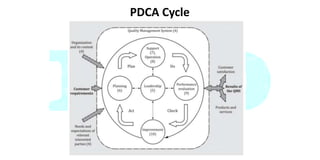
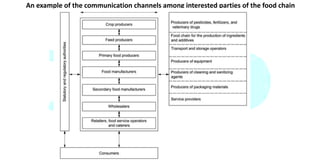
The document summarizes ISO 9000 and ISO 22000 quality management standards. It provides an overview of the evolution and principles of ISO 9000 from its initial publication in 1987 to the most recent 2015 version. Key changes included greater emphasis on leadership involvement, risk-based thinking, and continuous improvement. It also summarizes ISO 22000, which was published in 2005 to provide international harmonization for food safety management systems using HACCP principles.