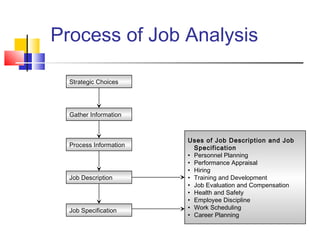
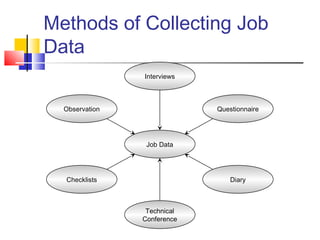
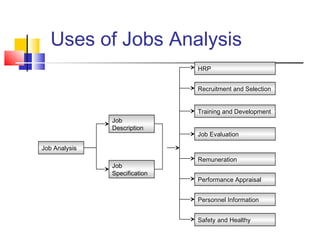
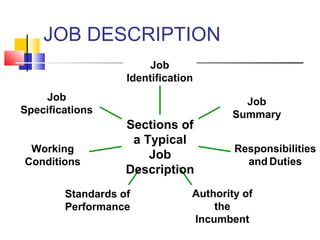
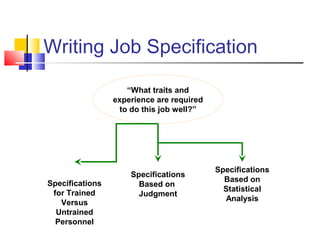
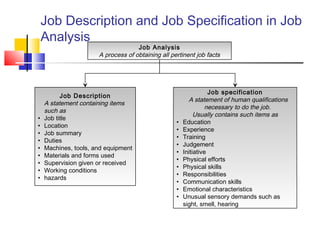
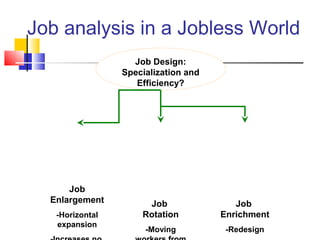
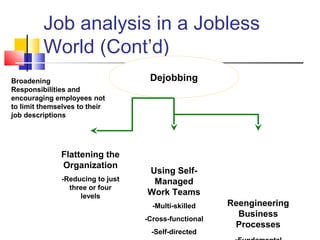
Job analysis is the process of determining the duties, skills, and qualifications required for a job. It involves gathering job data through methods like observation and interviews. This information is used to create job descriptions and specifications. A job description outlines the key responsibilities and requirements of a role, while a specification lists the necessary qualifications, skills, and traits for an individual to perform the job well. Together, job descriptions and specifications are used for strategic HR purposes like recruitment, performance management, and compensation. Job design aims to match job requirements to human attributes through approaches like job simplification, rotation, enlargement, and enrichment.