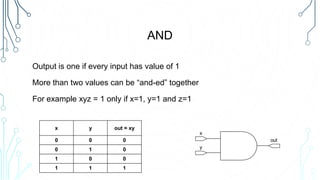
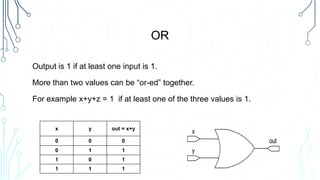
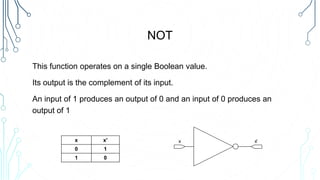
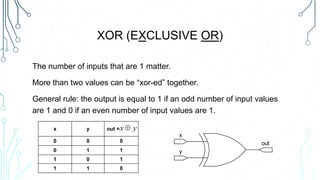
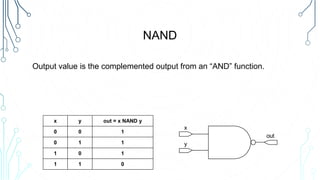
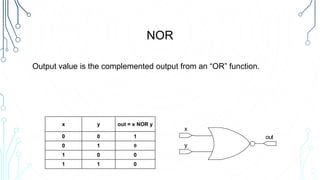
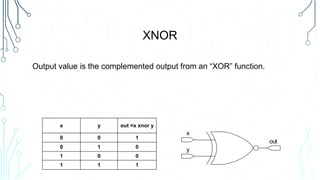
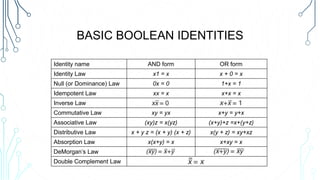
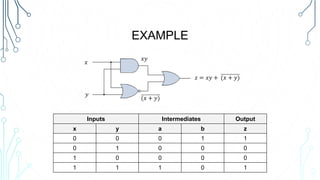
This document provides an overview of logical operations and Boolean algebra. It defines Boolean algebra values as being either true (1) or false (0). It then explains common logical operations like AND, OR, NOT, XOR, NAND and NOR and provides truth tables for each. The document also lists some basic Boolean identities and provides an example problem solving session using Boolean algebra.