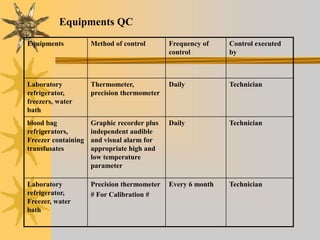
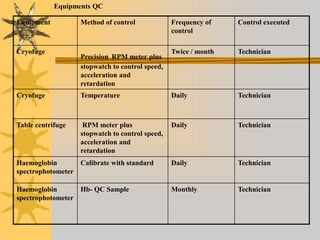
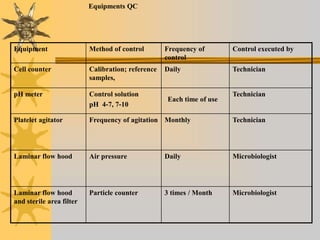
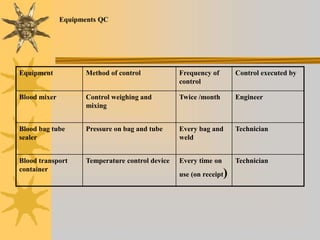
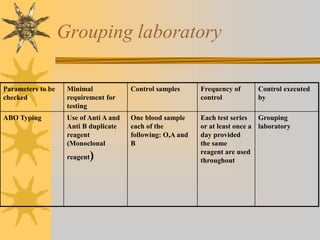
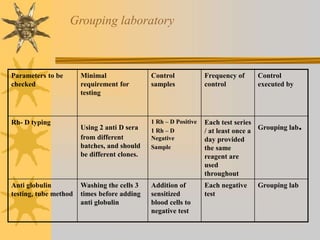
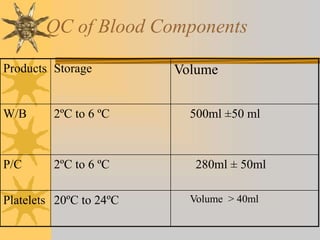
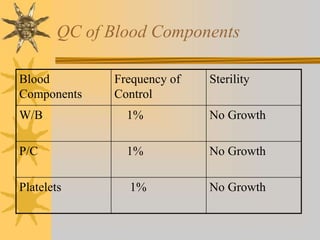
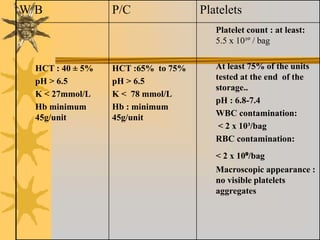
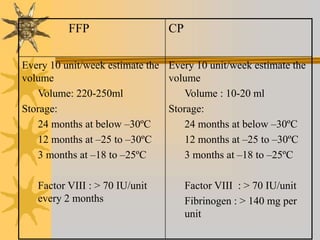
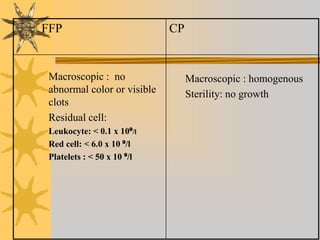
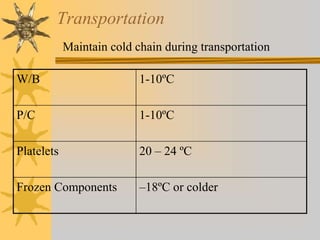
This document discusses quality assurance in blood banking. It outlines the quality control processes that should be followed at various stages of blood collection and processing, including donor selection, blood collection, component preparation, storage, and transportation. Key aspects of quality control covered are premises and facility requirements, equipment calibration and maintenance, reagent quality control, and infectious disease testing quality assurance. The document provides details on acceptable parameters and frequencies of quality control checks for various blood components.