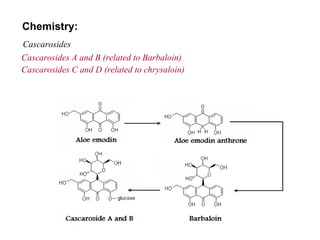
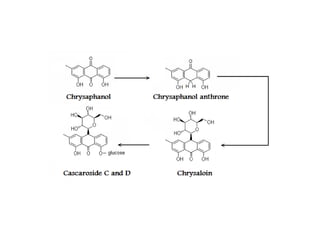
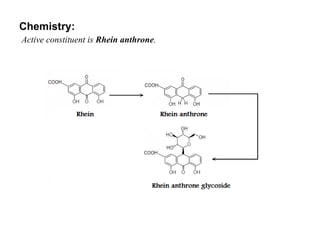
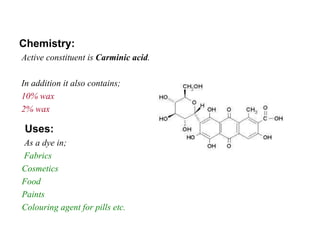
Anthraquinone glycosides are used as laxatives and purgatives. They are absorbed in the small intestine and excreted in the large intestine where they increase motility and produce laxation. Aglycons can cause griping so an antispasmodic is often prescribed. Five common sources are: Aloe, whose active ingredient is barbaloin; Cascara containing cascarosides; Rhubarb with rhein anthrone; Senna with sennosides; and Cochineal, a dye made from dried female insects containing carminic acid.