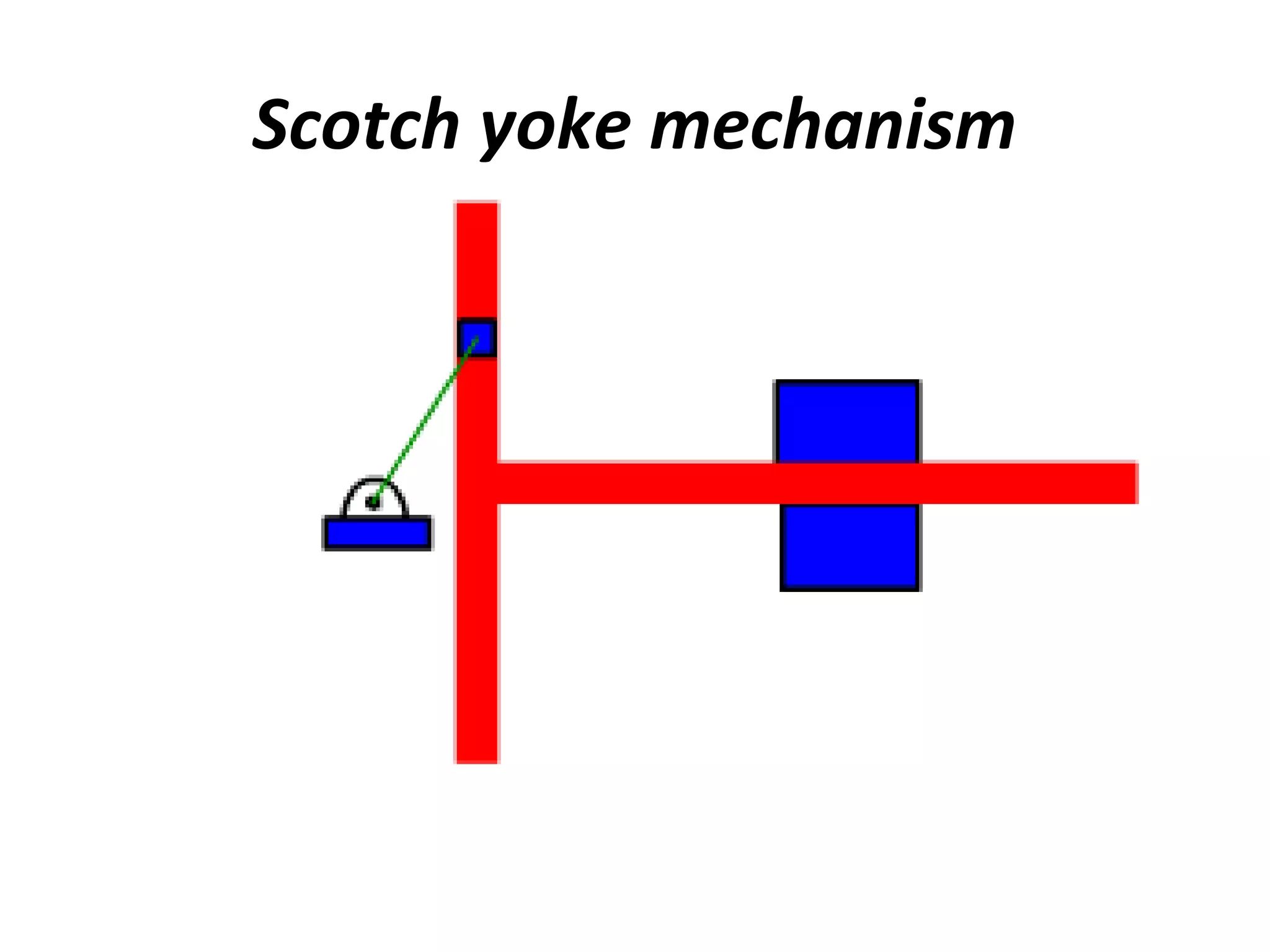
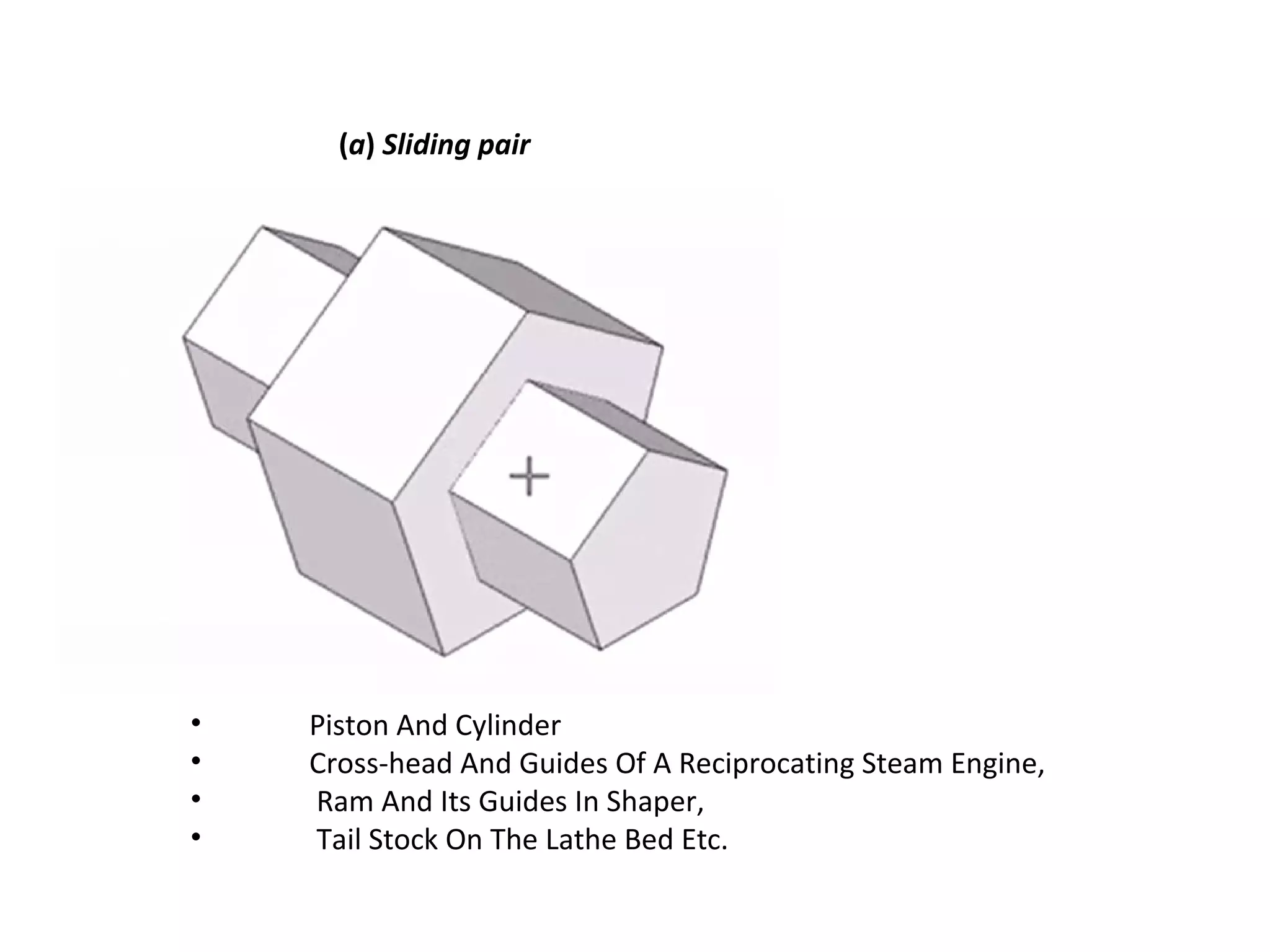
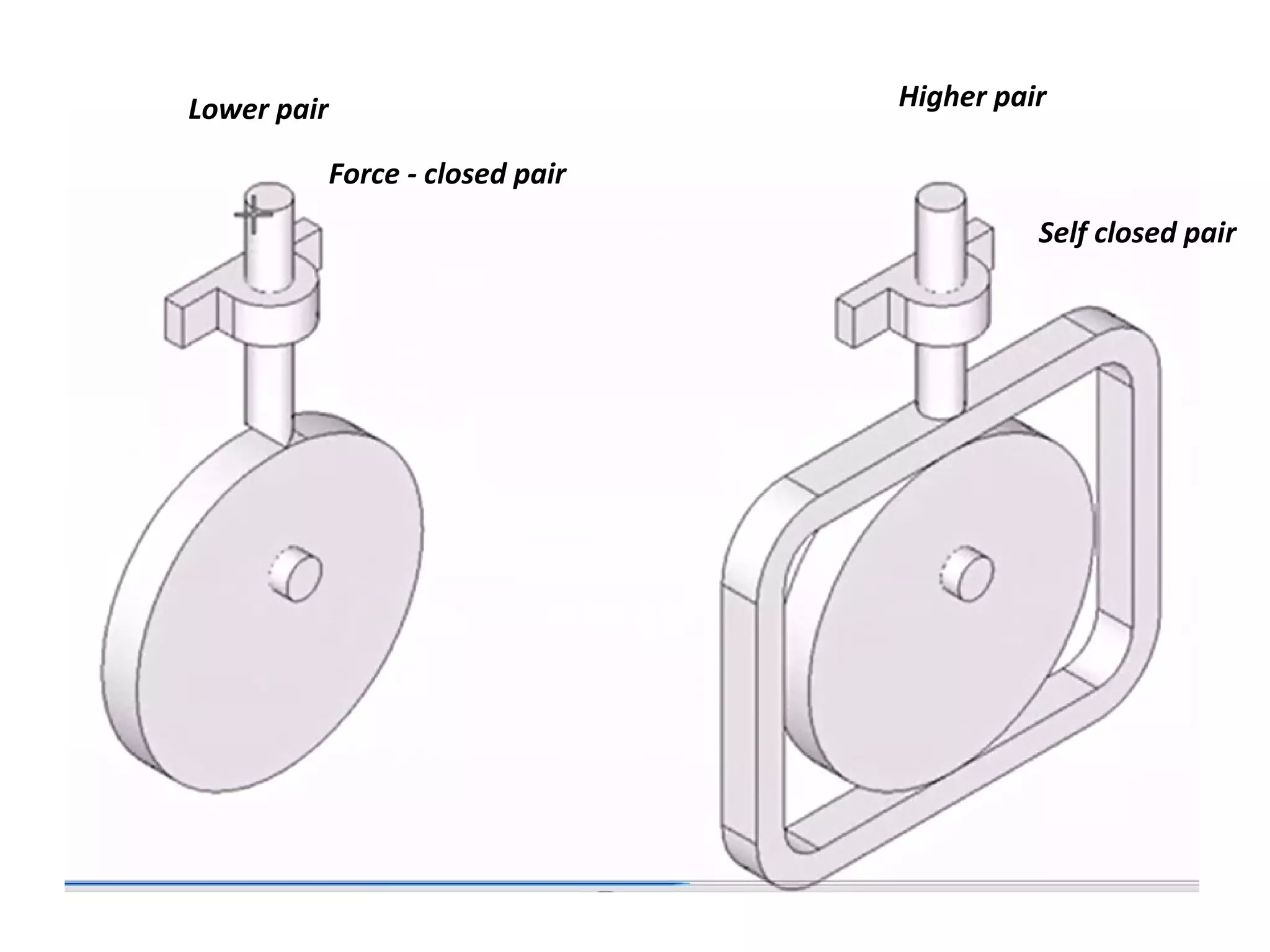
