The document discusses quantum computers as a future approach to computing, highlighting their significance due to the limitations of classical computers as per Moore's law. It outlines the differences between classical and quantum computing, emphasizing concepts like qubits, superposition, entanglement, and tunneling. Additionally, it addresses challenges in building quantum computers and their potential for revolutionary applications in various fields such as artificial intelligence, cryptography, and more.





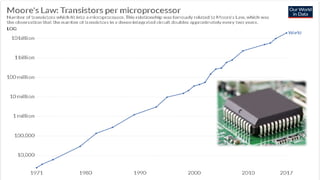
![“The world is running out of computing
capacity. Moore’s law is kinda running
out of steam … [we need quantum
computing to] create all of these rich
experiences we talk about, all of this
artificial intelligence.”
Satya Nadella , Microsoft CEO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atlast-grandfinale-qc-ppt-191212132911/85/Quantum-Computer-a-future-approach-in-computing-7-320.jpg)







































