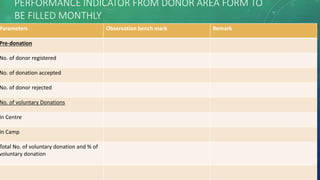
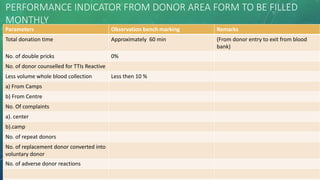
KPIs are quantifiable measures that help companies assess their performance against strategic goals. They measure both financial and operational metrics. Key advantages of KPIs include improved visibility of performance, more agile decision-making, and increased efficiency. There are different types of KPIs, including process, input, output, leading, and lagging indicators. Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound KPIs helps companies monitor progress and drive improvements.