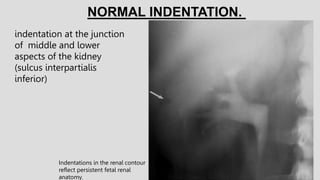
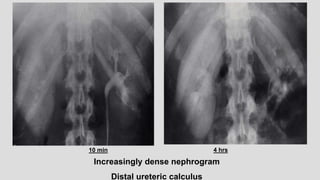
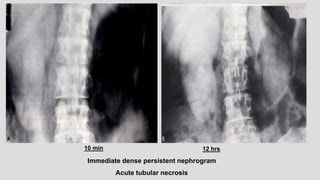
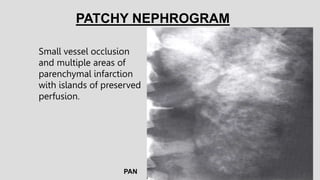
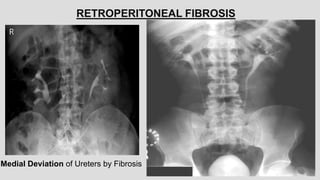
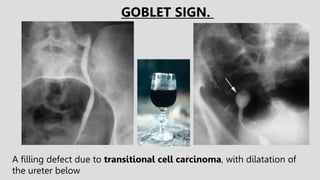
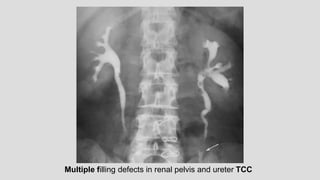
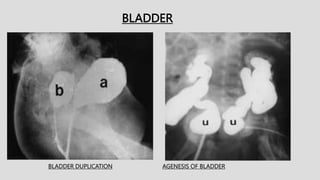
1. The document describes various findings that can be seen on intravenous urograms (IVUs) related to different renal, ureteral, and bladder conditions.
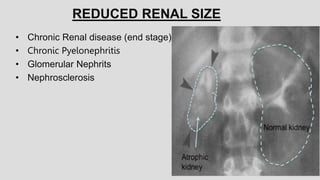
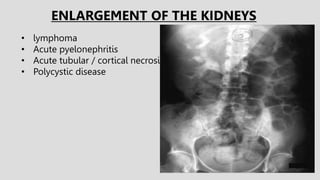
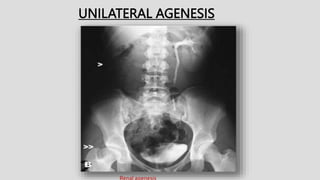
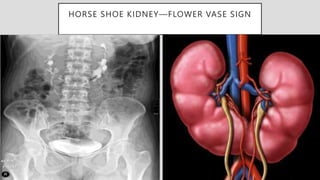
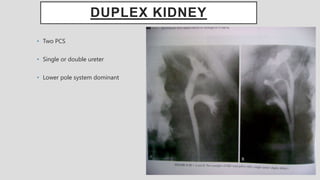
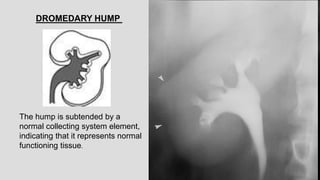
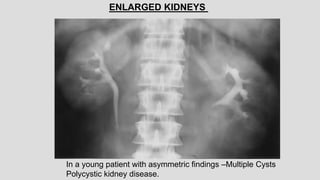
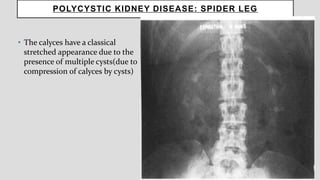
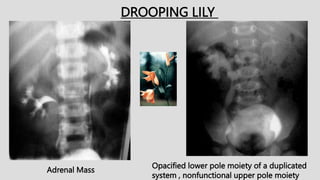
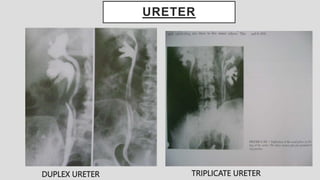
2. Common renal findings included reduced or enlarged kidney size related to conditions like chronic kidney disease or polycystic kidney disease. Congenital anomalies of the kidneys like horseshoe kidney or duplex kidney were also discussed.
