1. The document discusses science vocabulary terms related to electrons, ion formation, and chemical bonding.
2. It asks to identify examples as elements or compounds and identify elements as metals, non-metals, or metalloids.
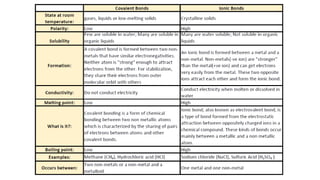
3. The main types of chemical bonding discussed are ionic bonding, covalent bonding, and metallic bonding. Ionic bonding involves transfer of electrons between metals and non-metals, covalent bonding is sharing of electrons between non-metals, and metallic bonding is the attraction of free-floating electrons within metals.