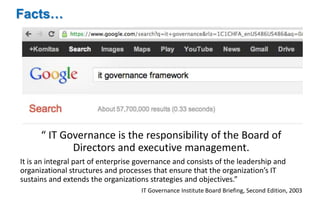
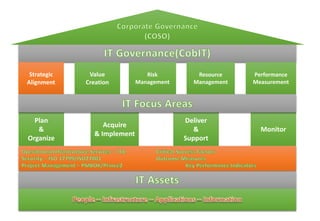
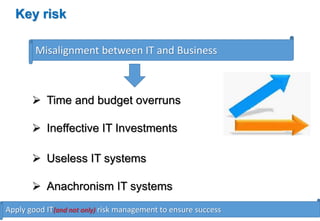
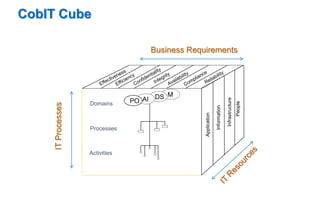
The USAID workshop on IT governance in banks highlighted critical management challenges and risks related to IT project implementation, with statistics showing high rates of project overruns and failures due to poor requirements and management controls. The discussion emphasized the importance of aligning IT strategy with business goals, encouraging organizations to adopt frameworks like COBIT to enhance governance and ensure effective IT investments. Key takeaways included the need for defined roles, accountability, and continuous improvement in IT governance as integral to corporate governance.