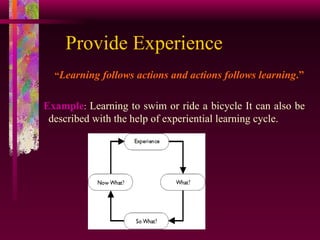
The document outlines the concept and importance of team facilitation in helping groups work efficiently towards common goals. It discusses the skills and characteristics needed for effective facilitation, barriers that may hinder teamwork, and strategies for improving facilitation practices. Benefits of facilitation include enhanced communication, conflict resolution, individual performance improvement, and overall team effectiveness.