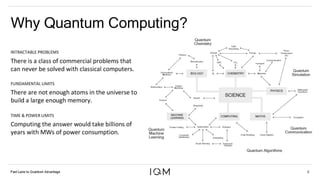
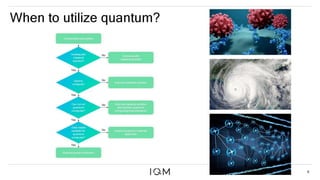
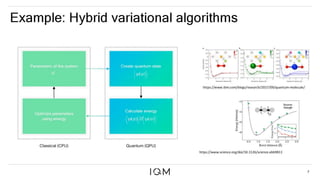
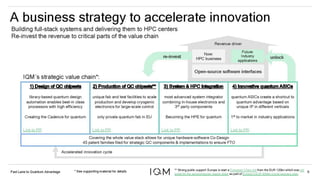
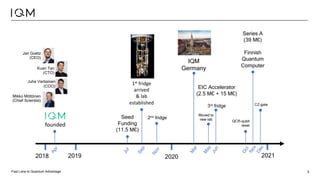
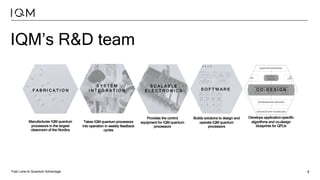
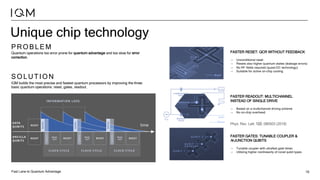
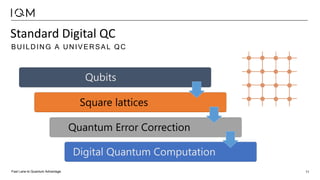
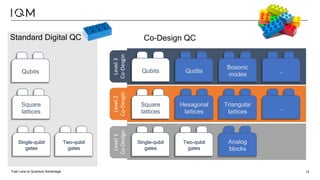
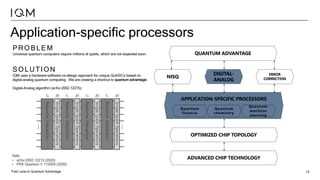
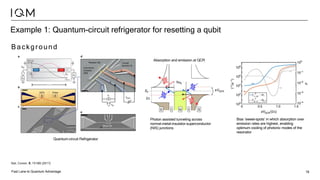
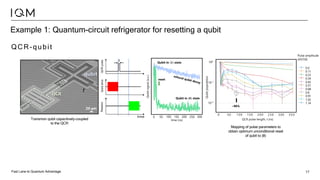
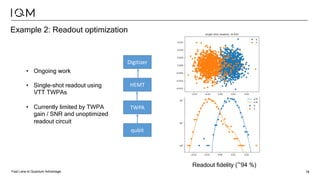
IQM is a Finnish startup focused on developing superconducting quantum computers, having been spun out from Aalto University and VTT in 2019. It emphasizes co-designing quantum computers to enhance precision and speed in quantum operations while collaborating with various institutions to strengthen the Finnish quantum ecosystem. The company is progressing towards deploying its first quantum computer and optimizing its technology for specific applications in chemistry and pharmaceuticals.