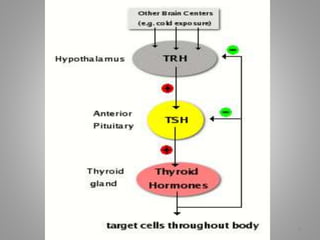
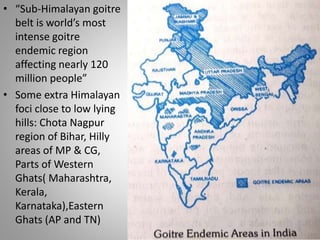
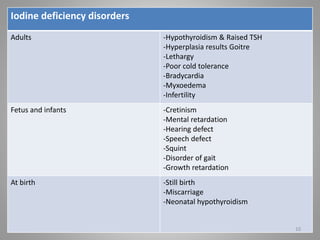
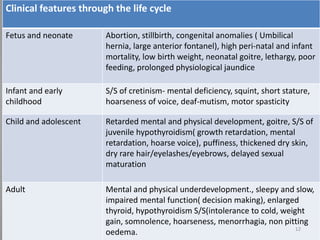
Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production. Iodine deficiency disorders affect over 7% of the global population and cause a spectrum of health issues from goiter to cretinism. Prevention focuses on universal salt iodization, iodized oil supplementation, monitoring iodine levels, training programs, and increasing public awareness. Controlling iodine deficiency through these measures can eliminate its health impacts across the lifespan.