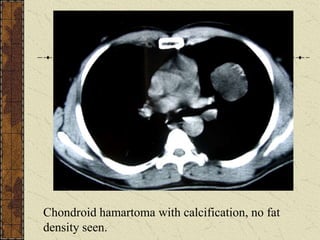
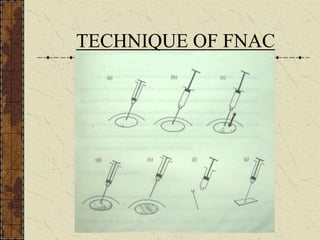
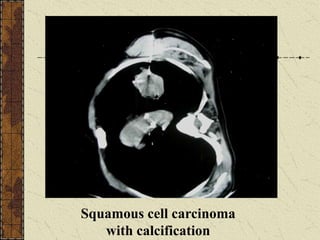
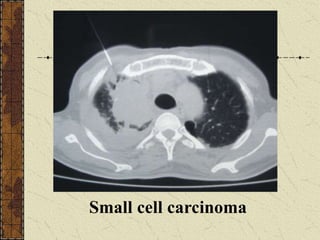
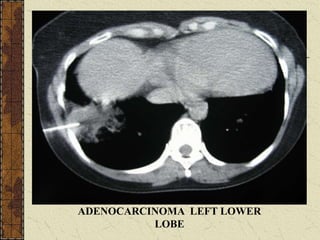
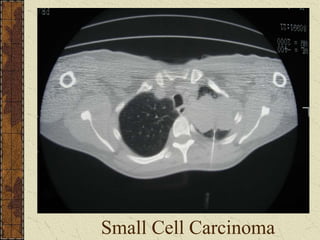
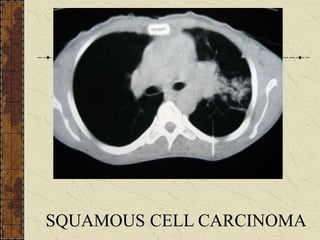
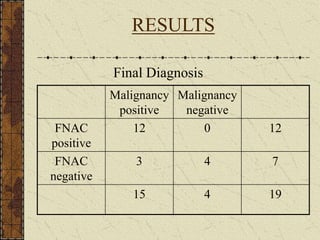
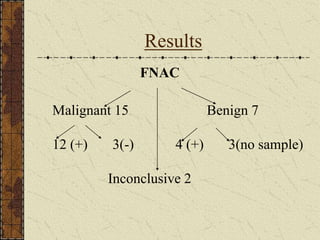
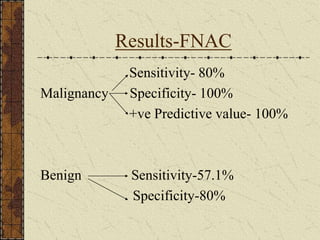
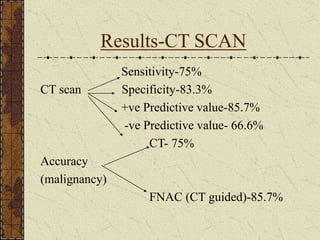
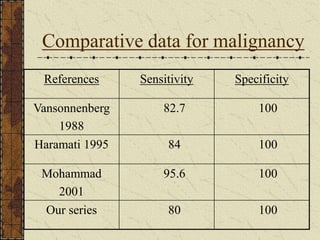
CT guided FNAC is a simple and effective technique for diagnosing complex pulmonary lesions. In a study of 28 patients, CT guided FNAC had a sensitivity of 80% and specificity of 100% for diagnosing malignancy. CT scanning alone had sensitivity of 75% and specificity of 83.3% for malignancy. Complications occurred in 3 patients (12.5%) and were minor and resolved with conservative treatment. The study concluded that CT guided FNAC is a highly sensitive and specific technique for characterizing pulmonary lesions.