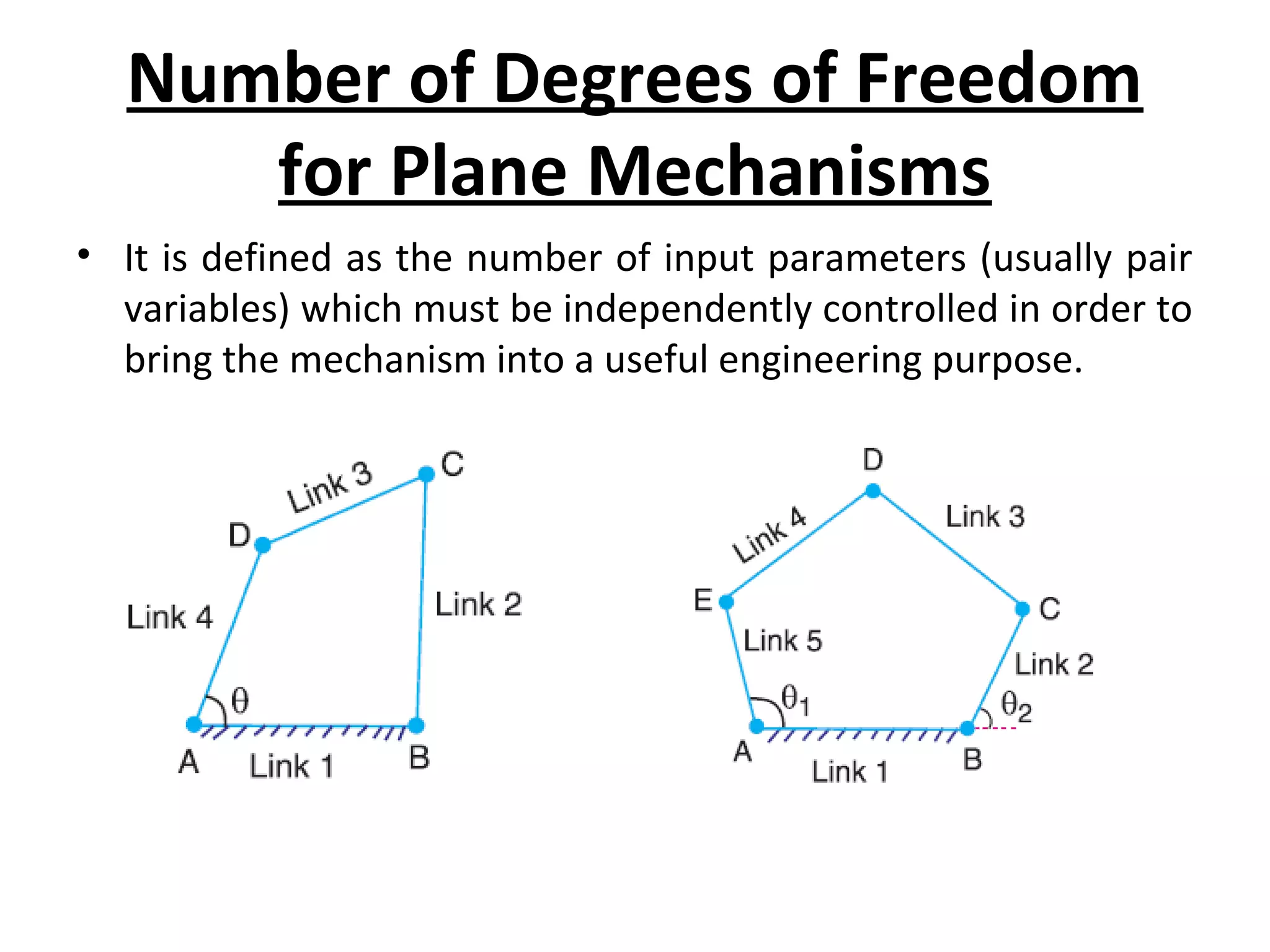
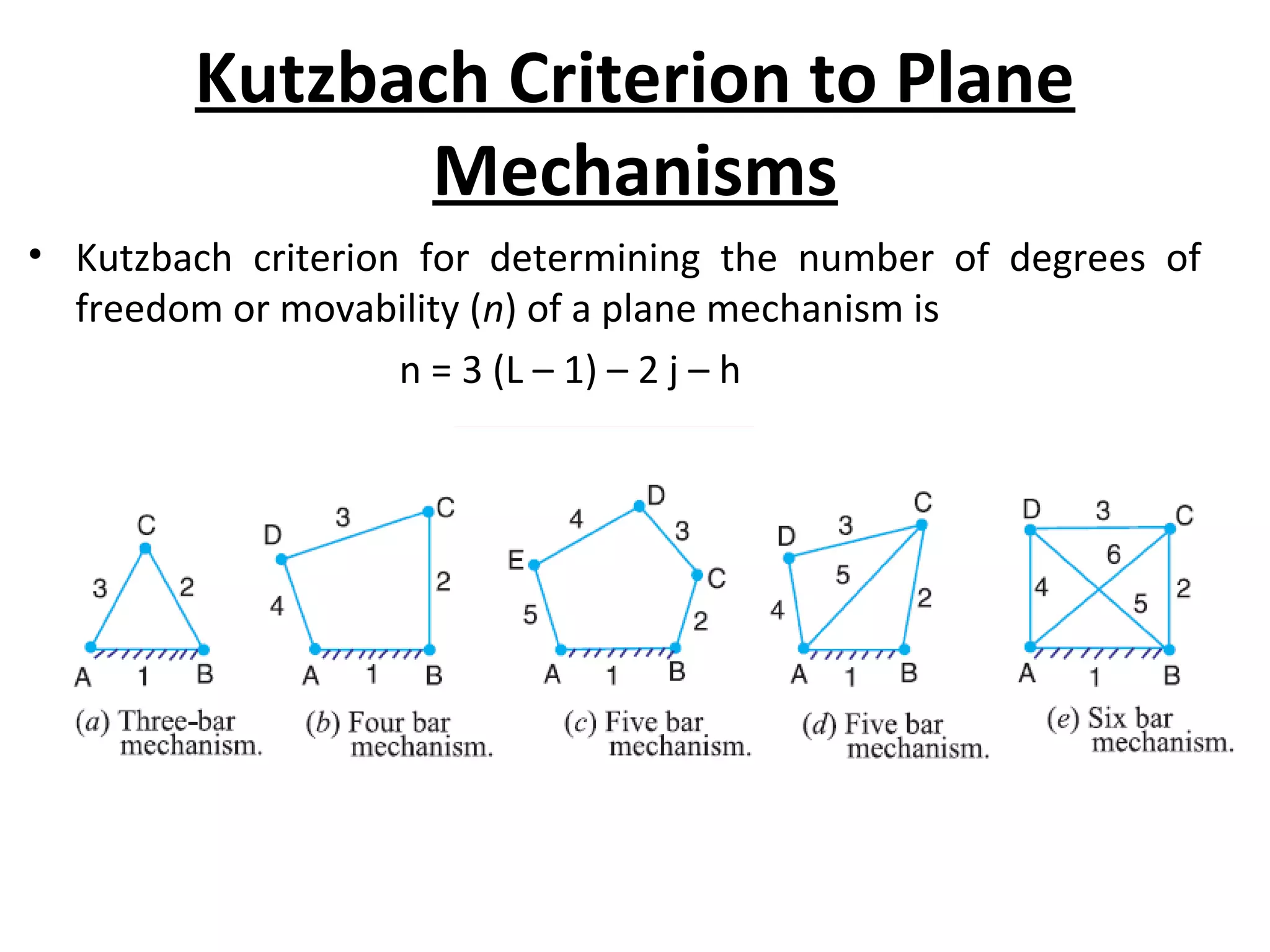
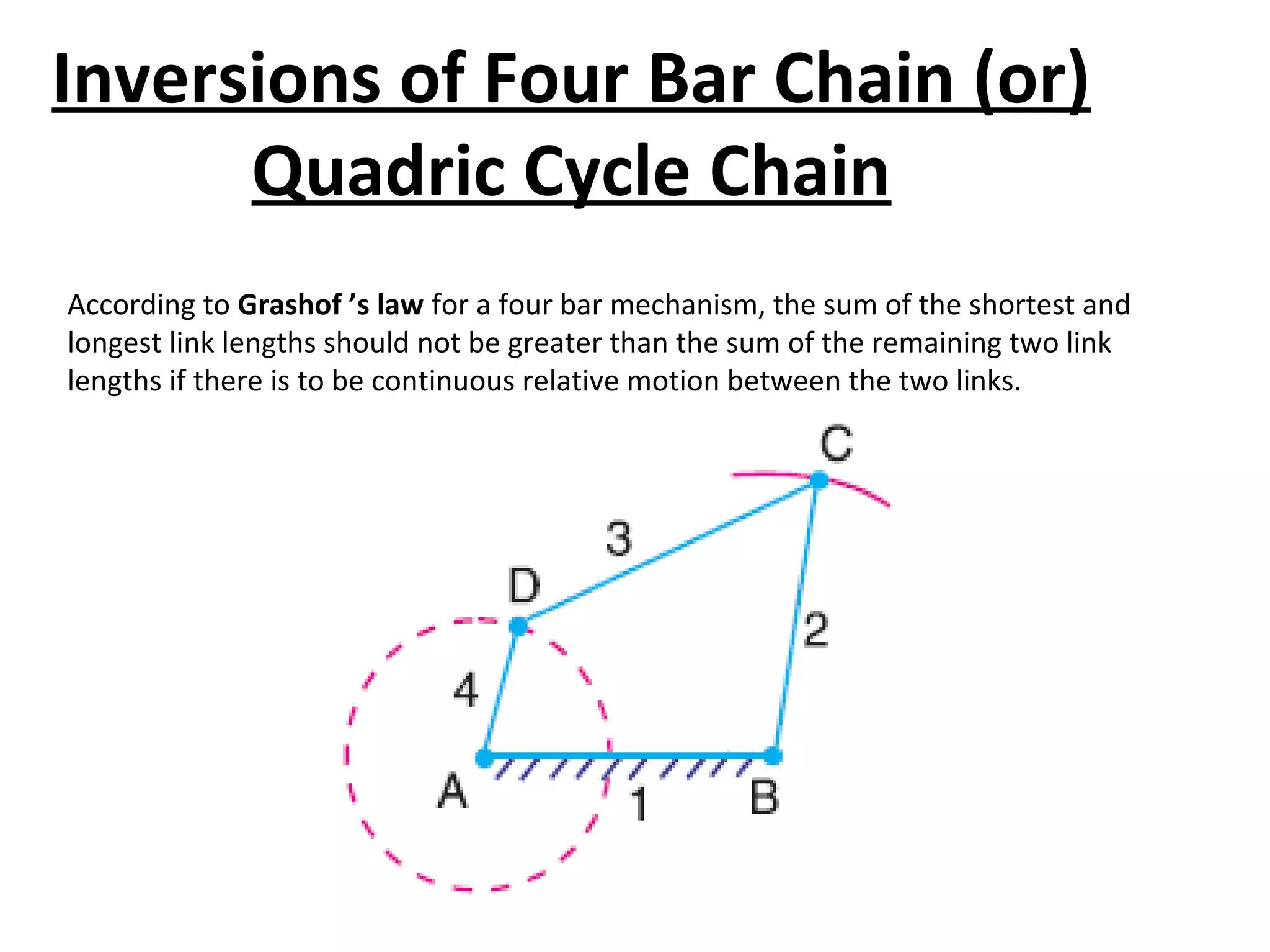
