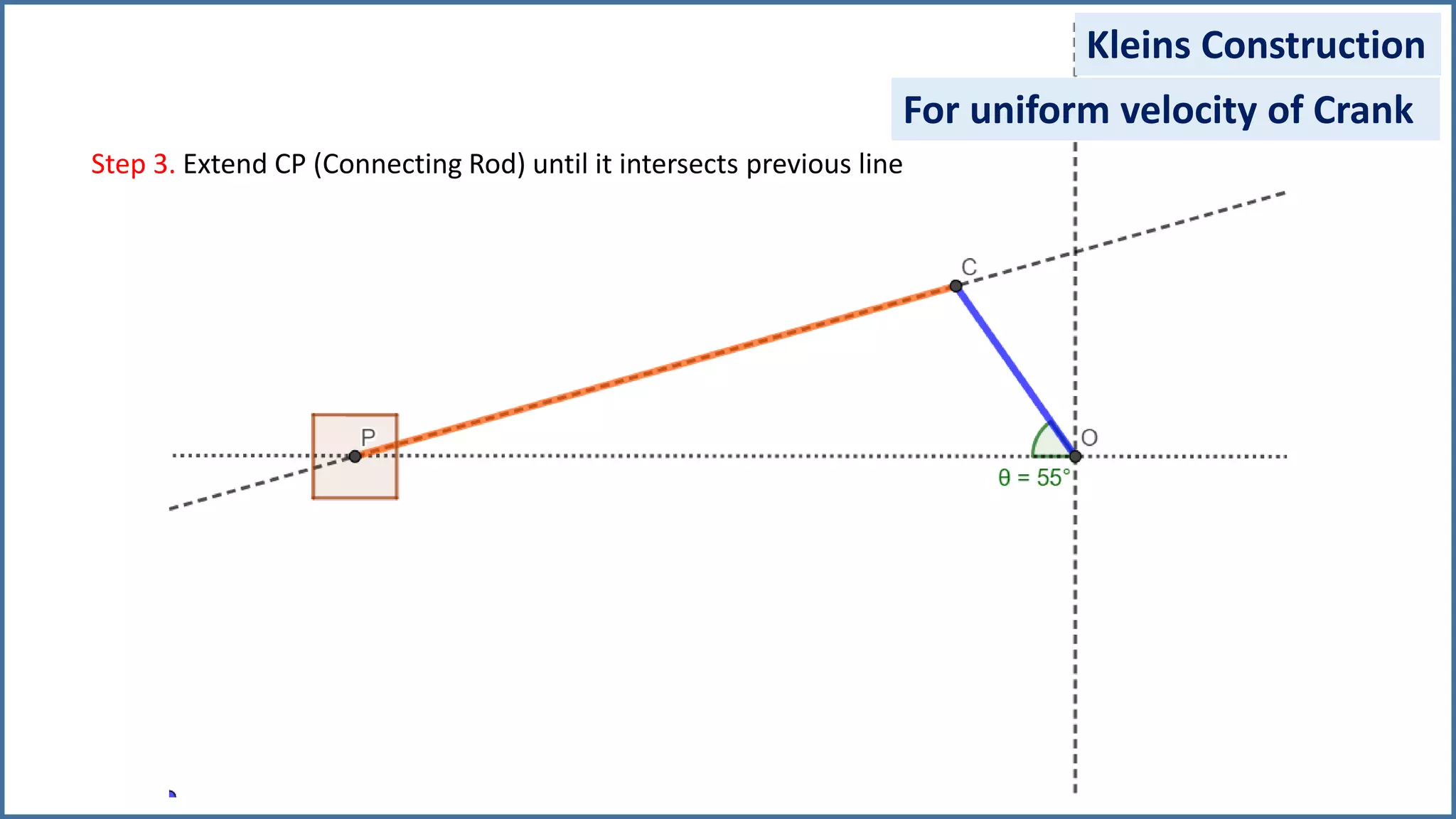
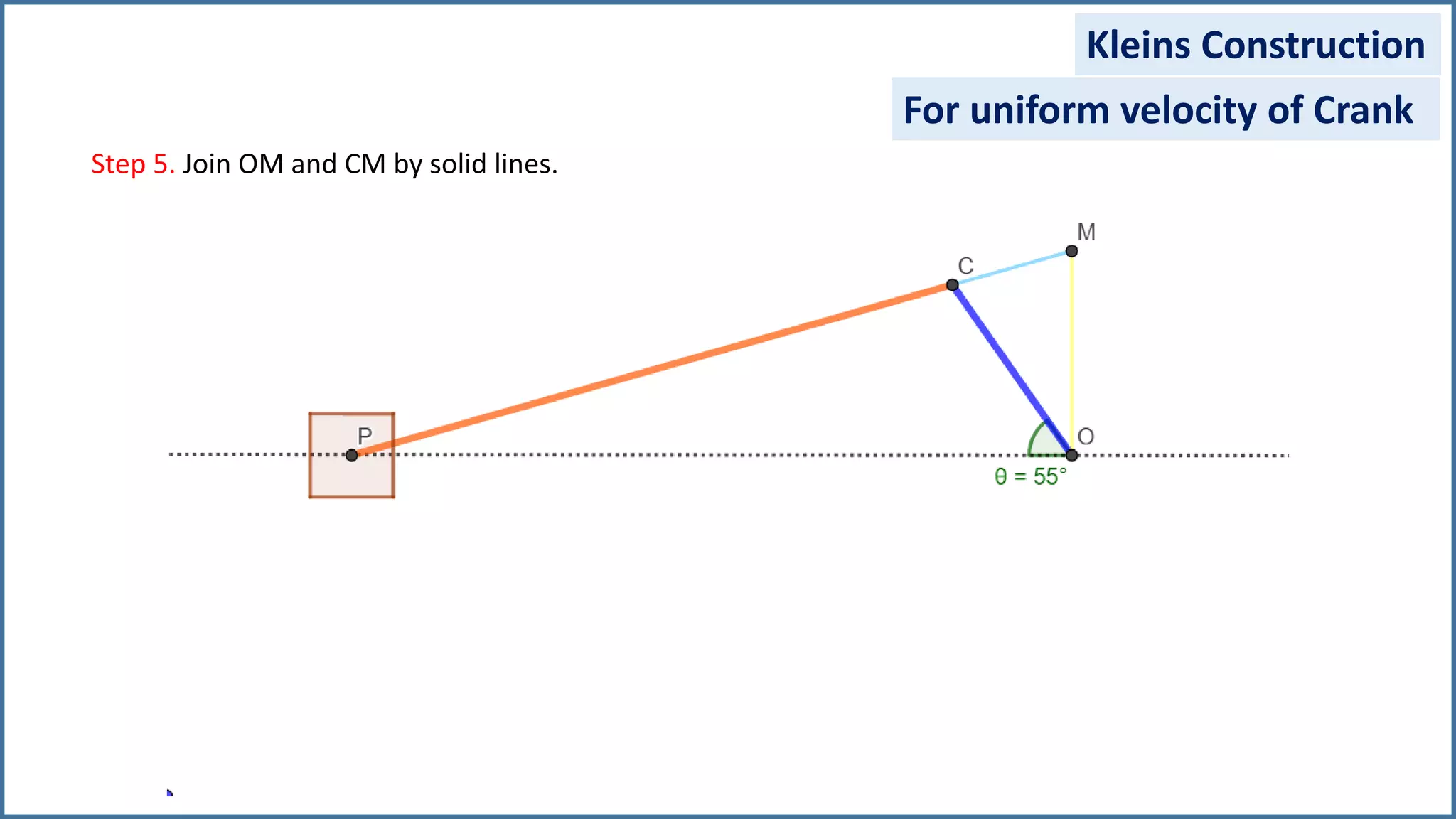
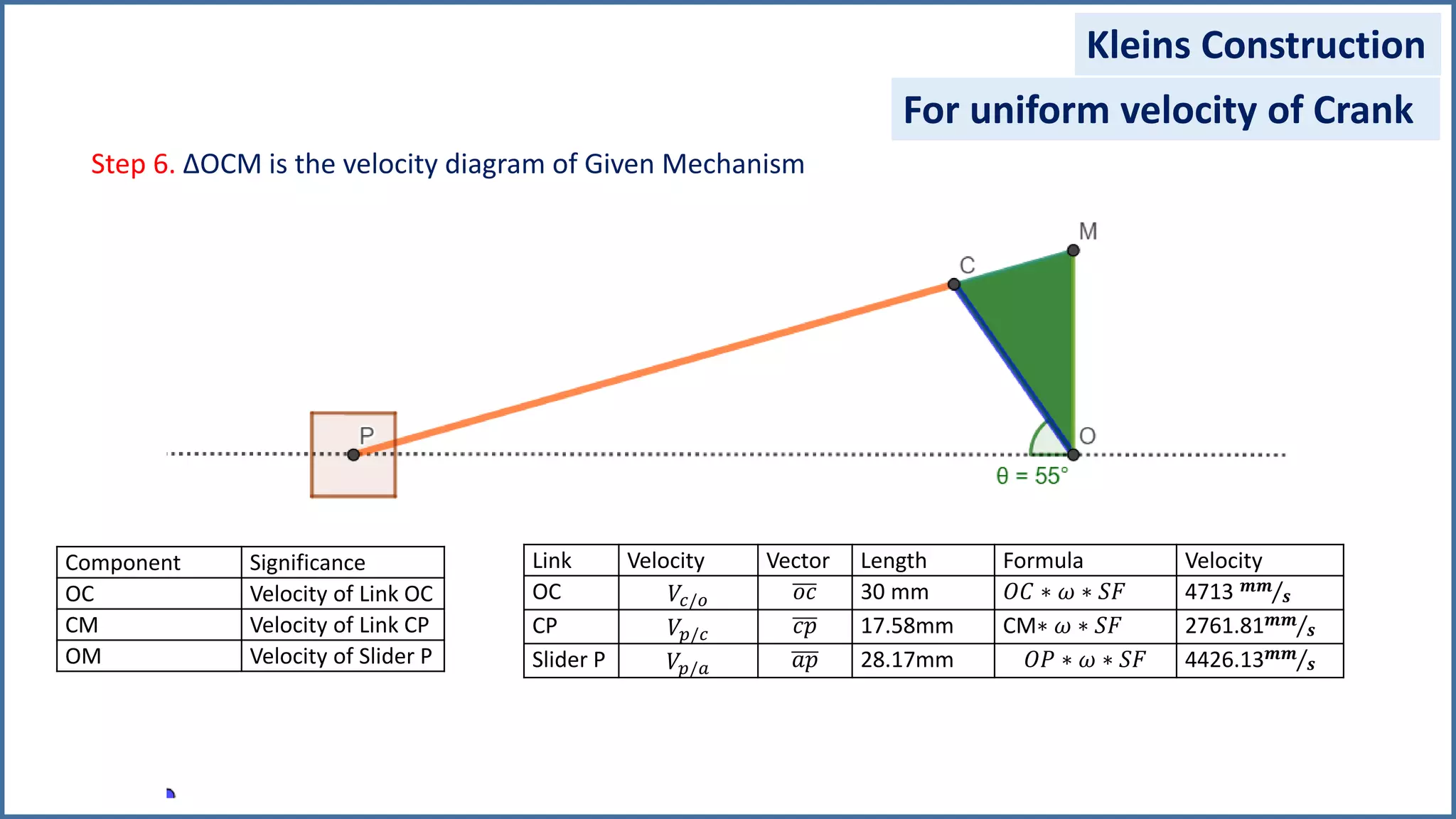
