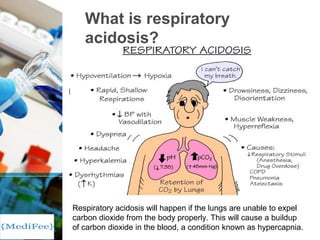
Acidosis is a condition characterized by an excessive acidic state in body fluids, leading to a blood pH below 7.35, which can cause irreversible cellular damage. There are two main causes of acidosis: respiratory acidosis due to carbon dioxide accumulation and metabolic acidosis resulting from the body's inability to filter fixed acids or excessive acid production. Treatment varies based on the type of acidosis and may include bronchodilators, bicarbonate infusions, and specific drugs for conditions like opioid overdose.