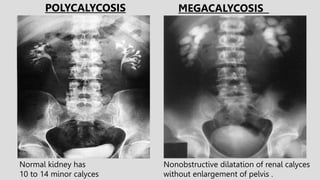
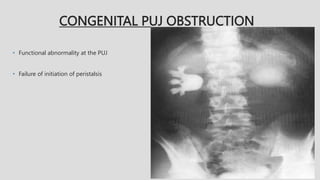
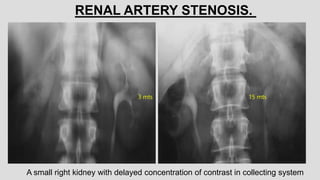
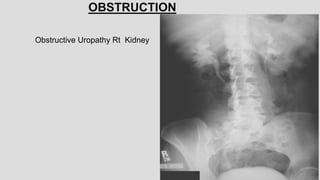
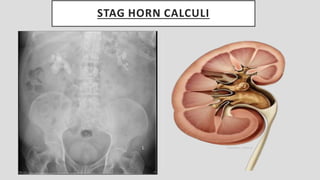
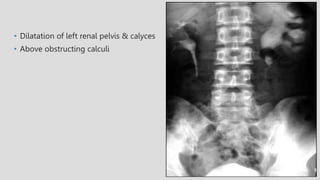
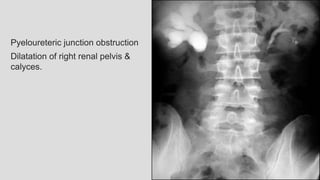
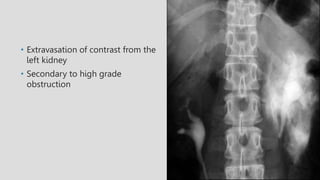
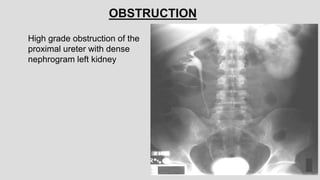
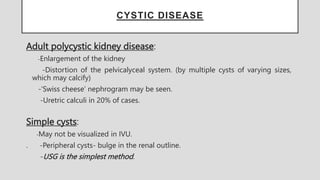
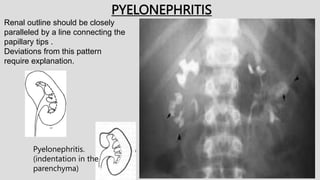
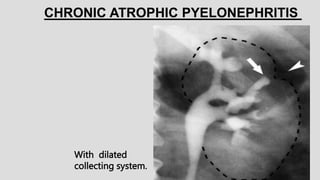
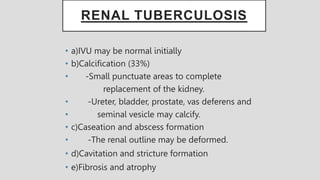
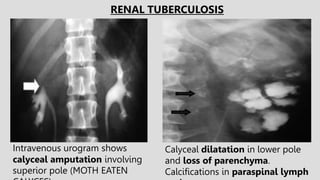
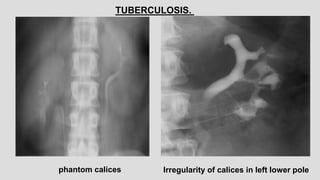
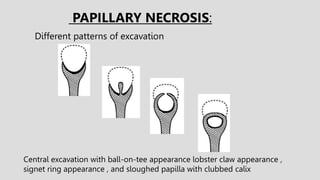
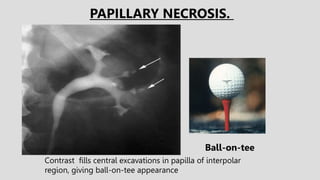
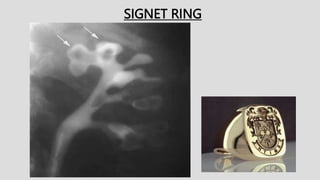
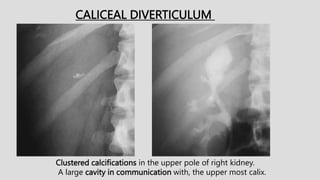
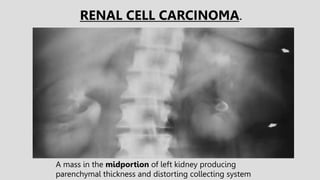
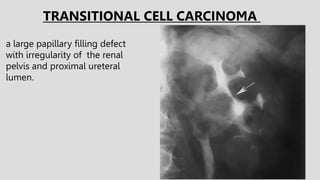
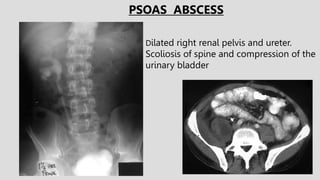
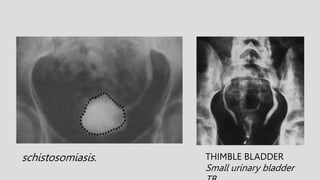
3. Pathologies of the collecting system like hydronephrosis due to obstruction or cystic disease were summarized. Specific conditions like pyelonephritis, renal tuberculosis, papillary necrosis and tumors were also outlined.
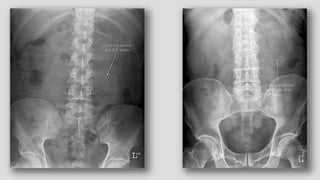
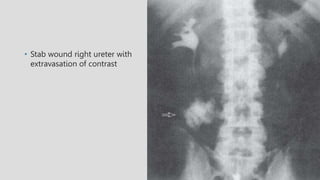
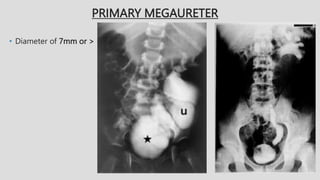
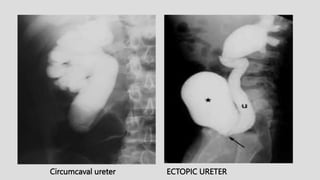
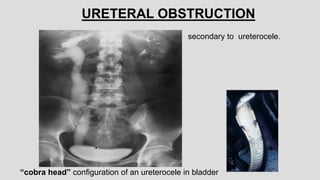
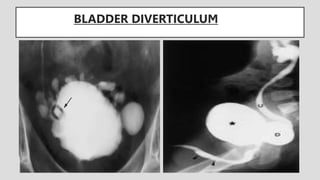
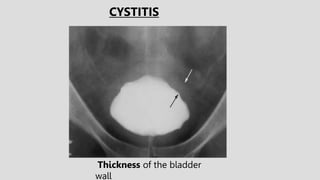
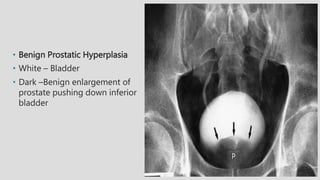
4. Common ureteral and bladder findings involved abnormalities in size, filling defects