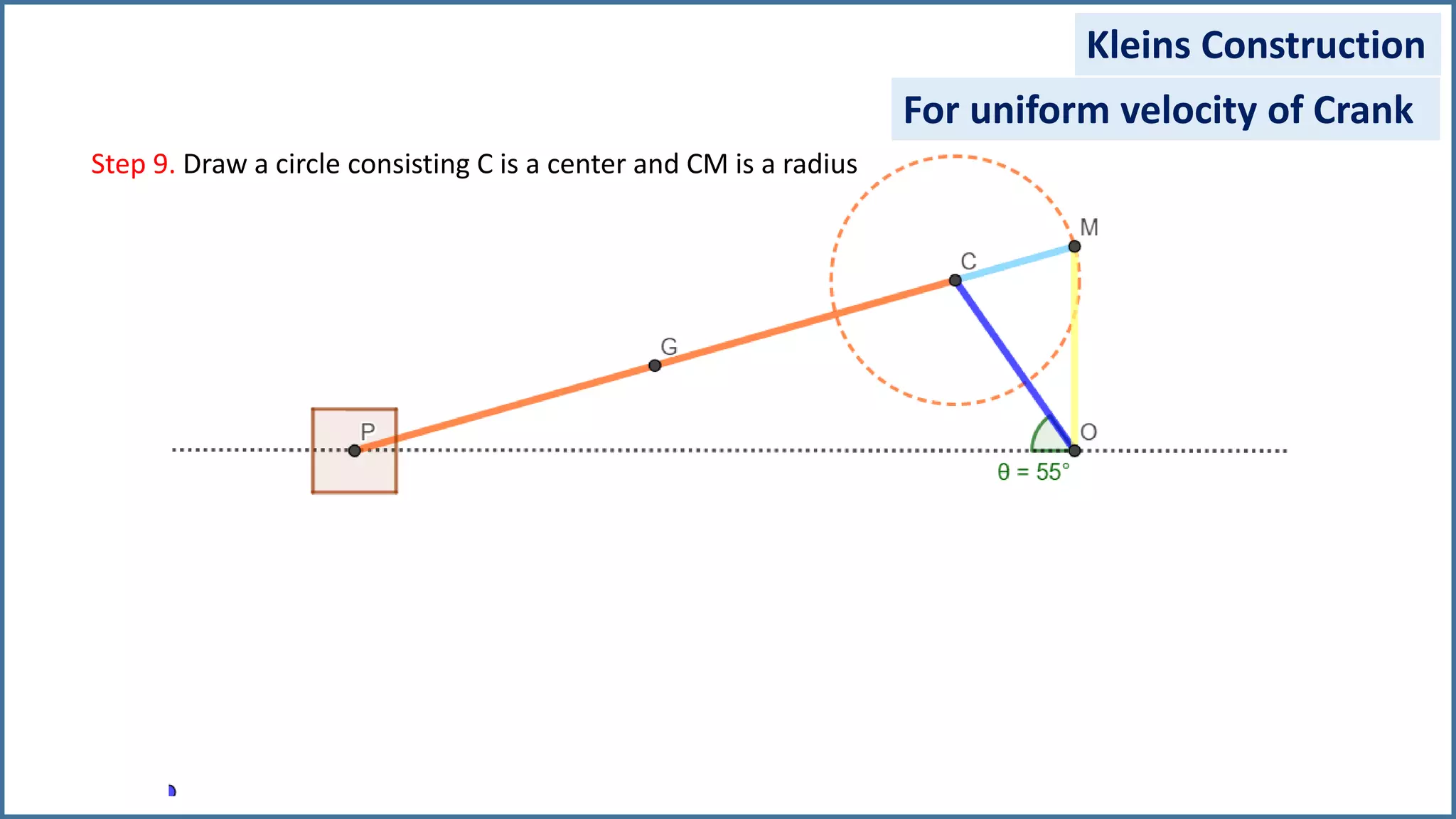
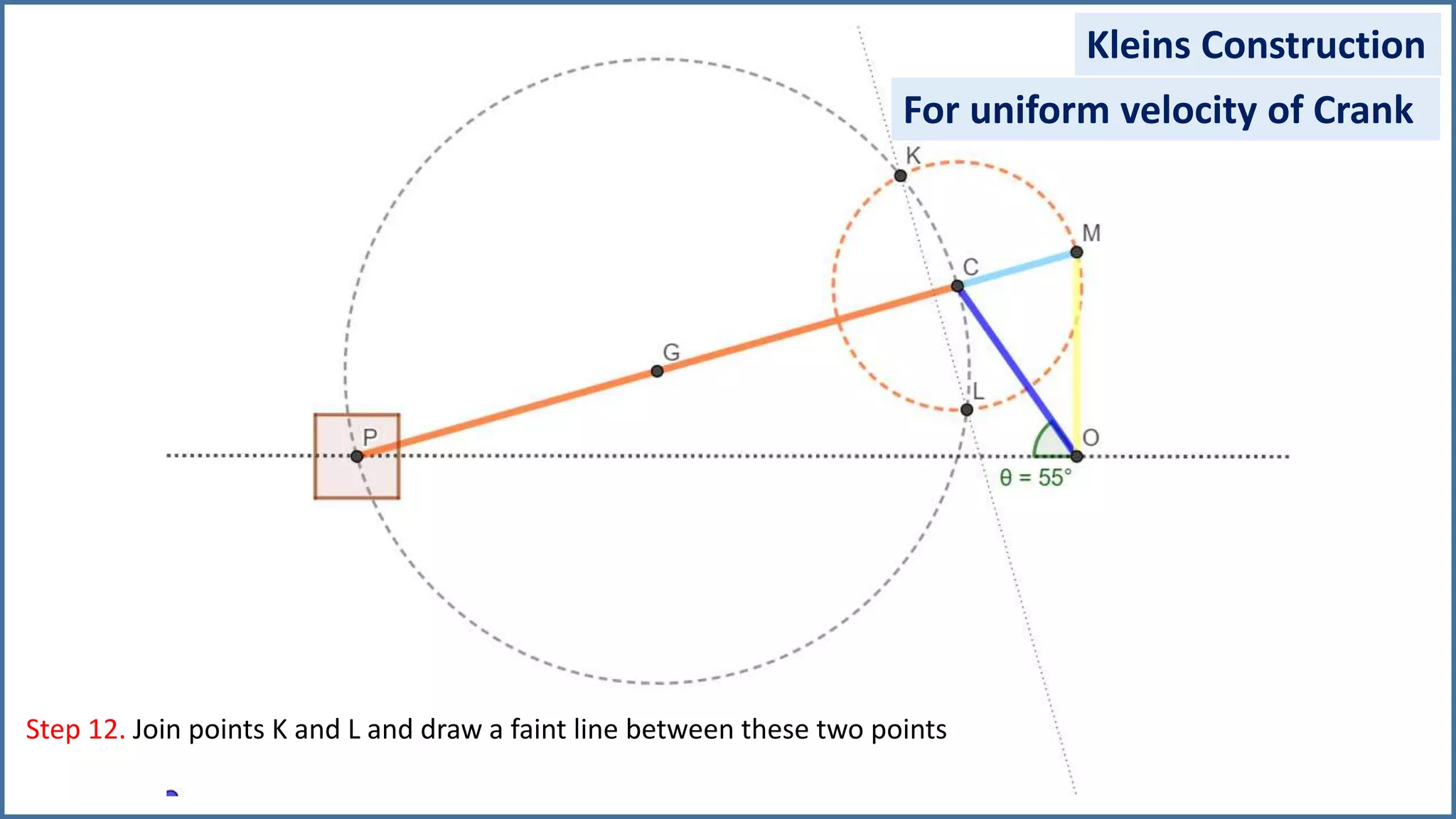
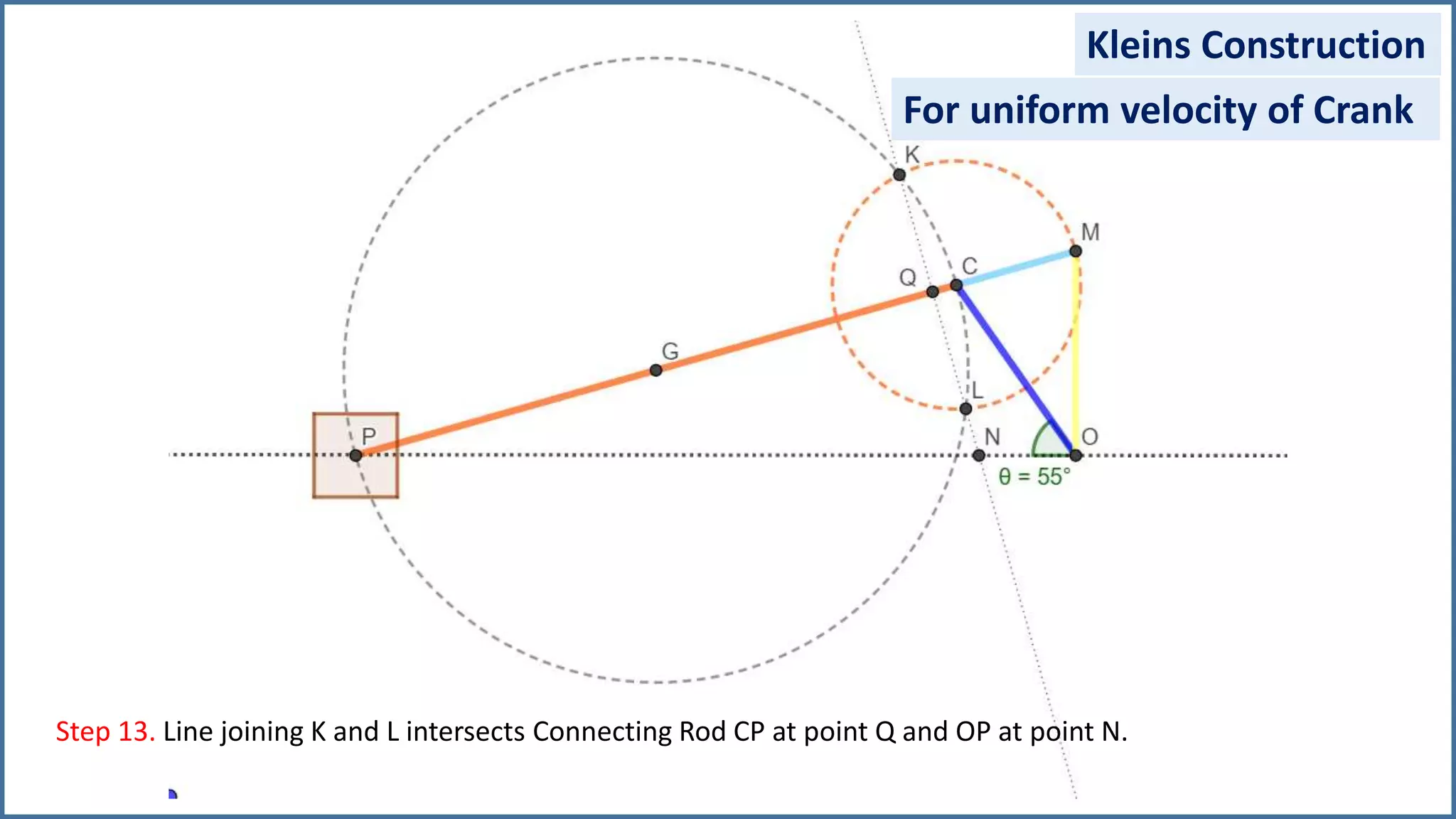