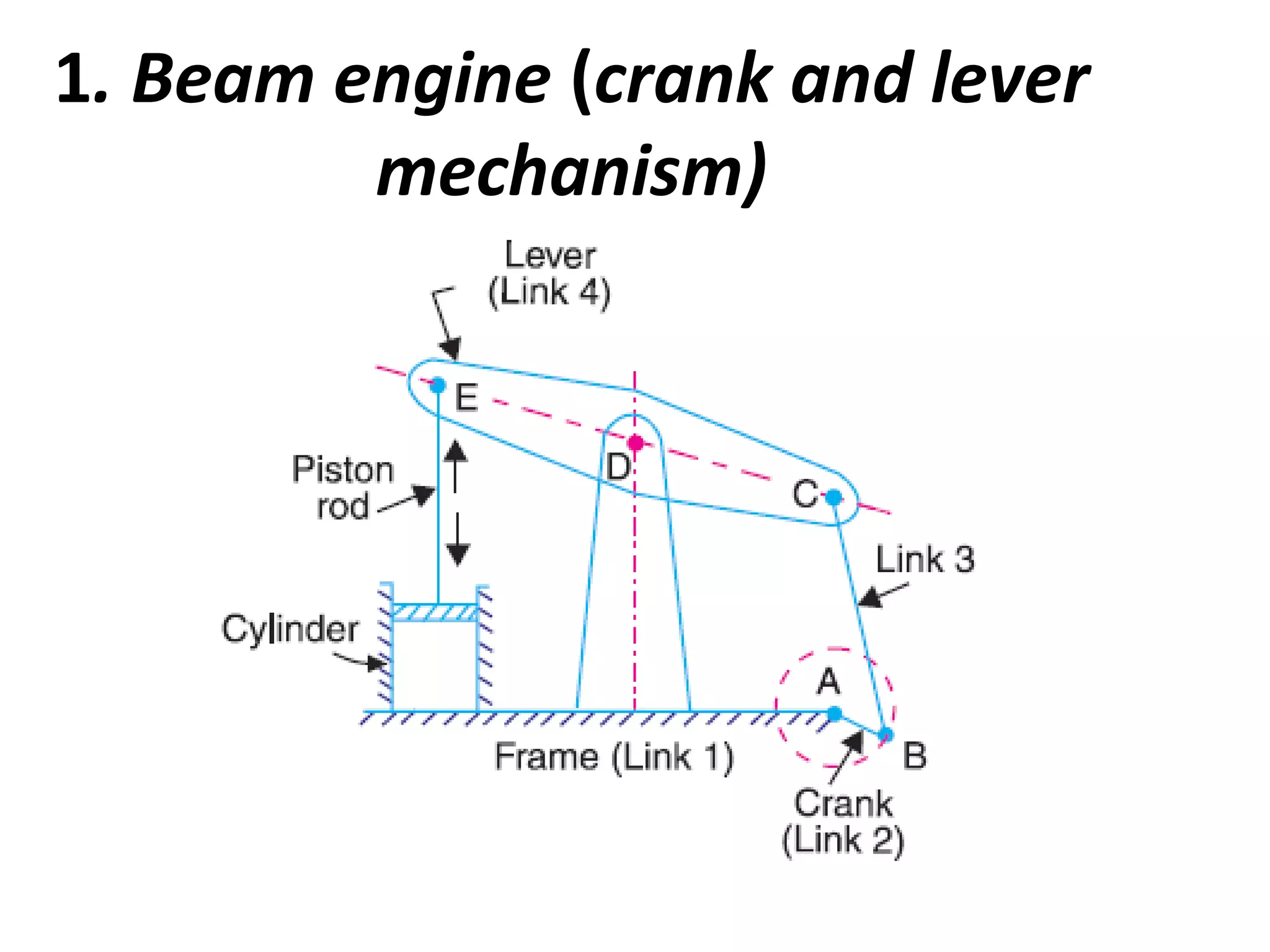
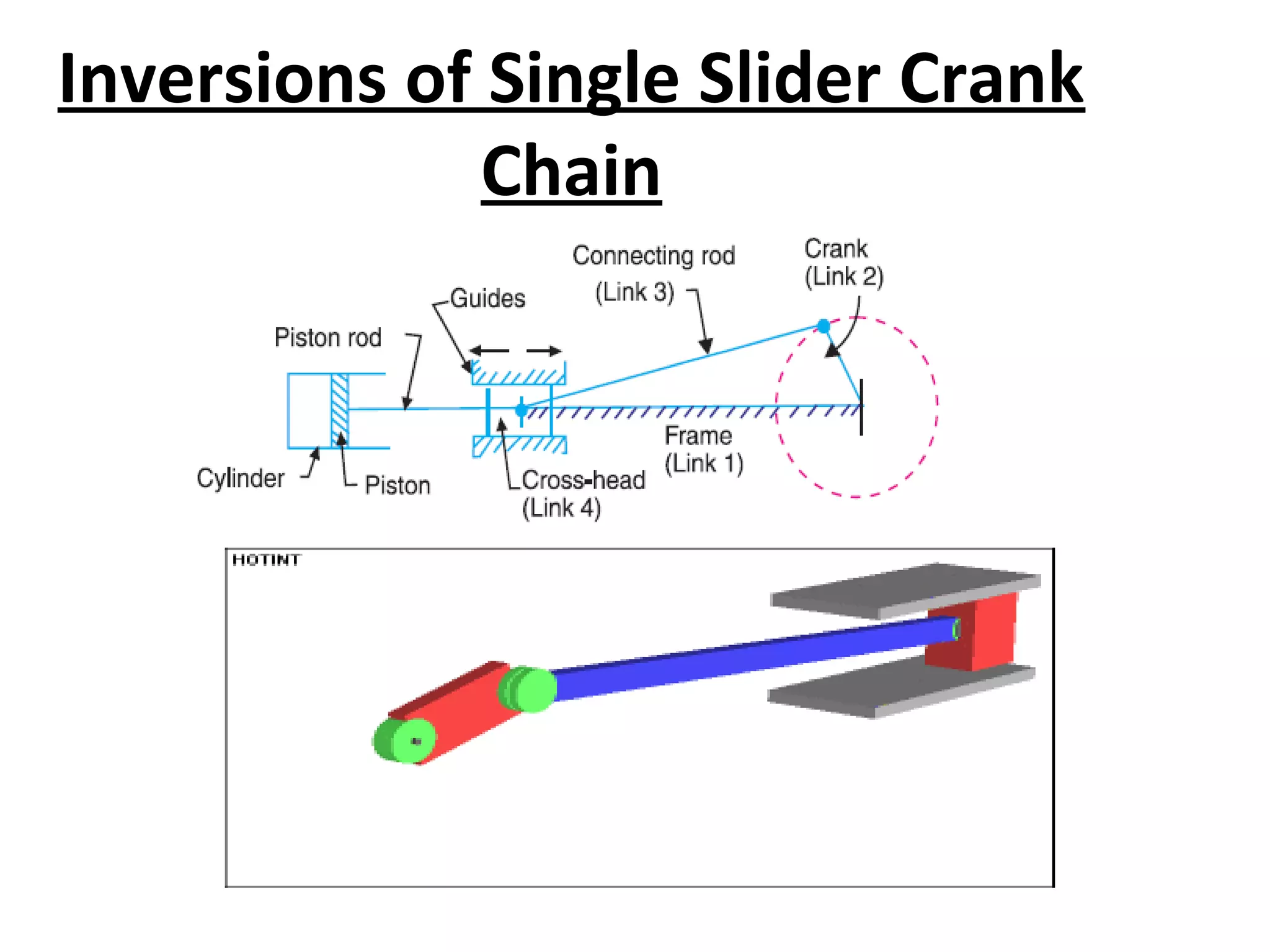
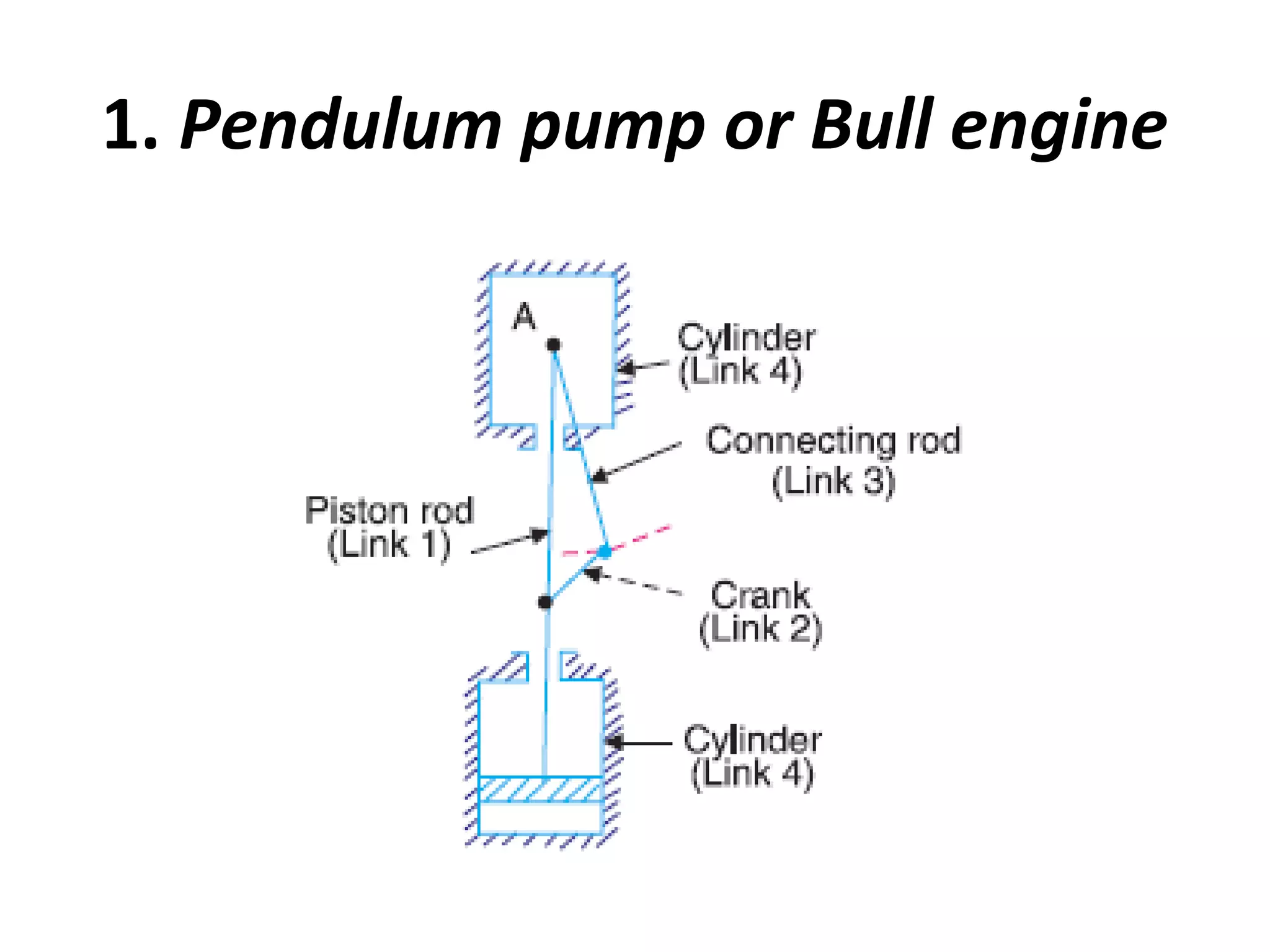
