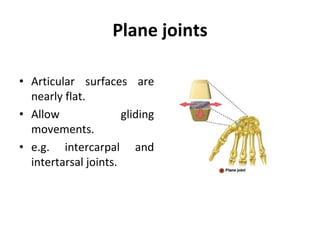
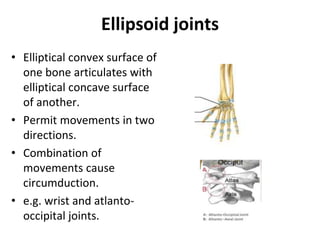
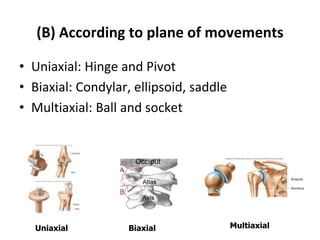
This document provides an overview of arthrology, which is the study of joints. It classifies joints based on their structure and function. Structurally, joints are either fibrous, cartilaginous, or synovial. Functionally, joints are categorized as synarthroses, amphiarthroses, or diarthroses based on their degree of mobility. The most mobile and complex joints are synovial joints, which have a fluid-filled cavity and allow for various movements. The document describes and provides examples of different types of synovial joints classified based on their shape, plane of movement, and number of articulating bones.