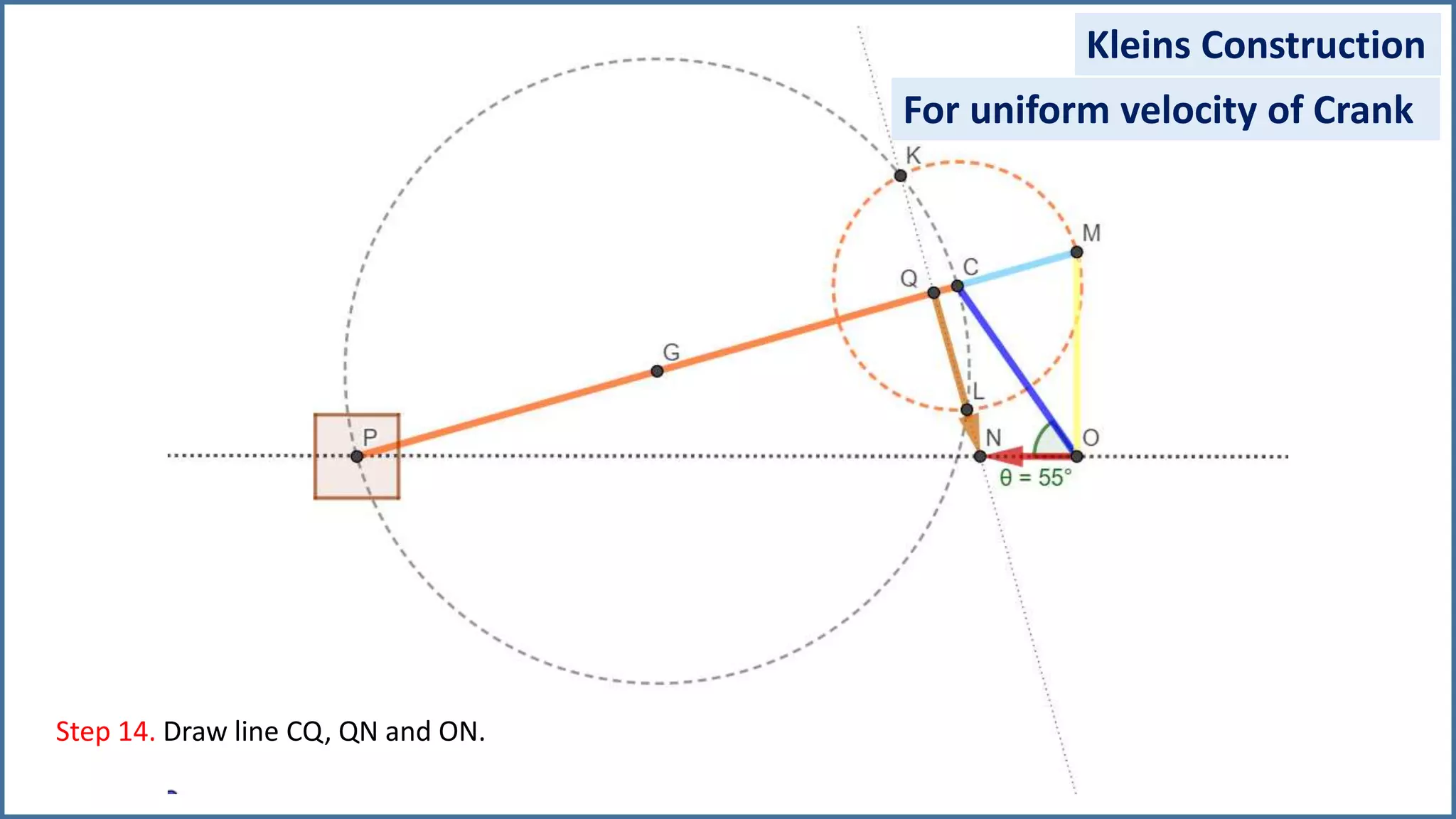
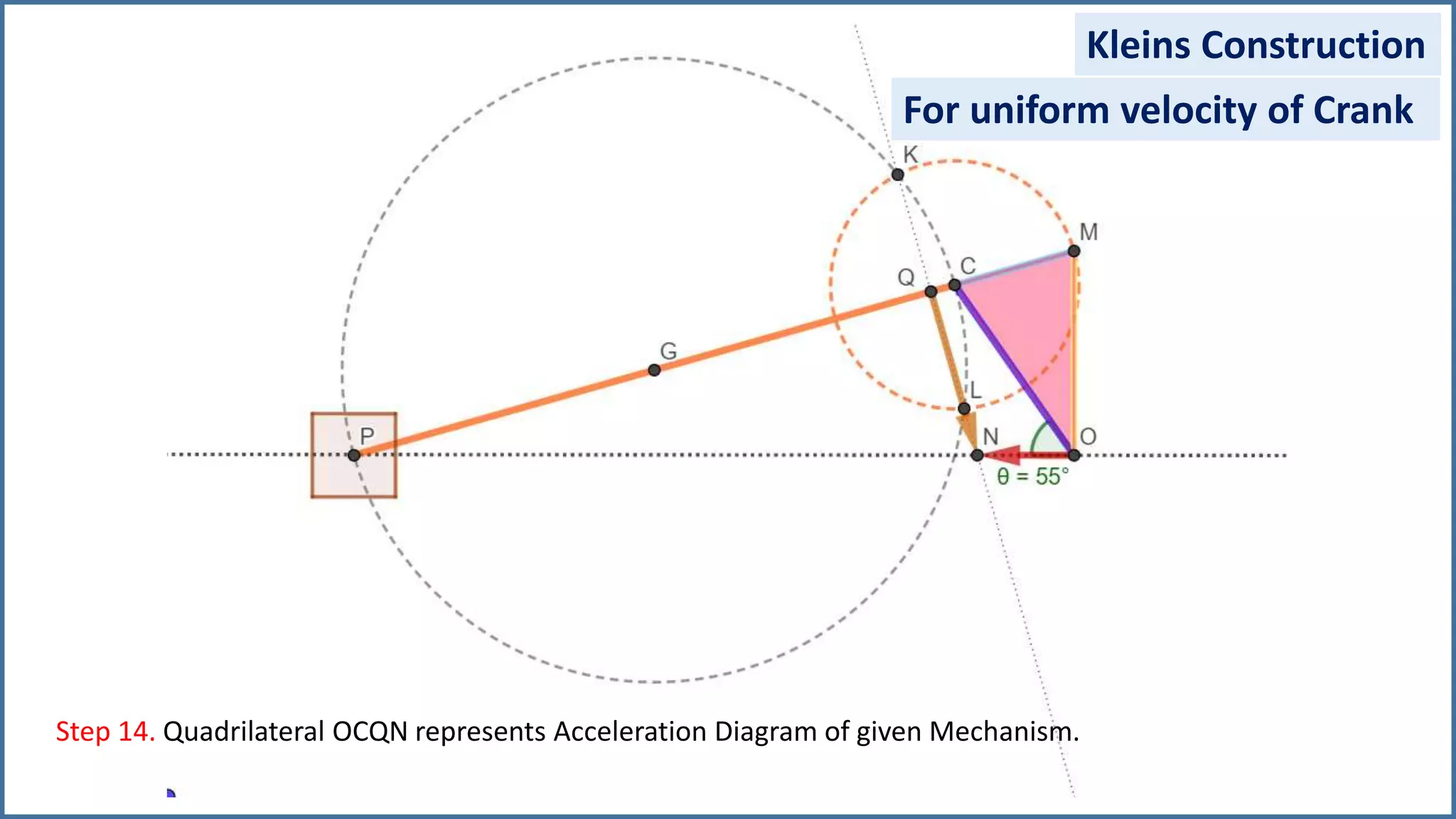
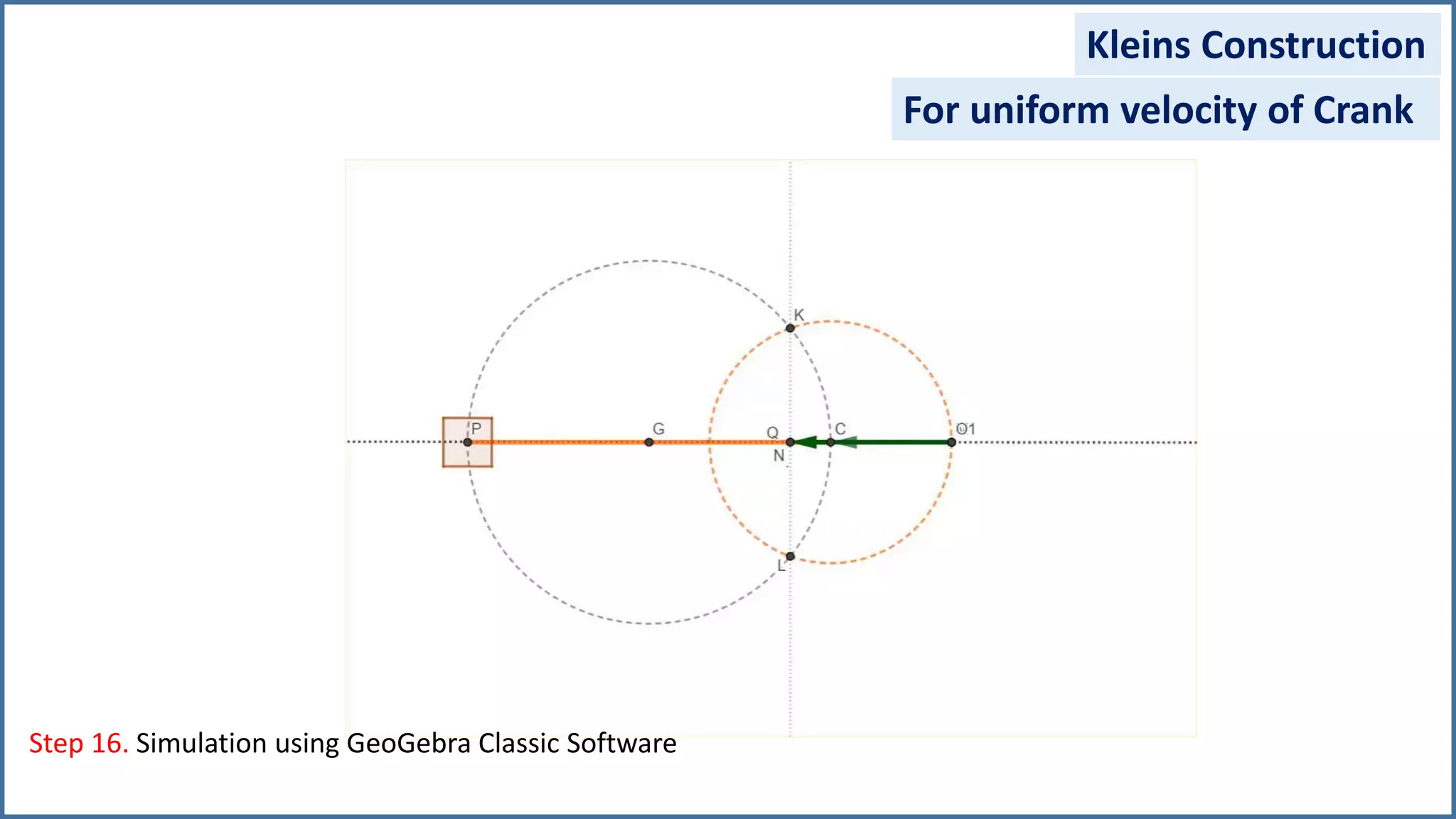
