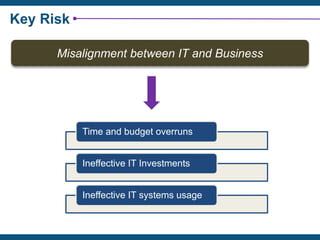
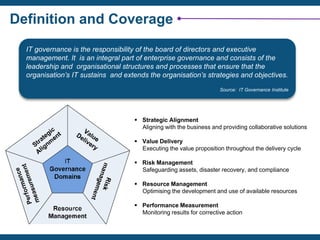
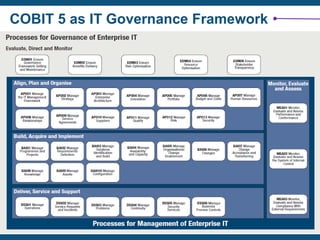
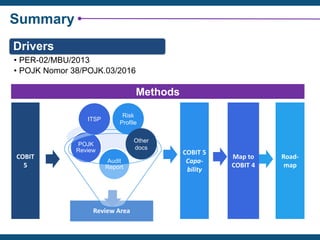
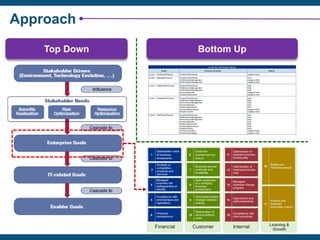
The document discusses the critical importance of IT governance in aligning IT strategies with business objectives and mitigating risks associated with IT projects, citing statistics on project failures due to poor ownership and management involvement. It emphasizes the need for a structured governance framework, such as COBIT 5, to enhance accountability and optimize IT resource usage. Key success factors identified include board commitment, transparency, and strategic alignment within IT management practices.