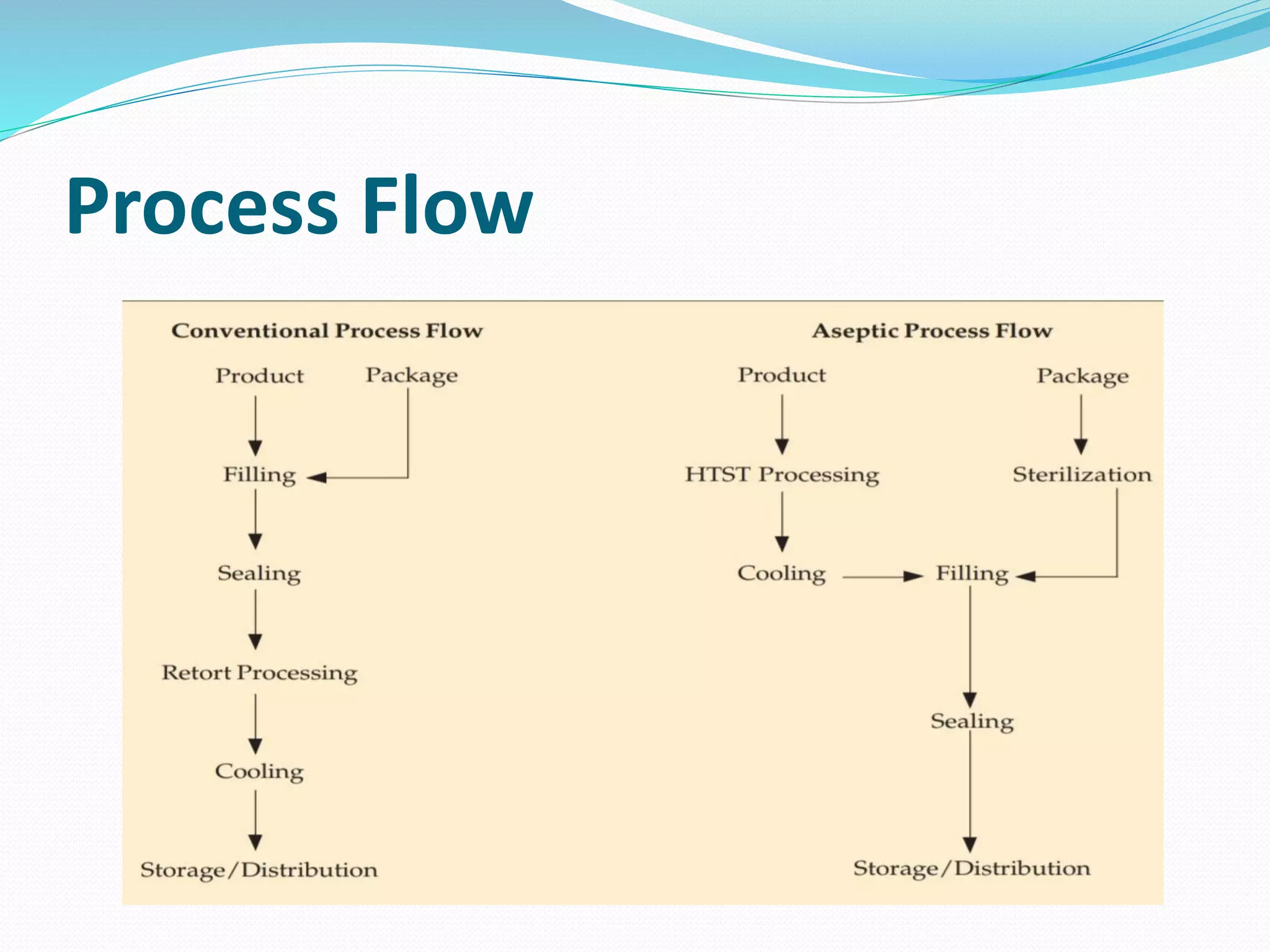
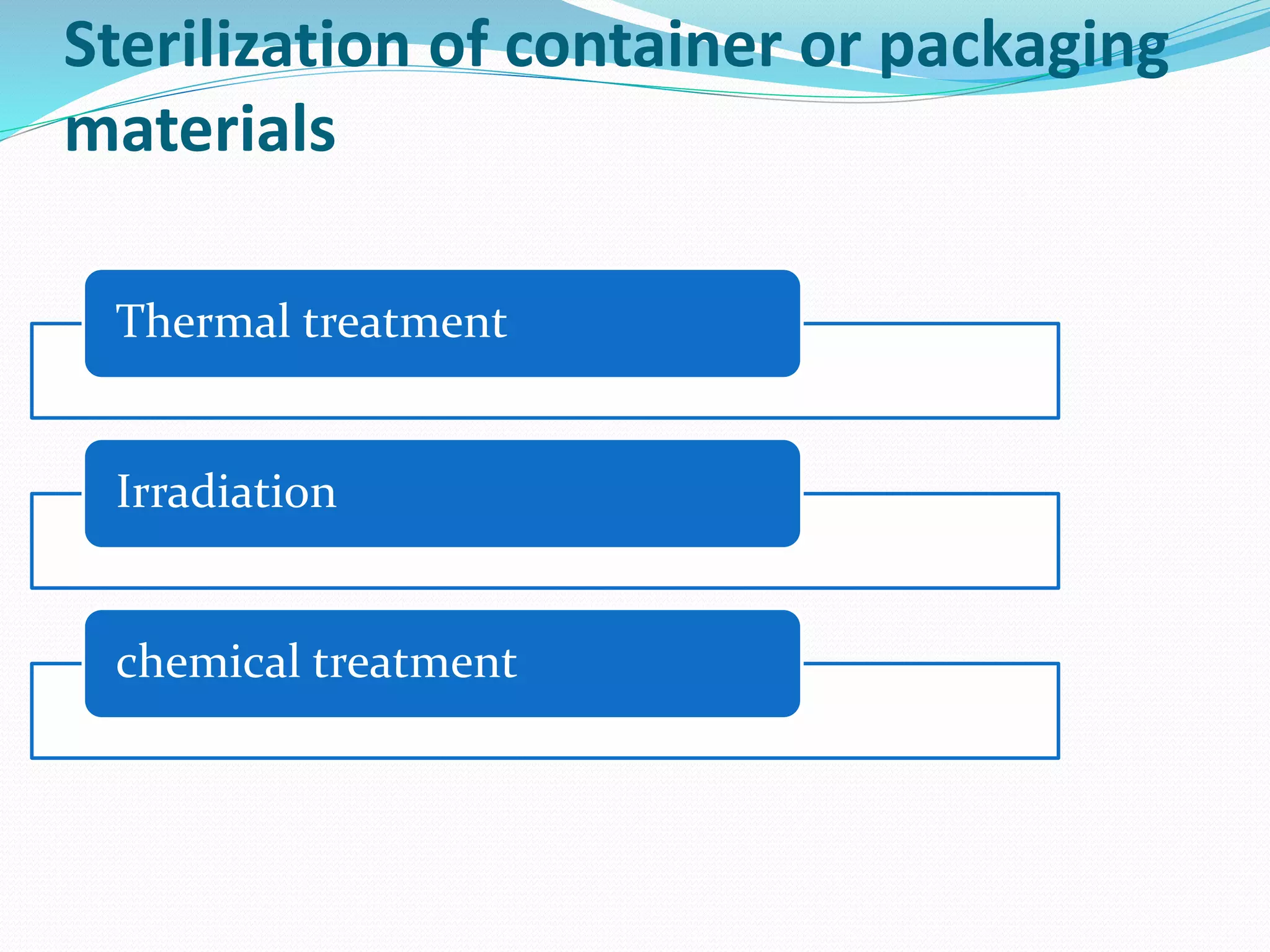
The document discusses aseptic packaging, which involves filling sterile containers with commercially sterile products under aseptic conditions to prevent contamination. It outlines the sterilization processes for products and packaging materials, including methods such as heat, radiation, and chemical treatments. Aseptic packaging extends shelf life, maintains product quality, and reduces the need for refrigeration while offering various packaging systems like bottles, pouches, and cups.