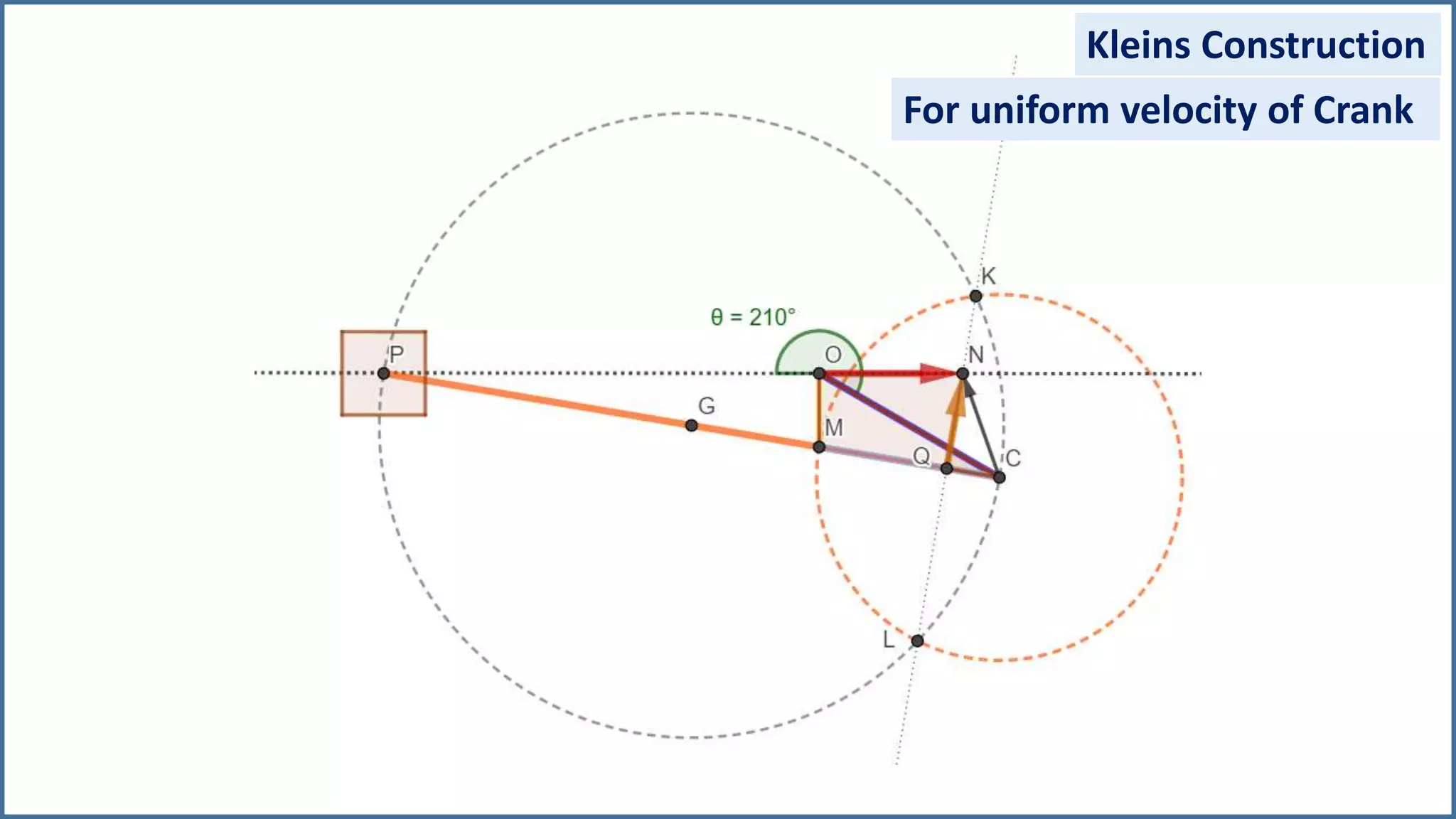
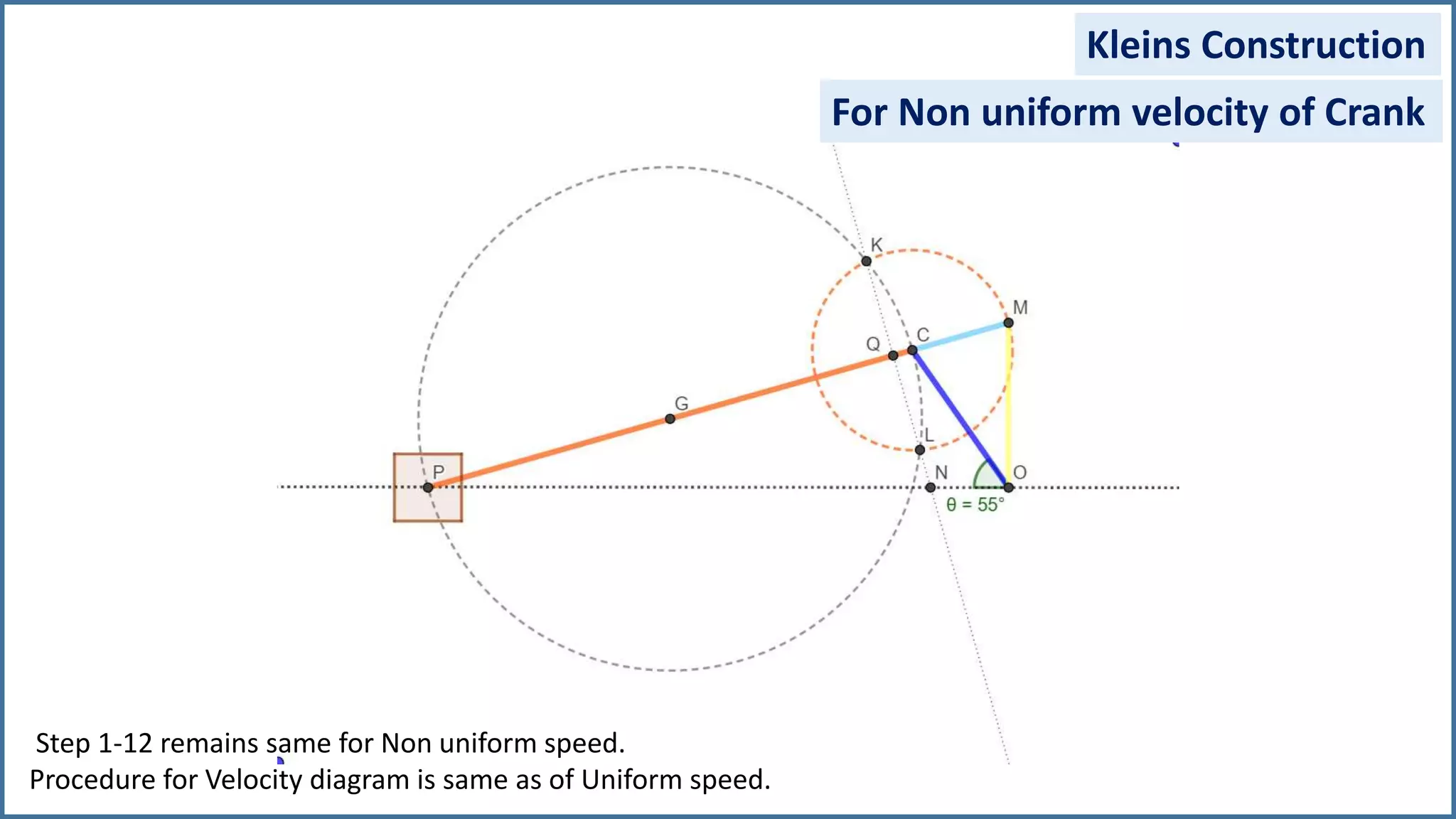
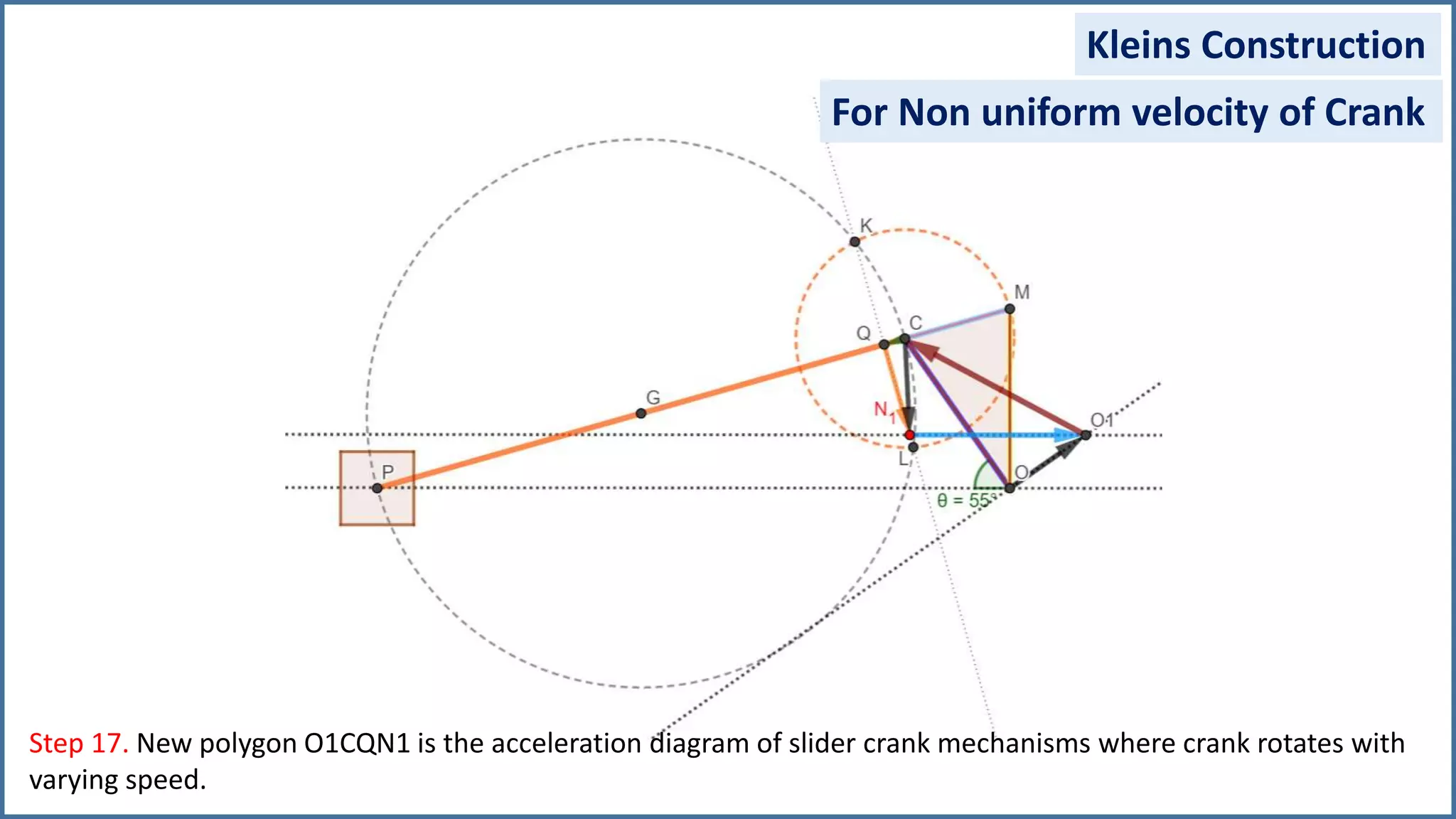