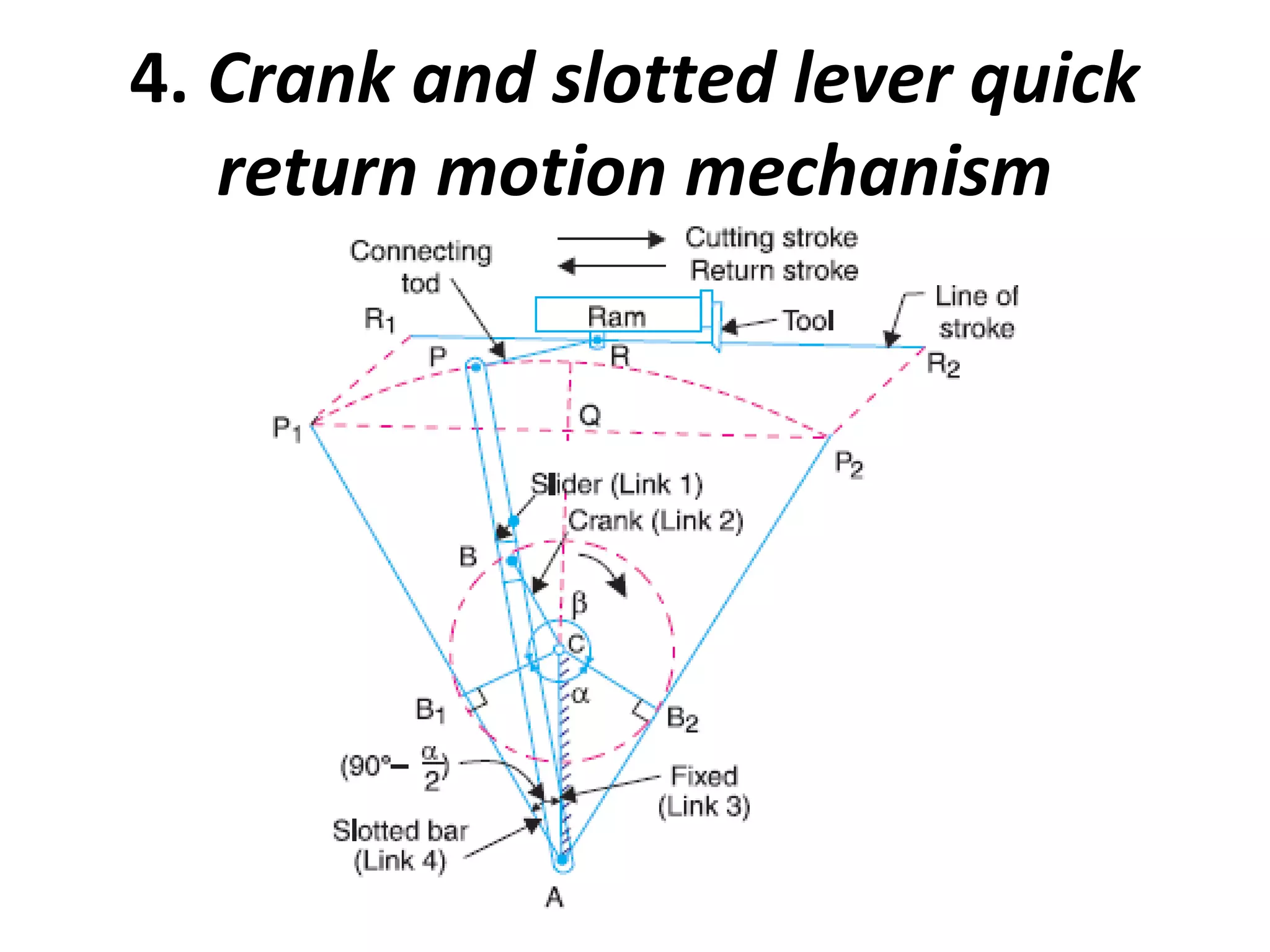
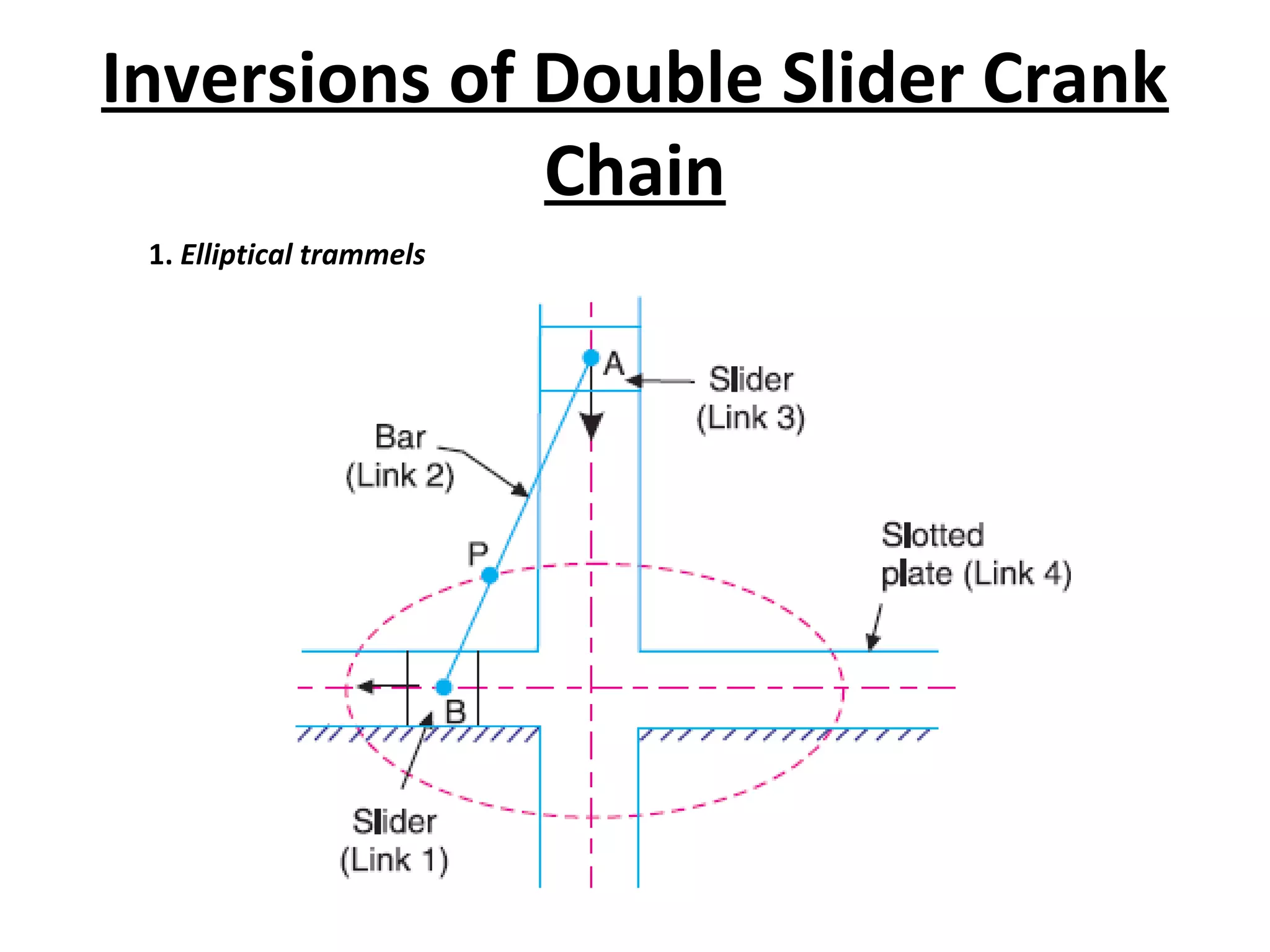
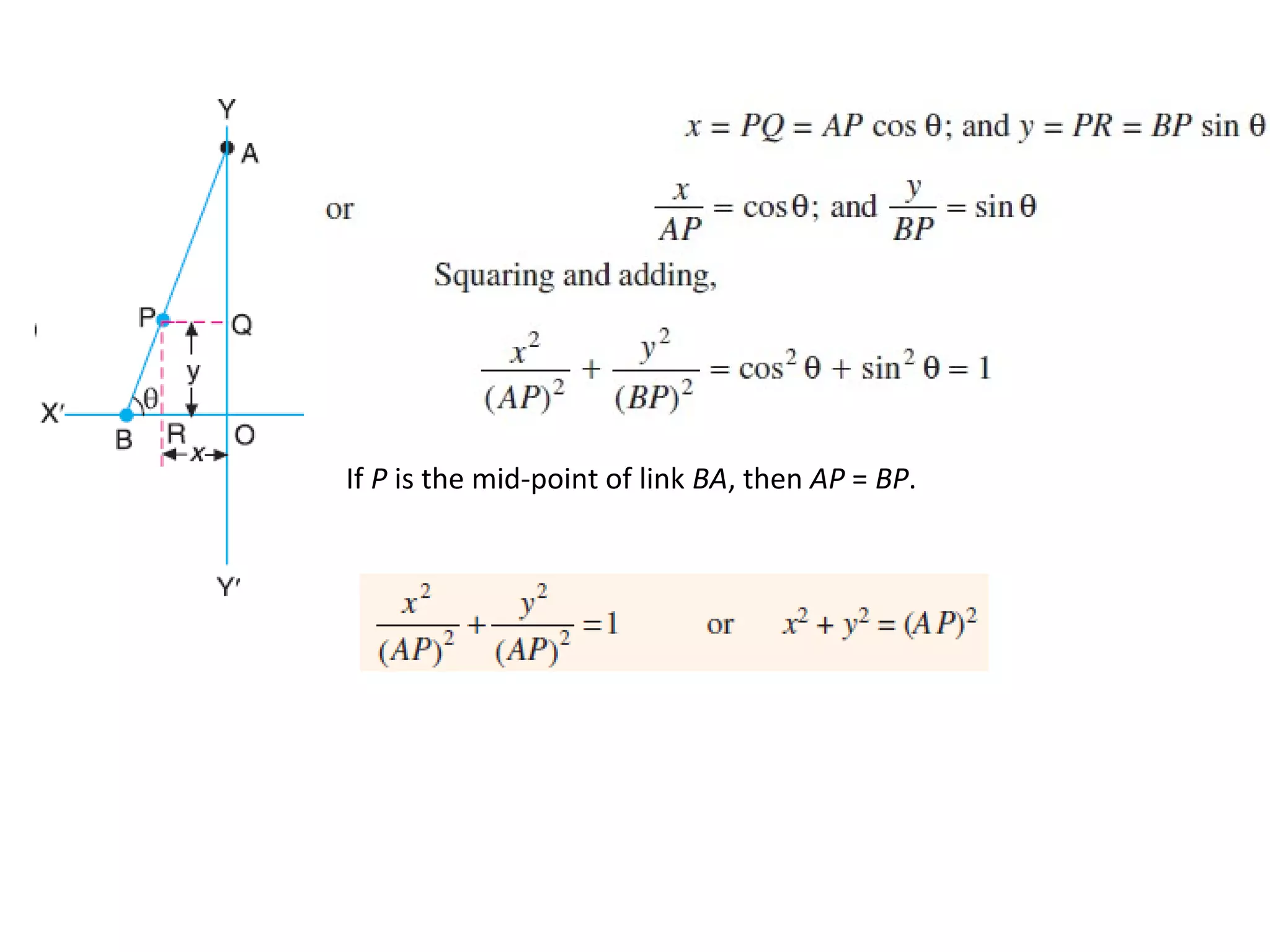
