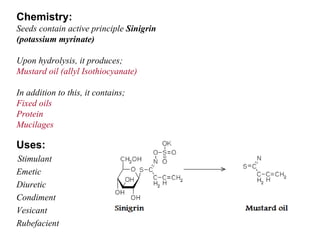
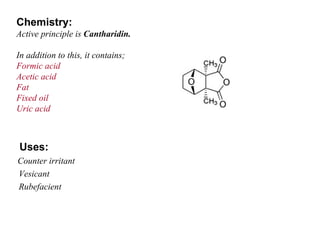
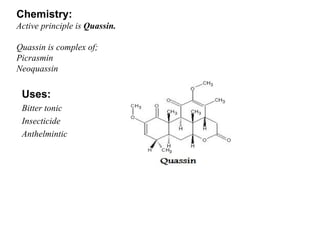
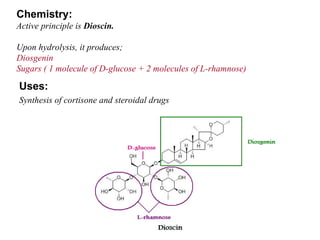
Isothiocyanate glycosides yield mustard oil upon hydrolysis and provide non-specific resistance to plants against infection. These agents act as vesicants, rubefacients, and irritants. Lactone glycosides and aldehyde glycosides are also found in plants and insects, yielding active principles like cantharidin, vanillin, and gentiopicrin upon hydrolysis. Miscellaneous glycosides contain complex mixtures that are used for their bitterness, insecticidal properties, and as precursors to steroidal drugs.