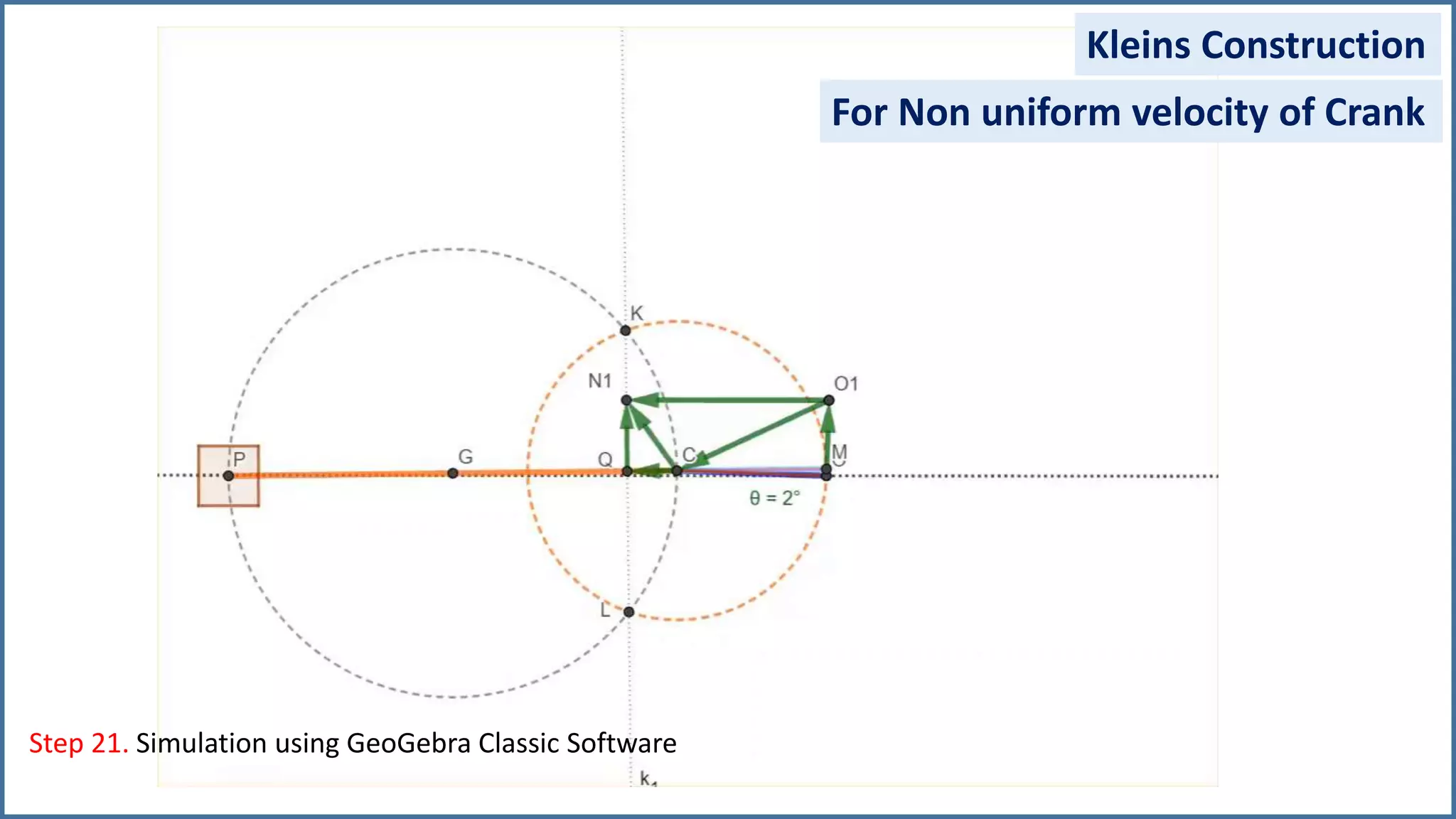
The document discusses the velocity and acceleration analysis of a slider crank mechanism using Klein's construction method. It provides specific calculations for linear and angular velocities and accelerations at a crank angle of 55°, considering both uniform and non-uniform crank speeds. The analysis includes step-by-step procedures for constructing configuration and acceleration diagrams, as well as simulations using GeoGebra software.