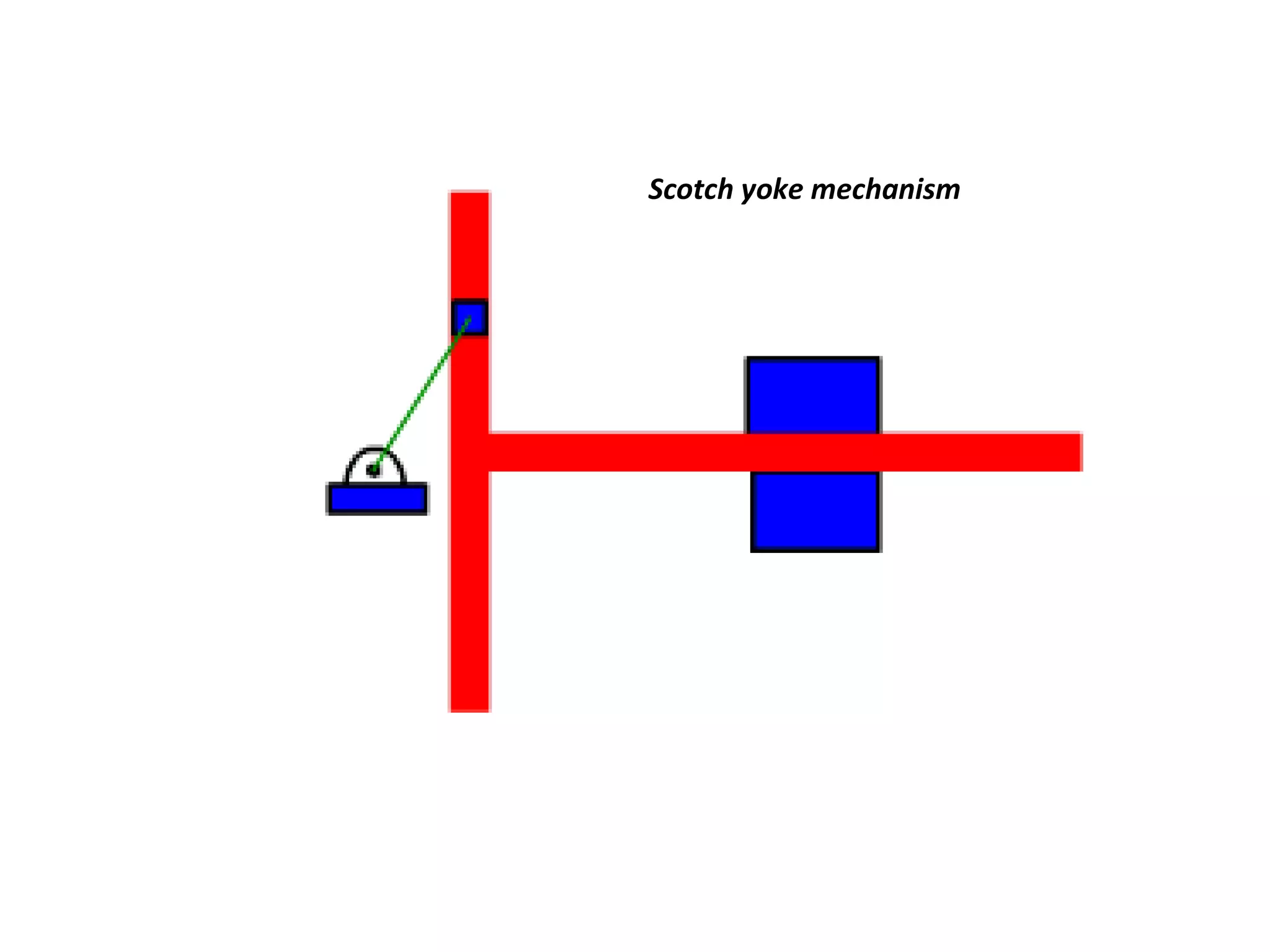
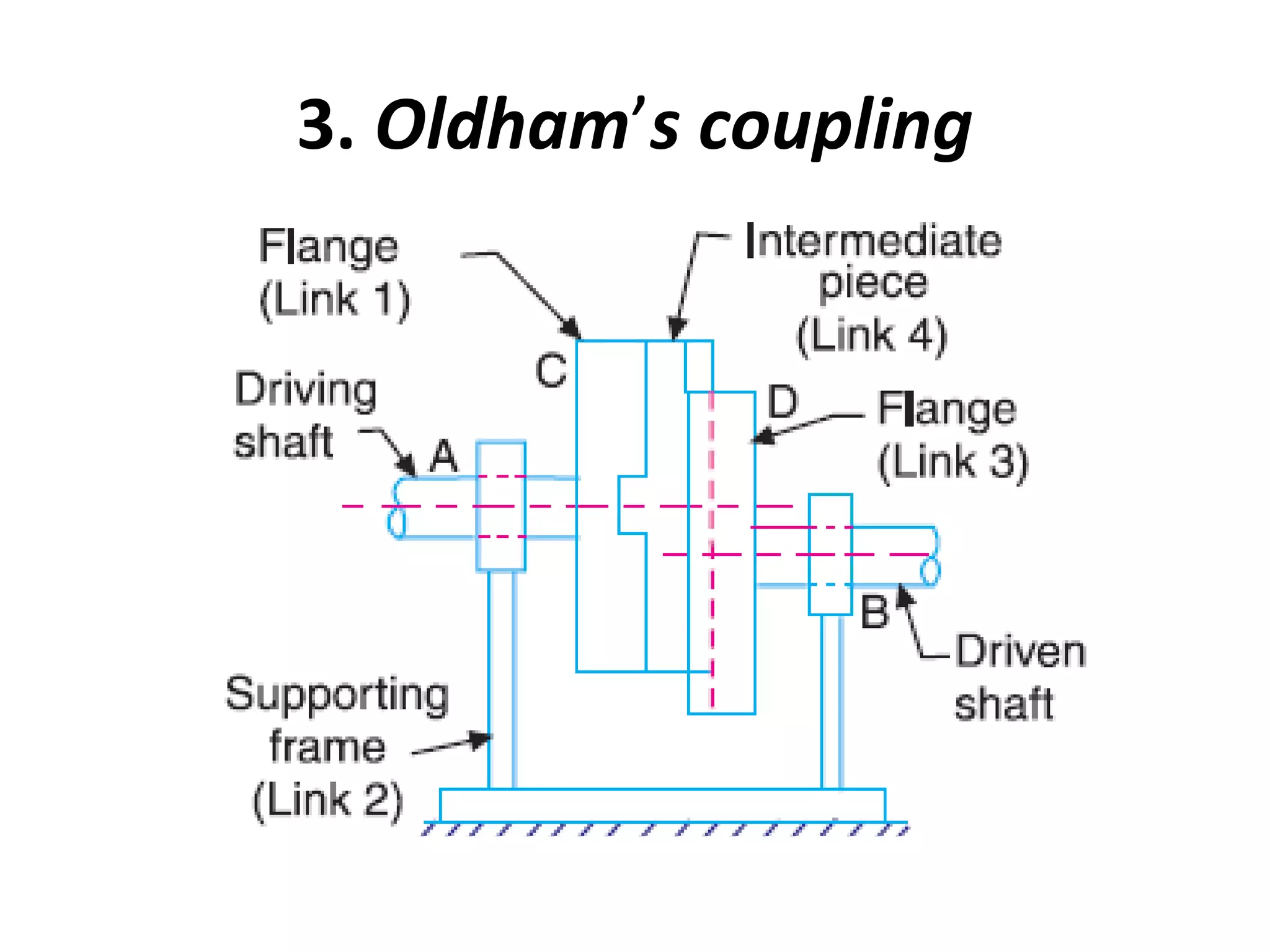
This document discusses mechanisms and kinematic pairs. It defines the different types of links and kinematic pairs, including sliding, turning, rolling, screw and spherical pairs. It also describes degrees of freedom, Grubler's criterion, and Kutzbach's criterion for determining degrees of freedom in planar mechanisms. Common mechanisms are discussed like the four bar linkage, slider crank mechanism, and inversions of mechanisms.