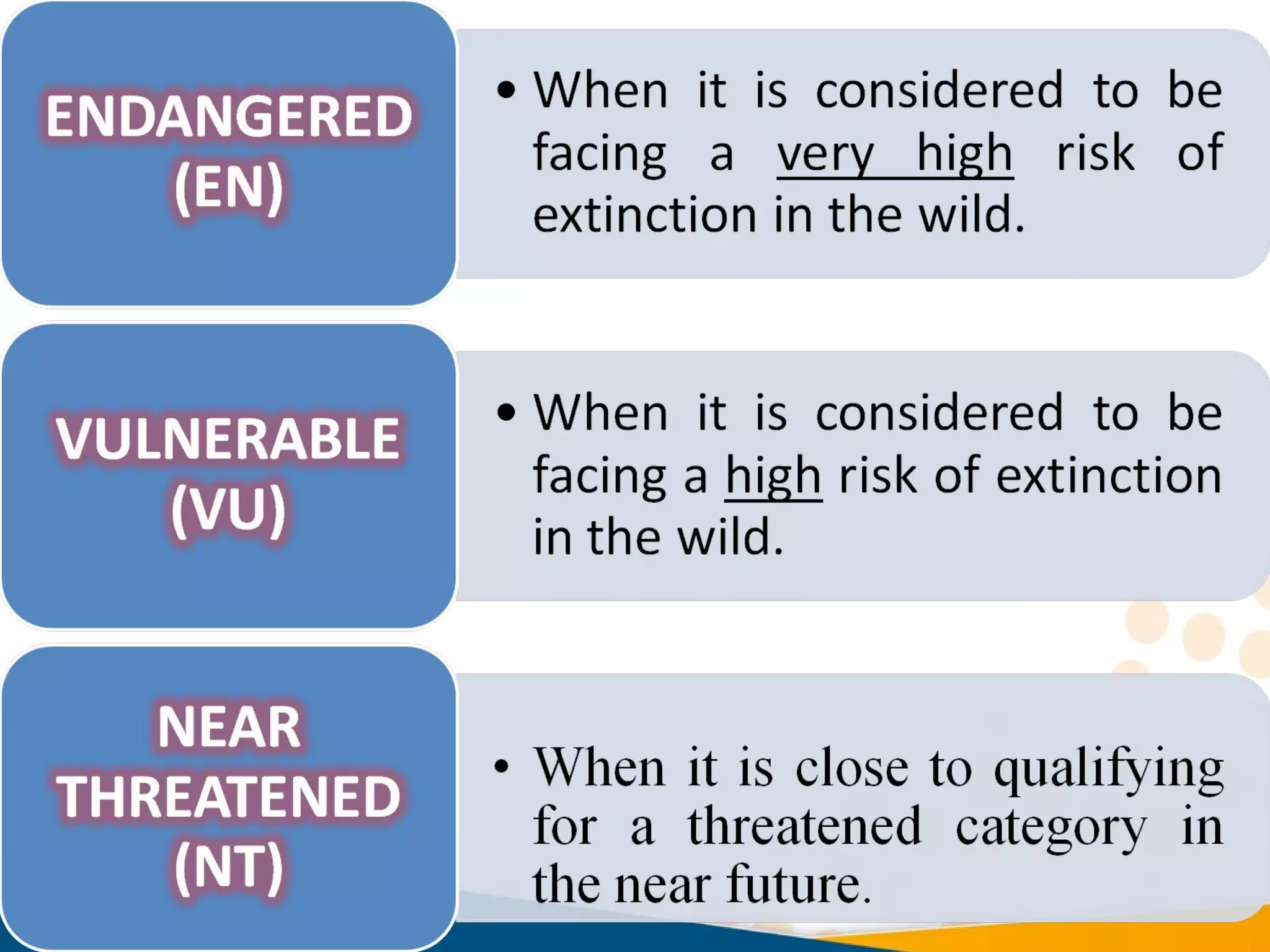
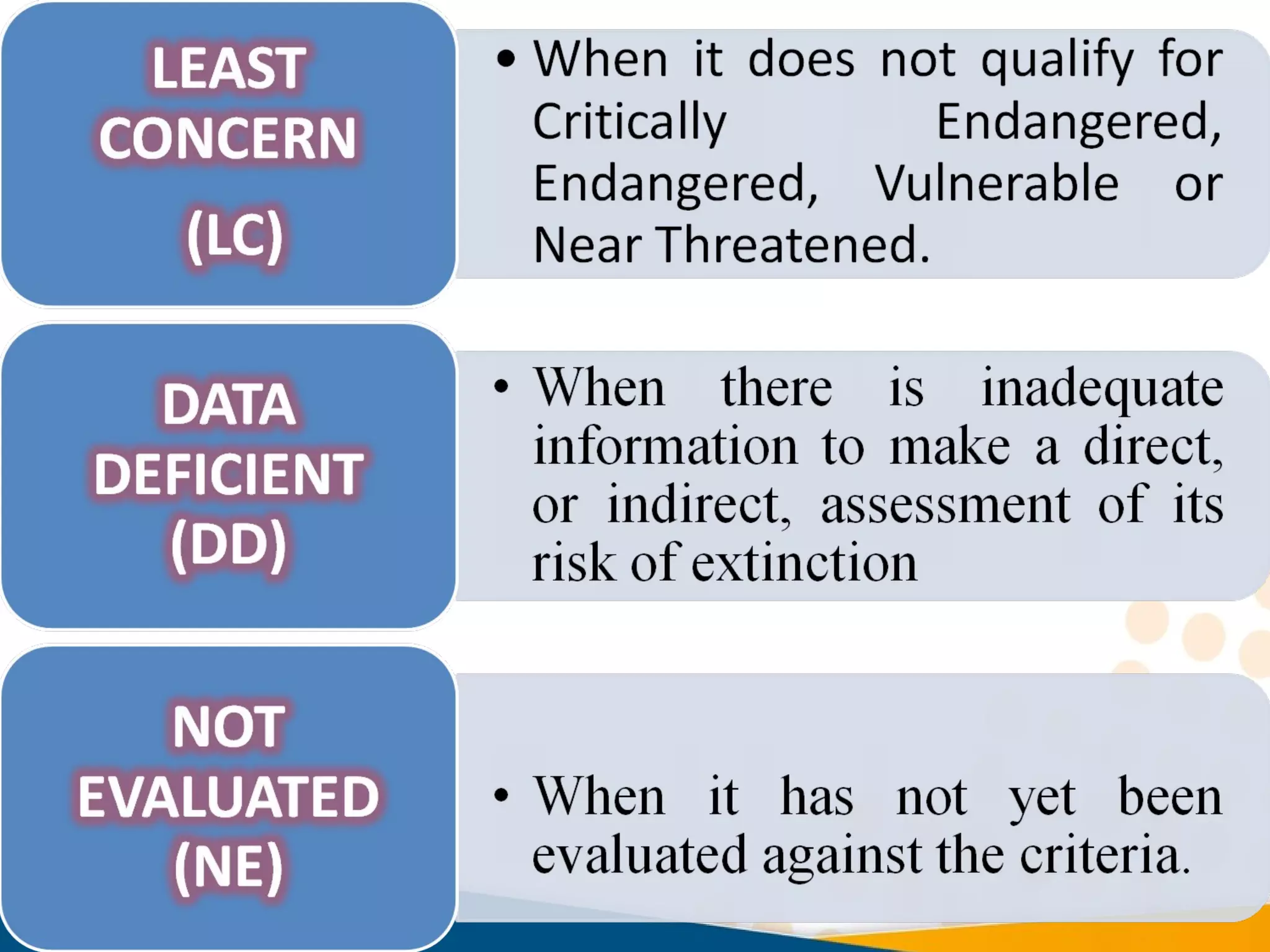
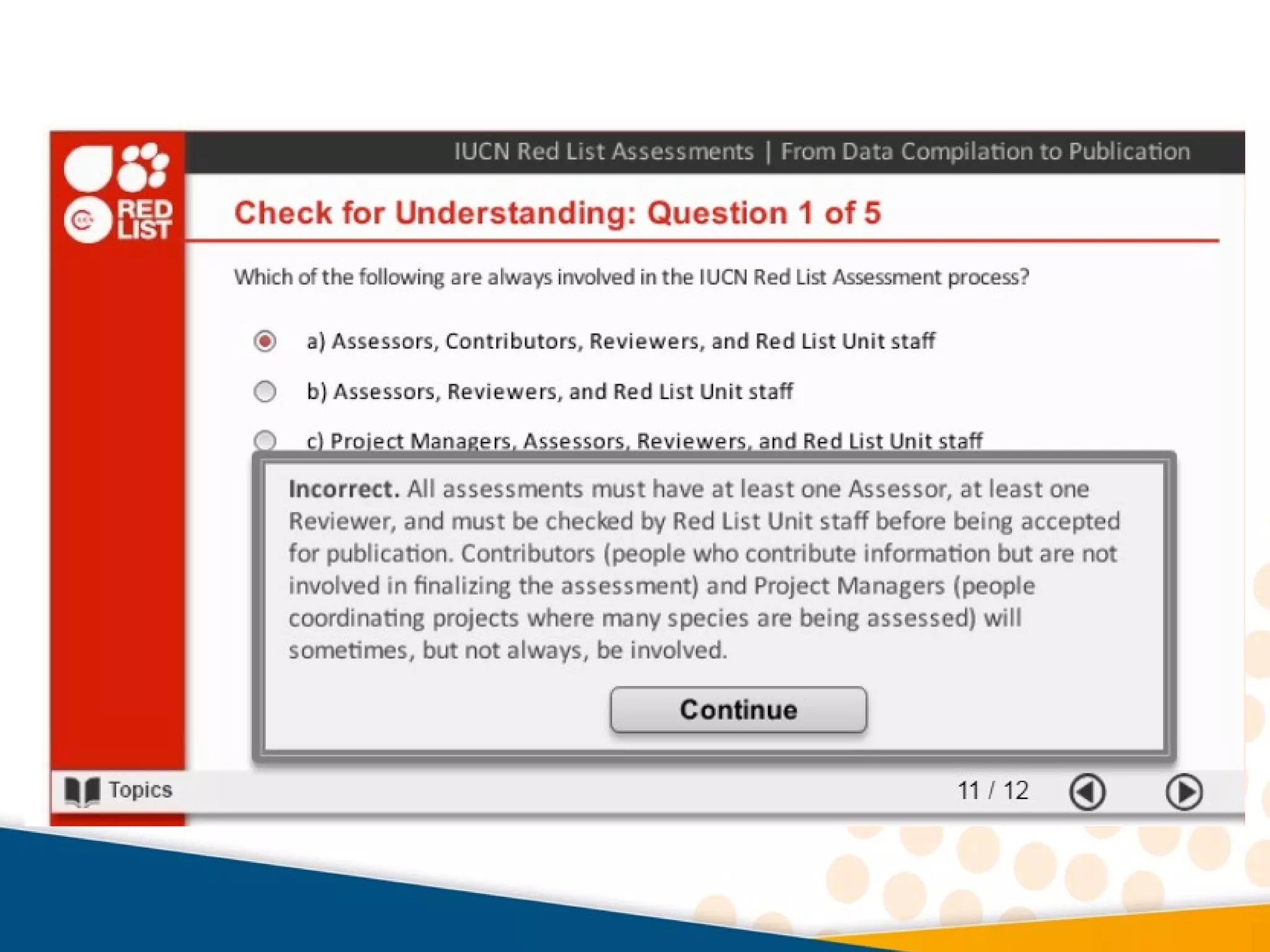
This document discusses biodiversity conservation and the IUCN Red List. It explains that upon completing this module, one will understand issues of endemism and extinction, learn about the goal and aims of the IUCN Red List to assess threatened species, know who produces the Red List and what percentage of biodiversity has been assessed. Threats to biodiversity like habitat loss and overexploitation are also outlined, as well as conservation approaches like protected areas and restoration.