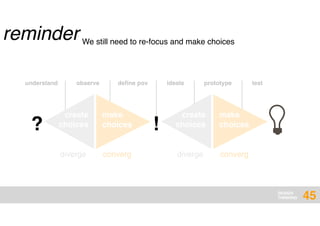
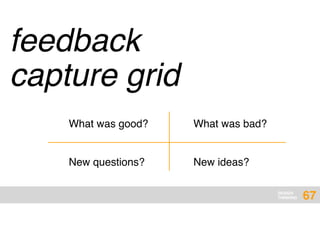
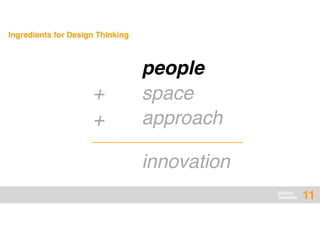
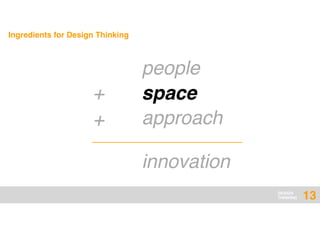
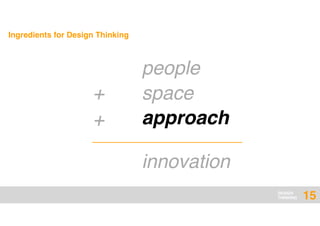
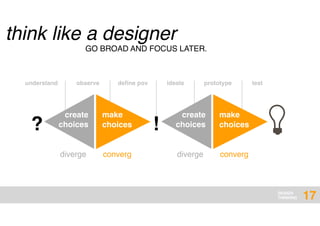
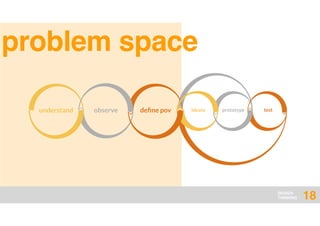
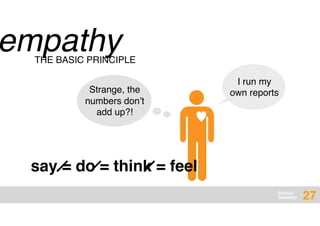
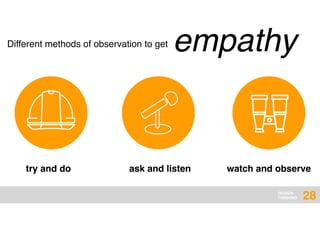
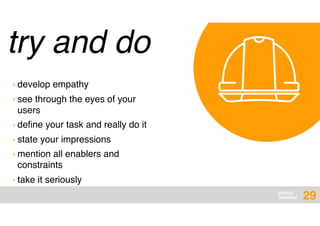
The document presents an overview of design thinking, highlighting its importance in solving complex problems and fostering innovation through interdisciplinary teamwork and user-centric approaches. It outlines key steps in the design thinking process, including empathizing with users, defining problems, ideating solutions, prototyping, and testing ideas, alongside various techniques for effective collaboration and iteration. The document emphasizes the need for creativity, flexibility, and user feedback in achieving successful design outcomes.


























![DESIGN
THINKING
point of viewComing up with a
The Point of View is one sentence that creates an
image in your mind. Based on an understanding of a
user group and an insight into a specific need, it
narrows the focus and makes the problem specific.
Template:
[User] needs (to) [Need] because [Insight]
Example:
The Department Supervisor needs time with
customers, since knowing who they are enables her
to optimize her ordering plan.
POV = USER + NEED + INSIGHT
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itmpdtsummitgraz2016-161020081309/85/ITMP-Design-Thinking-Summit-Graz-2016-38-320.jpg)