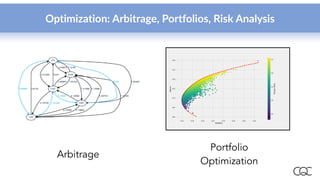
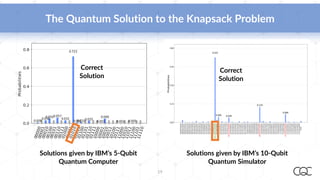
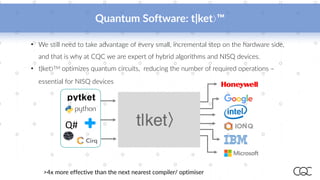
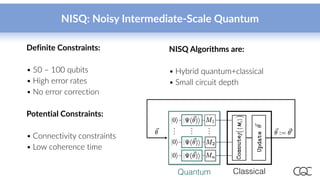
Cambridge Quantum Computing, established in 2014, specializes in quantum software and security technology, offering innovative solutions in various fields such as quantum chemistry, machine learning, and cybersecurity. As quantum computing hardware rapidly evolves, the company aims to leverage the burgeoning capabilities of quantum algorithms to solve complex problems more efficiently than classical computers. Notably, they have developed a quantum development platform and provide access to leading quantum hardware, highlighting the importance of early development in quantum computing advancements.