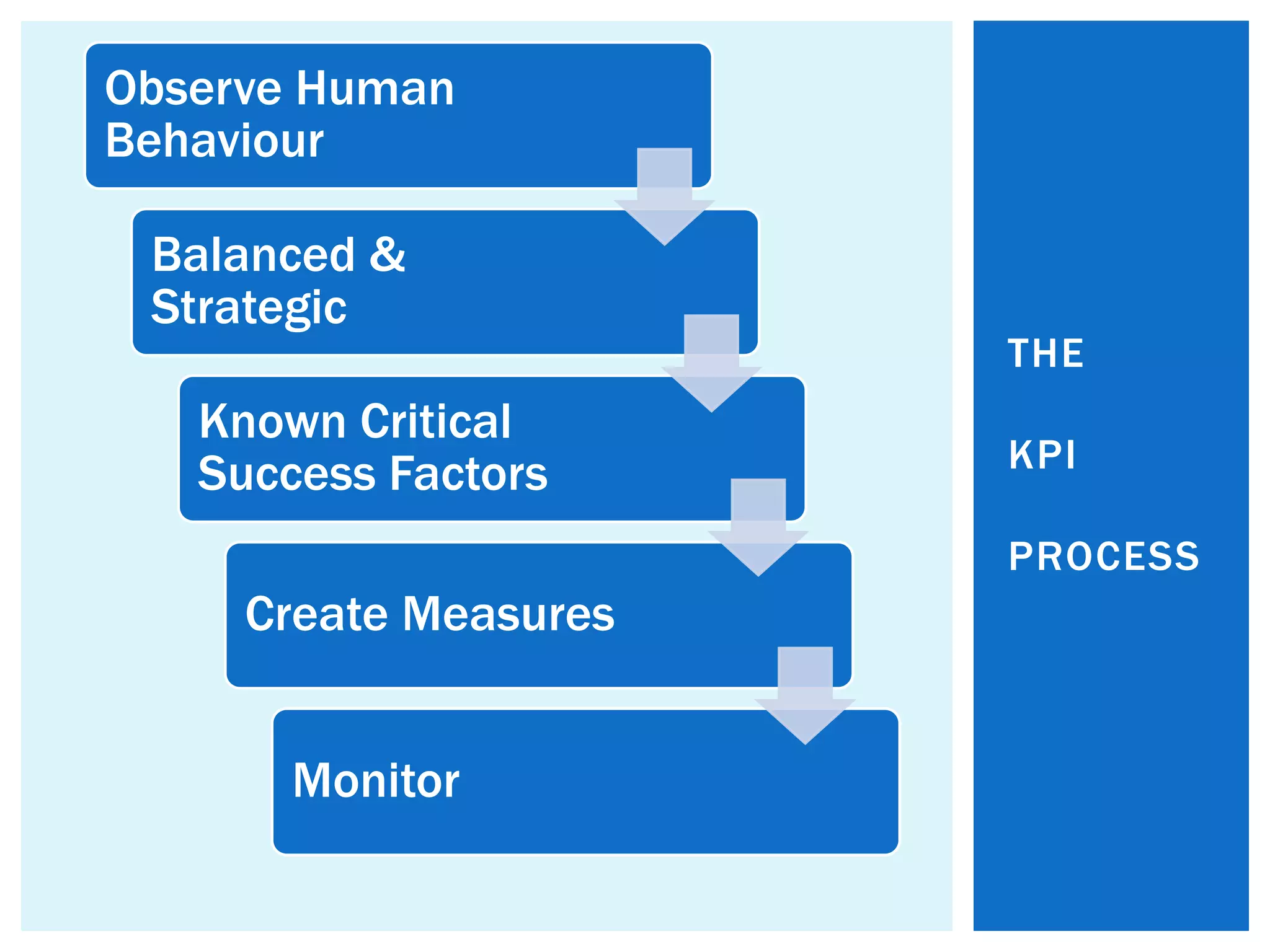
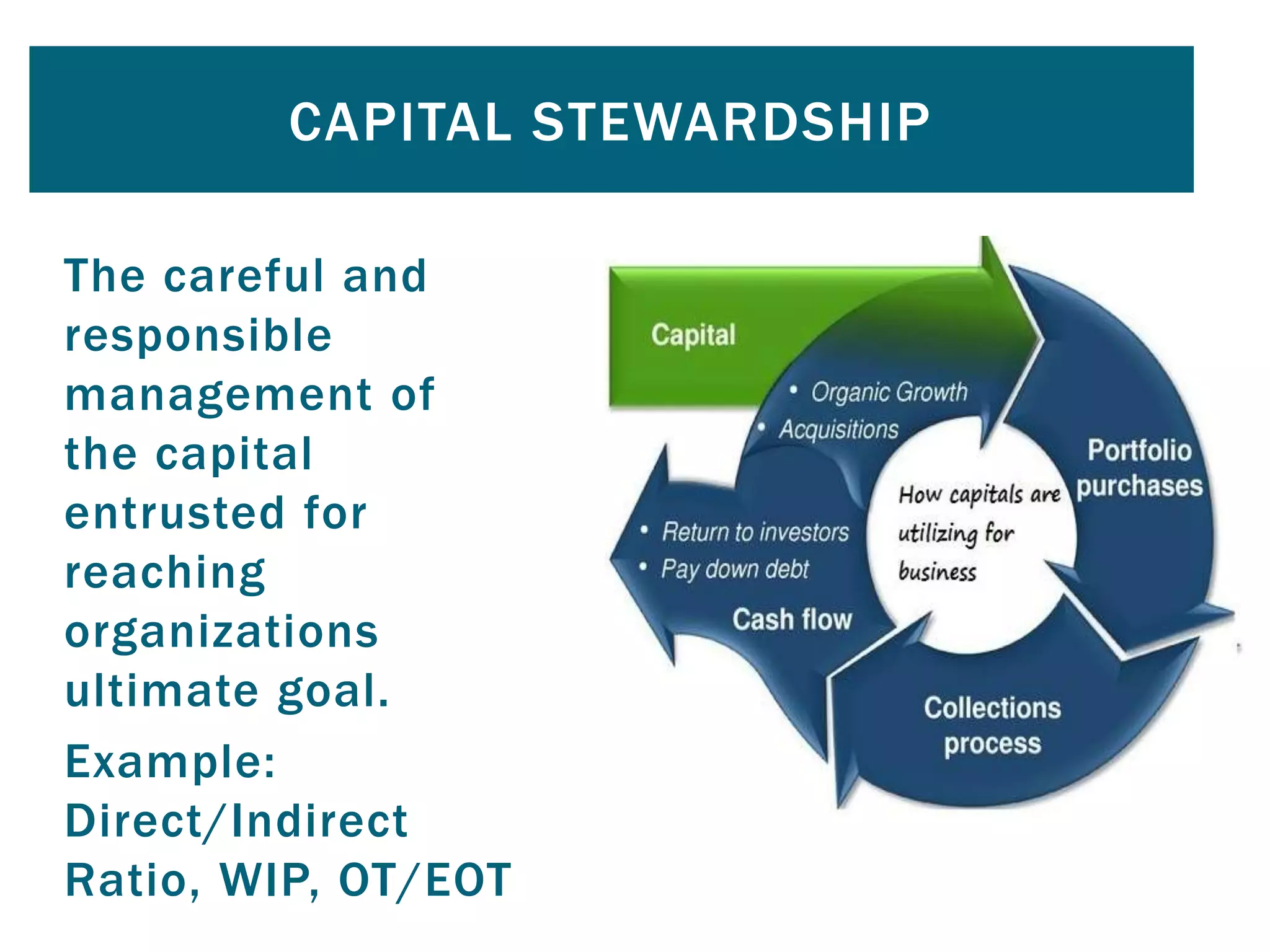
This document provides an introduction to key performance indicators (KPIs). It discusses why organizations use KPIs, how to create them, and how to monitor them. KPIs measure critical success factors to focus on today's and tomorrow's success. The document outlines a KPI process that involves observing behavior, identifying critical success factors, creating measures, and monitoring them. It also discusses how to create a balanced scorecard across operational excellence, capital stewardship, profitability, and organizational development. Examples of KPIs are provided for various categories.