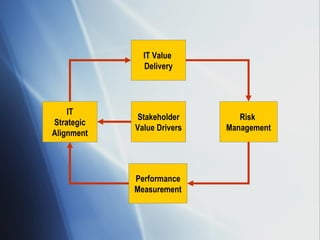
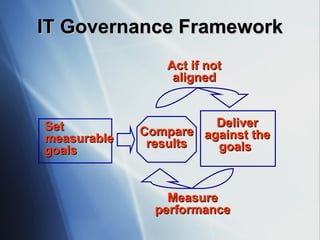
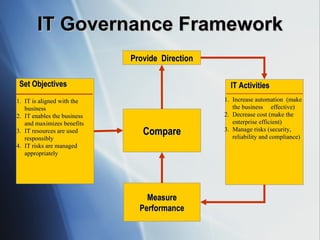
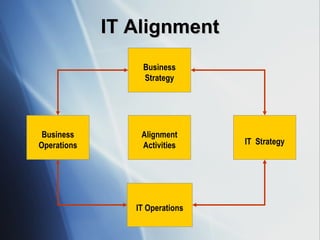
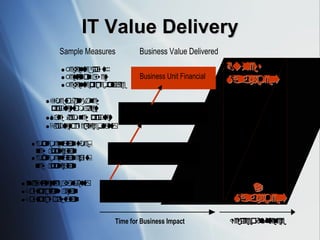
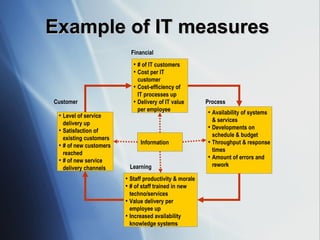
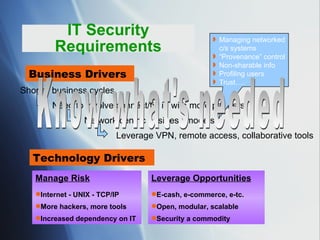
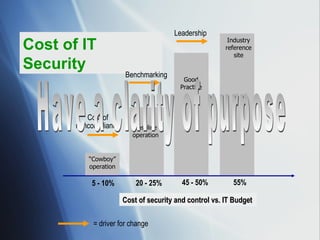
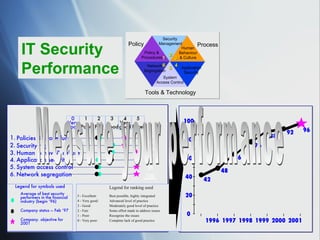
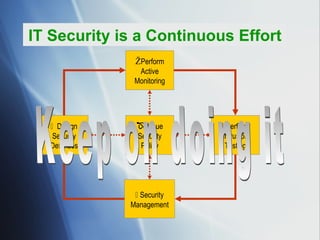
The document discusses the evolving role of IT governance, emphasizing its importance for boards of directors in aligning IT with business strategies and managing associated risks. It highlights the need for effective organizational structures, performance measurement, and stakeholder value while addressing challenges such as operational risks and technology failures. Furthermore, it outlines recommendations for both management and boards to enhance IT governance framework, ensuring it contributes positively to organizational objectives.