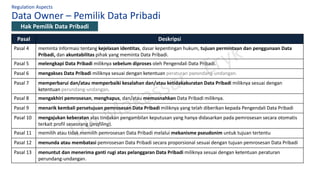
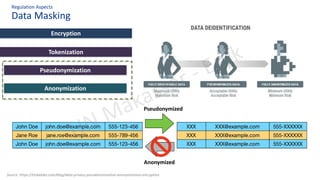
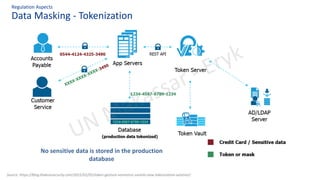
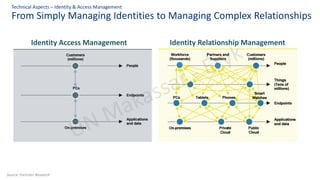
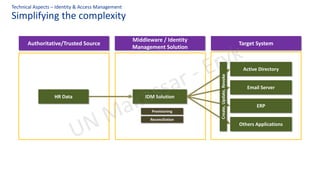
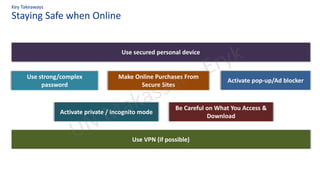
The document discusses personal data protection in Indonesia, highlighting regulation and technical aspects related to data privacy and cybersecurity. It emphasizes the importance of explicit consent from data owners for data processing and outlines the responsibilities of data controllers and processors. Furthermore, it presents various technical measures, such as data loss prevention and incident management strategies, alongside best practices for cyber hygiene.