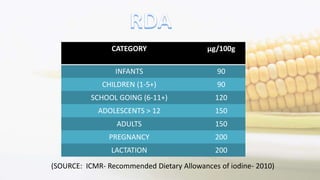
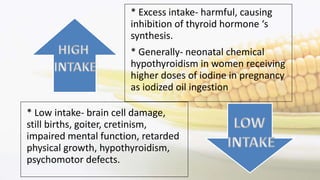
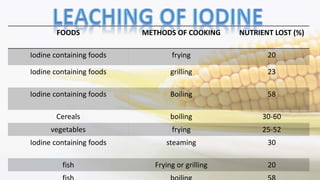
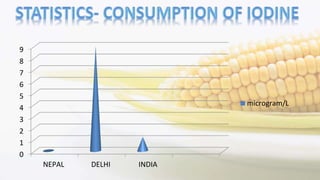
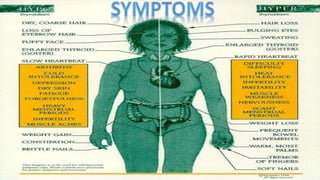
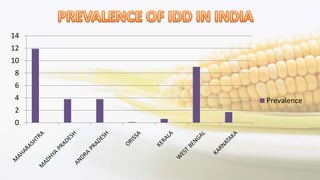
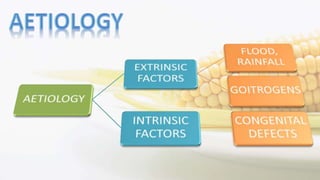
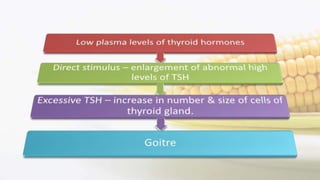
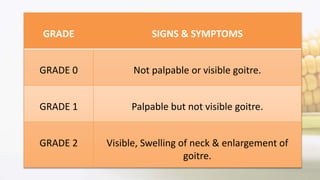
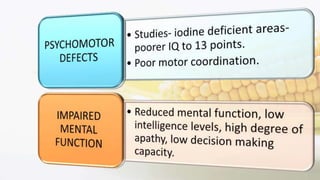
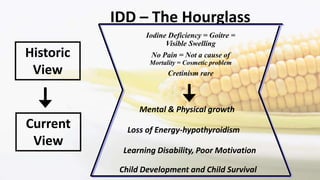
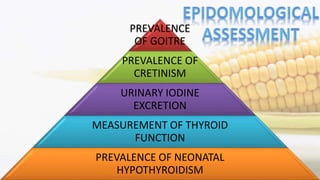
Iodine is an essential trace element necessary for thyroid hormone synthesis and plays a crucial role in brain development and metabolic regulation. Iodine deficiency disorders (IDD) affect 1.5 billion people globally, leading to severe health issues such as goiter, cretinism, and mental impairment. The document highlights dietary sources, recommended intake levels, cooking methods that affect iodine content, and the importance of addressing iodine deficiency as a major public health concern.